
Bcl-2 family
Encyclopedia
Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2, BH is a family of evolutionarily related proteins
. These proteins govern mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization
(MOMP) and can be either pro-apoptotic
(Bax
, BAD
, Bak
and Bok
among others) or anti-apoptotic (including Bcl-2 proper, Bcl-xL
, and Bcl-w, among an assortment of others). There are a total of 25 genes in the Bcl-2 family known to date.
) is induced by events such as growth factor
withdrawal and toxins. It is controlled by regulators, which have either an inhibitory effect on programmed cell death (anti-apoptotic) or block the protective effect of inhibitors (pro-apoptotic). Many viruses have found a way of countering defensive apoptosis by encoding their own anti-apoptosis genes preventing their target-cells from dying too soon.
 There are a number of theories concerning how the Bcl-2 gene family exert their pro- or anti-apoptotic effect. An important one states that this is achieved by activation or inactivation of an inner mitochondrial permeability transition pore
There are a number of theories concerning how the Bcl-2 gene family exert their pro- or anti-apoptotic effect. An important one states that this is achieved by activation or inactivation of an inner mitochondrial permeability transition pore
, which is involved in the regulation of matrix Ca2+
, pH
, and voltage. It is also thought that some Bcl-2 family proteins can induce (pro-apoptotic members) or inhibit (anti-apoptotic members) the release of cytochrome c
into the cytosol
which, once there, activates caspase-9 and caspase-3, leading to apoptosis. Although Zamzami et al. suggest that the release of cytochrome c is indirectly mediated by the PT pore on the inner mitochondrial membrane, strong evidence suggest an earlier implication of the MAC pore on the outer membrane.
Another theory suggests that Rho proteins play a role in Bcl-2, Mcl-1 and Bid activation. Rho inhibition reduces the expression of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 proteins and increases protein levels of pro-apoptotic Bid but had no effect on Bax or FLIP levels. Rho inhibition induces caspase-9 and caspase-3-dependent apoptosis of cultured human endothelial cells.
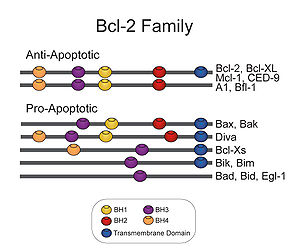
The members of the Bcl-2 family share one or more of the four characteristic domain
s of homology
entitled the Bcl-2 homology (BH) domains (named BH1, BH2, BH3 and BH4) (see the figure on the left). The BH domains are known to be crucial for function, as deletion of these domains via molecular cloning
affects survival/apoptosis rates. The anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins, such as Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL
, conserve all four BH domains. The BH domains also serve to subdivide the pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins into those with several BH domains (e.g. Bax
and Bak
) or those proteins that have only the BH3 domain (e.g. Bid, Bim
and Bad). The Bcl-2 family has a general structure that consists of a hydrophobic
helix surrounded by amphipathic helices. Many members of the family have transmembrane domains. The site of action for the Bcl-2 family is mostly on the outer mitochondrial membrane. Within the mitochondria are apoptogenic factors (cytochrome c, Smac/Diablo homolog
, Omi) that if released activate the executioners of apoptosis, the caspase
s. Depending on their function, once activated, Bcl-2 proteins either promote the release of these factors, or keep them sequestered in the mitochondria. Whereas the activated pro-apoptotic Bak and/or Bax would form MAC and mediate the release of cytochrome c, the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 would block it, possibly through inhibition of Bax and/or Bak.
. The BH3-only family members are BAD
, Bim
and others. Various apoptotic stimuli induce expression and/or activation of specific BH3-only family members, which translocate to the mitochondria and initiate Bax/Bak-dependent apoptosis.
protein ced-9.
Human genes encoding proteins that belong to this family include:
Protein family
A protein family is a group of evolutionarily-related proteins, and is often nearly synonymous with gene family. The term protein family should not be confused with family as it is used in taxonomy....
. These proteins govern mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization
Semipermeable membrane
A semipermeable membrane, also termed a selectively permeable membrane, a partially permeable membrane or a differentially permeable membrane, is a membrane that will allow certain molecules or ions to pass through it by diffusion and occasionally specialized "facilitated diffusion".The rate of...
(MOMP) and can be either pro-apoptotic
Apoptosis
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
(Bax
Bcl-2-associated X protein
The Bcl-2–associated X protein, or Bax is a protein of the Bcl-2 gene family. It promotes apoptosis by competing with Bcl-2 proper.The BAX gene was the first identified pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 protein family....
, BAD
Bcl-2-associated death promoter
The Bcl-2-associated death promoter protein is a pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 gene family which is involved in initiating apoptosis. BAD is a member of the BH3-only family...
, Bak
Bcl-2 homologous antagonist killer
Bcl-2 homologous antagonist/killer is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BAK1 gene. BAK1 orthologs have been identified in most mammals for which complete genome data are available....
and Bok
BOK (gene)
Bcl-2-related ovarian killer protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BOK gene.-Further reading:...
among others) or anti-apoptotic (including Bcl-2 proper, Bcl-xL
Bcl-xL
B-cell lymphoma-extra large is a transmembrane molecule in the mitochondria. It is involved in the signal transduction pathway of the FAS-L. It is one of several anti-apoptotic proteins which are members of the Bcl-2 family of proteins. It has been implicated in the survival of cancer cells. Other...
, and Bcl-w, among an assortment of others). There are a total of 25 genes in the Bcl-2 family known to date.
Function
Active cell suicide (apoptosisApoptosis
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
) is induced by events such as growth factor
Growth factor
A growth factor is a naturally occurring substance capable of stimulating cellular growth, proliferation and cellular differentiation. Usually it is a protein or a steroid hormone. Growth factors are important for regulating a variety of cellular processes....
withdrawal and toxins. It is controlled by regulators, which have either an inhibitory effect on programmed cell death (anti-apoptotic) or block the protective effect of inhibitors (pro-apoptotic). Many viruses have found a way of countering defensive apoptosis by encoding their own anti-apoptosis genes preventing their target-cells from dying too soon.

Mitochondrial permeability transition pore
The Mitochondrial Permeability Transition, or MPT, is defined as an increase in the permeability of the mitochondrial membranes to molecules of less than 1500 Daltons in molecular weight. MPT results from the opening of a mitochondrial permeability transition pore, also known as the MPT pore or MPTP...
, which is involved in the regulation of matrix Ca2+
Calcium in biology
Calcium plays a pivotal role in the physiology and biochemistry of organisms and the cell. It plays an important role in signal transduction pathways, where it acts as a second messenger, in neurotransmitter release from neurons, contraction of all muscle cell types, and fertilization...
, pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
, and voltage. It is also thought that some Bcl-2 family proteins can induce (pro-apoptotic members) or inhibit (anti-apoptotic members) the release of cytochrome c
Cytochrome c
The Cytochrome complex, or cyt c is a small heme protein found loosely associated with the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. It belongs to the cytochrome c family of proteins. Cytochrome c is a highly soluble protein, unlike other cytochromes, with a solubility of about 100 g/L and is an...
into the cytosol
Cytosol
The cytosol or intracellular fluid is the liquid found inside cells, that is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into compartments....
which, once there, activates caspase-9 and caspase-3, leading to apoptosis. Although Zamzami et al. suggest that the release of cytochrome c is indirectly mediated by the PT pore on the inner mitochondrial membrane, strong evidence suggest an earlier implication of the MAC pore on the outer membrane.
Another theory suggests that Rho proteins play a role in Bcl-2, Mcl-1 and Bid activation. Rho inhibition reduces the expression of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 proteins and increases protein levels of pro-apoptotic Bid but had no effect on Bax or FLIP levels. Rho inhibition induces caspase-9 and caspase-3-dependent apoptosis of cultured human endothelial cells.
The members of the Bcl-2 family share one or more of the four characteristic domain
Protein domain
A protein domain is a part of protein sequence and structure that can evolve, function, and exist independently of the rest of the protein chain. Each domain forms a compact three-dimensional structure and often can be independently stable and folded. Many proteins consist of several structural...
s of homology
Homology (biology)
Homology forms the basis of organization for comparative biology. In 1843, Richard Owen defined homology as "the same organ in different animals under every variety of form and function". Organs as different as a bat's wing, a seal's flipper, a cat's paw and a human hand have a common underlying...
entitled the Bcl-2 homology (BH) domains (named BH1, BH2, BH3 and BH4) (see the figure on the left). The BH domains are known to be crucial for function, as deletion of these domains via molecular cloning
Cloning
Cloning in biology is the process of producing similar populations of genetically identical individuals that occurs in nature when organisms such as bacteria, insects or plants reproduce asexually. Cloning in biotechnology refers to processes used to create copies of DNA fragments , cells , or...
affects survival/apoptosis rates. The anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins, such as Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL
Bcl-xL
B-cell lymphoma-extra large is a transmembrane molecule in the mitochondria. It is involved in the signal transduction pathway of the FAS-L. It is one of several anti-apoptotic proteins which are members of the Bcl-2 family of proteins. It has been implicated in the survival of cancer cells. Other...
, conserve all four BH domains. The BH domains also serve to subdivide the pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins into those with several BH domains (e.g. Bax
Bcl-2-associated X protein
The Bcl-2–associated X protein, or Bax is a protein of the Bcl-2 gene family. It promotes apoptosis by competing with Bcl-2 proper.The BAX gene was the first identified pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 protein family....
and Bak
Bcl-2 homologous antagonist killer
Bcl-2 homologous antagonist/killer is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BAK1 gene. BAK1 orthologs have been identified in most mammals for which complete genome data are available....
) or those proteins that have only the BH3 domain (e.g. Bid, Bim
BCL2L11
Bcl-2-like protein 11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BCL2L11 gene.-Interactions:BCL2L11 has been shown to interact with DYNLL1, MCL1, BCL2-like 1, BCL2L2 and Bcl-2.-Further reading:...
and Bad). The Bcl-2 family has a general structure that consists of a hydrophobic
Hydrophobe
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is repelled from a mass of water....
helix surrounded by amphipathic helices. Many members of the family have transmembrane domains. The site of action for the Bcl-2 family is mostly on the outer mitochondrial membrane. Within the mitochondria are apoptogenic factors (cytochrome c, Smac/Diablo homolog
Diablo homolog
Diablo homolog, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DIABLO gene . DIABLO is also referred to as second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases or SMAC.- Function :...
, Omi) that if released activate the executioners of apoptosis, the caspase
Caspase
Caspases, or cysteine-aspartic proteases or cysteine-dependent aspartate-directed proteases are a family of cysteine proteases that play essential roles in apoptosis , necrosis, and inflammation....
s. Depending on their function, once activated, Bcl-2 proteins either promote the release of these factors, or keep them sequestered in the mitochondria. Whereas the activated pro-apoptotic Bak and/or Bax would form MAC and mediate the release of cytochrome c, the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 would block it, possibly through inhibition of Bax and/or Bak.
Structure
All proteins belonging to the Bcl-2 family contain either a BH1, BH2, BH3, or BH4 domain. All anti-apoptotic proteins contain BH1 and BH2 domains, some of them contain an additional N-terminal BH4 domain (Bcl-2, Bcl-x(L), Bcl-w), which is never seen in pro-apoptotic proteins, except for Bcl-x(S). On the other hand, all pro-apoptotic proteins contain a BH3 domain (except for Bad) necessary for dimerization with other proteins of Bcl-2 family and crucial for their killing activity, some of them also contain BH1 and BH2 domains (Bax, Bak). The BH3 domain is also present in some anti-apoptotic protein, such as Bcl-2 or Bcl-x(L).BH3-only family
BH3-only family of proteins includes those of the Bcl-2 family proteins, which contain only a single BH-domain. The BH3-only family members play a key role in promoting apoptosisApoptosis
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
. The BH3-only family members are BAD
Bcl-2-associated death promoter
The Bcl-2-associated death promoter protein is a pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 gene family which is involved in initiating apoptosis. BAD is a member of the BH3-only family...
, Bim
BCL2L11
Bcl-2-like protein 11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BCL2L11 gene.-Interactions:BCL2L11 has been shown to interact with DYNLL1, MCL1, BCL2-like 1, BCL2L2 and Bcl-2.-Further reading:...
and others. Various apoptotic stimuli induce expression and/or activation of specific BH3-only family members, which translocate to the mitochondria and initiate Bax/Bak-dependent apoptosis.
Examples
Proteins that are known to contain these domains include vertebrate Bcl-2 (alpha and beta isoforms) and Bcl-x (isoforms (Bcl-x(L) and Bcl-x(S)); mammalian proteins Bax and Bak; mouse protein Bid; Xenopus laevis proteins Xr1 and Xr11; human induced myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein MCL1 and Caenorhabditis elegansCaenorhabditis elegans
Caenorhabditis elegans is a free-living, transparent nematode , about 1 mm in length, which lives in temperate soil environments. Research into the molecular and developmental biology of C. elegans was begun in 1974 by Sydney Brenner and it has since been used extensively as a model...
protein ced-9.
Human genes encoding proteins that belong to this family include:
- BAK1
- BAXBcl-2-associated X proteinThe Bcl-2–associated X protein, or Bax is a protein of the Bcl-2 gene family. It promotes apoptosis by competing with Bcl-2 proper.The BAX gene was the first identified pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 protein family....
- BCL2Bcl-2Bcl-2 is the founding member of the Bcl-2 family of apoptosis regulator proteins encoded by the BCL2 gene. Bcl-2 derives its name from B-cell lymphoma 2, as it is the second member of a range of proteins initially described in chromosomal translocations involving chromosomes 14 and 18 in...
, BCL2A1 - BCL2L1BCL2-like 1 (gene)Bcl-2-like protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BCL2L1 gene.-Interactions:BCL2-like 1 has been shown to interact with RAD9A, RTN1, BAK1, Reticulon 4, Bcl-2-associated X protein, BCAP31, Bcl-2-interacting killer, PPP1CA, Noxa, VDAC1, BCL2L11, Bcl-2-associated death promoter,...
, BCL2L2BCL2L2Bcl-2-like protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BCL2L2 gene.This gene encodes a pro-survival member of the bcl-2 protein family. The proteins of this family form hetero- or homodimers and act as anti- and pro-apoptotic regulators. Expression of this gene in cells has been shown...
, BCL2L10BCL2L10Bcl-2-like protein 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BCL2L10 gene.-Further reading:...
, BCL2L13BCL2L13BCL2-like 13 , also known as BCL2L13 or Bcl-rambo, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the BCL2L13 gene.- Function :Bcl-rambo is a member of the Bcl-2 family of proteins that regulate apoptosis...
, BCL2L14BCL2L14Apoptosis facilitator Bcl-2-like protein 14 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BCL2L14 gene.-Further reading:... - BOKBOK (gene)Bcl-2-related ovarian killer protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BOK gene.-Further reading:...
- MCL1MCL1Induced myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein Mcl-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MCL1 gene.- Function :The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the Bcl-2 family. Alternative splicing occurs at this locus and two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been...

