.gif)
Counting (music)
Encyclopedia
In music
, counting is a system of regularly occurring sound
s that serve to assist with the performance
or audition
of music by allowing the easy identification of the beat
. Commonly, this involves verbally counting
the beats in each measure
as they occur. In addition to helping to normalize the time taken up by each beat, counting allows easier identification of the beats that are stressed. Counting is most commonly used with rhythm
and form and often involves subdivision.
 In lieu of simply counting the beats of a measure, other systems can be used which may be more appropriate to the particular piece of music. Depending on the tempo
In lieu of simply counting the beats of a measure, other systems can be used which may be more appropriate to the particular piece of music. Depending on the tempo
, the divisions of a beat may be vocalized as well (for slower times), or skipping numbers altogether (for faster times). As an alternative to counting, a metronome
can be used to accomplish the same function.
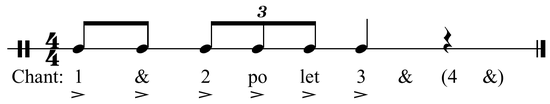
Triple meter, such as 3/4, is often counted 1 2 3, while compound meter, such as 6/8, is often counted in two and subdivided "One-and-ah-Two-and-ah" but may be articulated as "One-la-lee-Two-la-lee". For each subdivision employed a new syllable is used. For example, sixteenth notes in 4/4 are counted 1 e & a 2 e & a 3 e & a 4 e & a, using numbers for the quarter note, "&" for the eighth note
, and "e" and "a" for the sixteenth note level. Triplets may be counted "1 tri ple 2 tri ple 3 tri ple 4 tri ple" and sixteenth note triplets "1 la li + la li 2 la li + la li" (presumably saying "up" or "plus" for "+"). Quarter note triplets, due to their different rhythmic feel, may be articulated differently as "1 dra git 3 dra git".
Rather than numbers or nonsense syllables, a random word may be assigned to a rhythm to clearly count each beat. An example is with a triplet, so that a triplet
subdivision is often counted "tri-pl-et". The Kodály Method
uses "Ta" for quarter note
s and "Ti-Ti" for eighth notes. For sextuplets simply say triplet twice (see Sextuplet rhythm.png), while quintuplets may be articulated as "un-i-vers-i-ty". In some approaches, "rote-before-note", the fractional definitions of notes are not taught to children until after they are able to perform syllable or phrase-based versions of these rhythms.
"However the counting may be syllabized
, the important skill is to keep the pulse
steady and the division
exact."
Music
Music is an art form whose medium is sound and silence. Its common elements are pitch , rhythm , dynamics, and the sonic qualities of timbre and texture...
, counting is a system of regularly occurring sound
Sound
Sound is a mechanical wave that is an oscillation of pressure transmitted through a solid, liquid, or gas, composed of frequencies within the range of hearing and of a level sufficiently strong to be heard, or the sensation stimulated in organs of hearing by such vibrations.-Propagation of...
s that serve to assist with the performance
Performance
A performance, in performing arts, generally comprises an event in which a performer or group of performers behave in a particular way for another group of people, the audience. Choral music and ballet are examples. Usually the performers participate in rehearsals beforehand. Afterwards audience...
or audition
Hearing (sense)
Hearing is the ability to perceive sound by detecting vibrations through an organ such as the ear. It is one of the traditional five senses...
of music by allowing the easy identification of the beat
Beat (music)
The beat is the basic unit of time in music, the pulse of the mensural level . In popular use, the beat can refer to a variety of related concepts including: tempo, meter, rhythm and groove...
. Commonly, this involves verbally counting
Counting
Counting is the action of finding the number of elements of a finite set of objects. The traditional way of counting consists of continually increasing a counter by a unit for every element of the set, in some order, while marking those elements to avoid visiting the same element more than once,...
the beats in each measure
Bar (music)
In musical notation, a bar is a segment of time defined by a given number of beats of a given duration. Typically, a piece consists of several bars of the same length, and in modern musical notation the number of beats in each bar is specified at the beginning of the score by the top number of a...
as they occur. In addition to helping to normalize the time taken up by each beat, counting allows easier identification of the beats that are stressed. Counting is most commonly used with rhythm
Rhythm
Rhythm may be generally defined as a "movement marked by the regulated succession of strong and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions." This general meaning of regular recurrence or pattern in time may be applied to a wide variety of cyclical natural phenomena having a periodicity or...
and form and often involves subdivision.
Methods
The method involving numbers may termed count chant, "to identity it as a unique instructional process."
Tempo
In musical terminology, tempo is the speed or pace of a given piece. Tempo is a crucial element of any musical composition, as it can affect the mood and difficulty of a piece.-Measuring tempo:...
, the divisions of a beat may be vocalized as well (for slower times), or skipping numbers altogether (for faster times). As an alternative to counting, a metronome
Metronome
A metronome is any device that produces regular, metrical ticks — settable in beats per minute. These ticks represent a fixed, regular aural pulse; some metronomes also include synchronized visual motion...
can be used to accomplish the same function.
Triple meter, such as 3/4, is often counted 1 2 3, while compound meter, such as 6/8, is often counted in two and subdivided "One-and-ah-Two-and-ah" but may be articulated as "One-la-lee-Two-la-lee". For each subdivision employed a new syllable is used. For example, sixteenth notes in 4/4 are counted 1 e & a 2 e & a 3 e & a 4 e & a, using numbers for the quarter note, "&" for the eighth note
Eighth note
thumb|180px|right|Figure 1. An eighth note with stem facing up, an eighth note with stem facing down, and an eighth rest.thumb|right|180px|Figure 2. Four eighth notes beamed together....
, and "e" and "a" for the sixteenth note level. Triplets may be counted "1 tri ple 2 tri ple 3 tri ple 4 tri ple" and sixteenth note triplets "1 la li + la li 2 la li + la li" (presumably saying "up" or "plus" for "+"). Quarter note triplets, due to their different rhythmic feel, may be articulated differently as "1 dra git 3 dra git".
Rather than numbers or nonsense syllables, a random word may be assigned to a rhythm to clearly count each beat. An example is with a triplet, so that a triplet
Tuplet
In music a tuplet is "any rhythm that involves dividing the beat into a different number of equal subdivisions from that usually permitted by the...
subdivision is often counted "tri-pl-et". The Kodály Method
Kodály Method
The Kodály Method, also referred to as the Kodály Concept, is an approach to music education developed in Hungary during the mid-twentieth century by Zoltán Kodály...
uses "Ta" for quarter note
Quarter note
A quarter note or crotchet is a note played for one quarter of the duration of a whole note . Often people will say that a crotchet is one beat, however, this is not always correct, as the beat is indicated by the time signature of the music; a quarter note may or may not be the beat...
s and "Ti-Ti" for eighth notes. For sextuplets simply say triplet twice (see Sextuplet rhythm.png), while quintuplets may be articulated as "un-i-vers-i-ty". In some approaches, "rote-before-note", the fractional definitions of notes are not taught to children until after they are able to perform syllable or phrase-based versions of these rhythms.
"However the counting may be syllabized
Syllable
A syllable is a unit of organization for a sequence of speech sounds. For example, the word water is composed of two syllables: wa and ter. A syllable is typically made up of a syllable nucleus with optional initial and final margins .Syllables are often considered the phonological "building...
, the important skill is to keep the pulse
Pulse (music)
In music and music theory, the pulse or tactus consists of beats in a series of identical yet distinct periodic short-duration stimuli perceived as points in time occurring at the mensural level...
steady and the division
Beat (music)
The beat is the basic unit of time in music, the pulse of the mensural level . In popular use, the beat can refer to a variety of related concepts including: tempo, meter, rhythm and groove...
exact."

