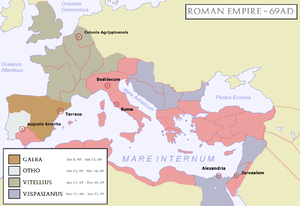
Battle of Bedriacum
Encyclopedia
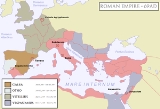
The Battle of Bedriacum refers to two battles fought during the Year of the Four Emperors
(69) near the village of Bedriacum (now Calvatone
), about 35 kilometres (21.7 mi) from the town of Cremona
in northern Italy
. The fighting in fact took place between Bedriacum and Cremona, and the battles are sometimes called "First Cremona" and "Second Cremona".
, with the support and aid of the Praetorian Guard
, had his predecessor Galba
murdered in January and claimed the throne for himself. However, legate Aulus Vitellius
, governor of the province of Germania Inferior
, had also claimed the throne earlier in the month and marched on Rome with his troops. Vitellius' forces were divided into two armies, one commanded by Aulus Caecina Alienus
and the other by Fabius Valens
. The Vitellian forces included legions XXI Rapax
, V Alaudae
and powerful vexillatio
nes from all the other legions stationed on the Rhine, together with a strong force of Batavian
auxiliaries, a force of around 70,000 in total. The forces commanded by Caecina crossed the Alps by the Great St. Bernard Pass
to reach northern Italy. They attacked Placentia
but were repulsed by the Othonian garrison and fell back on Cremona to await the arrival of Valens' army.
Otho left Rome on the March 14, and marched north to meet the challenge, leaving his brother Titianus in charge of Rome. He made his base at Brixellum
. His forces included legions I Adiutrix
, XIII Gemina
, a forward detachment of XIIII Gemina, the Praetorian Guard and a force of gladiator
s. His general staff included generals such as Gaius Suetonius Paulinus
, who, as governor of Britain, had defeated Boudica
eight years before, but Otho decided to call his brother Titianus from Rome to act as his commander in chief.
Before Titianus arrived, one engagement had already been fought. Caecina tried to set up an ambush at a village called Locus Castrorum, about half way between Bedriacum and Cremona on the Via Postumia
. However the Othonians were informed of this, and their army marched for Locus Castrorum, led by Suetonius Paulinus. The Othonians had the better of the fighting which followed, and Caecina's troops retreated to Cremona. Here they were joined by Valens' army, which had followed a longer route through Gaul
.
Titanius had now joined the Othonian armies and took command. It was decided to march on Cremona to give battle, against the advice of Paulinus and other generals, who wished to wait until other legions, known to be on the way, had arrived. Otho himself remained at Brixellum to await the outcome. On 14 April the two armies met on the Via Postumia, nearer Cremona than Bedriacum, with the Othonian troops already tired after a long march. Some of the heaviest fighting was where Otho's 1st Adiutrix legion, recently raised from the marines at Ravenna
, clashed with Vitellius' veteran Rapax. The Adiutrix acquitted itself well, capturing the eagle of the 21st, though its commanding officer was killed as the 21st strove to recover it. Elsewhere on the battlefield, however, Otho's 13th legion was defeated by Vitellius' Alaudae, and the Adiutrix eventually gave way when a force of Batavian auxiliaries took them in the flank. According to Dio Cassius
about 40,000 men were killed in the fighting. The Othonian troops fled back to their camp in Bedriacum, and the next day surrendered to the Vitellian forces and took the oath of allegiance to Vitellius.
When news of the defeat was brought to Brixellum, many of Otho's troops urged him to fight on, pointing out that more troops were on the way. Otho however decided to commit suicide rather than cause more deaths. He had been emperor for less than three months. Vitellius continued his march on Rome, where he made a triumphal entry and was recognized as emperor by the Senate.
had acclaimed Vespasian
as emperor. Vespasian had been given a special command in Iudaea by Nero
in 67 with the task of putting down the Great Jewish Revolt. He gained the support of the governor of Syria, Gaius Licinius Mucianus and a strong force drawn from the Judaean and Syrian legions marched on Rome under the command of Mucianus.
Before the eastern legions could reach Rome, the Danubian legions of the provinces of Raetia
and Moesia
also acclaimed Vespasian as Emperor in August. Three of these legions, III Gallica
, VIII Augusta
and VII Claudia
had been on their way to support Otho when they heard of his defeat at the first battle of Bedriacum. They had been made to swear allegiance to Vitellius, but when they heard of Vespasian's bid for power they switched their support to him. They persuaded the other two legions, VII Galbiana
and XIII Gemina to join them, which the thirteenth Gemina did all the more readily as they were one of the legions which had been defeated at First Bedriacum, and had been made to build amphitheatres for Valens and Caecina as punishment. Led by the commanding officer of the seventh Galbiana, Marcus Antonius Primus
, they marched on Rome, and having a shorter distance to march reached Italy before Mucianus' troops.
When Vitellius heard of Antonius' approach, he dispatched Caecina with a powerful army composed of XXI Rapax, V Alaudae, I Italica
and XXII Primigenia
together with detachments from seven other legions and a force of auxiliaries. The first of Antonius' legions had arrived at Verona
, but though urged to attack them before the remainder of the army arrived, Caecina declined to do so. Caecina had been plotting with Lucilius Bassus, commander of the fleet
at Ravenna, to switch their support to Vespasian. His troops refused to follow his lead however, and put him in chains. Valens, who had been delayed by illness, had by now set out from Rome.
Caecina's army, now without their general, advanced on Cremona. Antonius was now based at Bedriacum, and advanced towards Cremona with a force of cavalry. They encountered the vanguard of the Vitellian army between Bedriacum and Cremona on the 24 October and a battle followed, with Antonius sending back to Bedriacum for the legions. Antonius' troops had the better of the fighting, and the Vitellian troops retreated to their camp outside Cremona.
Antonius' forces advanced along the Via Postuma towards Cremona. They were opposed by a powerful Vitellian army, who had been reinforced by other legions including legion IIII Macedonica, but were still without a commander as Valens had not yet arrived. By now night had fallen and the battle continued through the hours of darkness. The seventh Galbiana, Antonius' own legion, suffered heavy casualties and lost its eagle for a while, though one of its centurions later sacrificed his own life to win it back. Eventually Antonius' forces began to gain the upper hand, and the turning point came when dawn broke. Antonius' third Gallica had served in Syria for many years and while there had adopted a local custom. As the sun rose they turned to the east to salute it, and this was misinterpreted by the Vitellian forces who thought that they were greeting reinforcements from the east and lost heart. The Vitellian forces were driven back into their camp, which was taken by Antonius' forces. Antonius then attacked Cremona itself, which surrendered. Cremona was burned by the victorious troops.
Antonius continued to Rome, where Vitellius was taken prisoner and shortly afterwards killed. The way was thus cleared for Vespasian to ascend the throne near the end of this bloody year of crisis.
Year of the Four Emperors
The Year of the Four Emperors was a year in the history of the Roman Empire, AD 69, in which four emperors ruled in a remarkable succession. These four emperors were Galba, Otho, Vitellius, and Vespasian....
(69) near the village of Bedriacum (now Calvatone
Calvatone
Calvatone is a comune in the Province of Cremona in the Italian region Lombardy, located about 110 km southeast of Milan and about 35 km east of Cremona. Its territory is crossed by the Oglio River....
), about 35 kilometres (21.7 mi) from the town of Cremona
Cremona
Cremona is a city and comune in northern Italy, situated in Lombardy, on the left bank of the Po River in the middle of the Pianura Padana . It is the capital of the province of Cremona and the seat of the local City and Province governments...
in northern Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
. The fighting in fact took place between Bedriacum and Cremona, and the battles are sometimes called "First Cremona" and "Second Cremona".

First Battle of Bedriacum
Marcus Salvius OthoOtho
Otho , was Roman Emperor for three months, from 15 January to 16 April 69. He was the second emperor of the Year of the four emperors.- Birth and lineage :...
, with the support and aid of the Praetorian Guard
Praetorian Guard
The Praetorian Guard was a force of bodyguards used by Roman Emperors. The title was already used during the Roman Republic for the guards of Roman generals, at least since the rise to prominence of the Scipio family around 275 BC...
, had his predecessor Galba
Galba
Galba , was Roman Emperor for seven months from 68 to 69. Galba was the governor of Hispania Tarraconensis, and made a bid for the throne during the rebellion of Julius Vindex...
murdered in January and claimed the throne for himself. However, legate Aulus Vitellius
Vitellius
Vitellius , was Roman Emperor for eight months, from 16 April to 22 December 69. Vitellius was acclaimed Emperor following the quick succession of the previous emperors Galba and Otho, in a year of civil war known as the Year of the Four Emperors...
, governor of the province of Germania Inferior
Germania Inferior
Germania Inferior was a Roman province located on the left bank of the Rhine, in today's Luxembourg, southern Netherlands, parts of Belgium, and North Rhine-Westphalia left of the Rhine....
, had also claimed the throne earlier in the month and marched on Rome with his troops. Vitellius' forces were divided into two armies, one commanded by Aulus Caecina Alienus
Aulus Caecina Alienus
Aulus Caecina Alienus, Roman general, was born in Vicetia .He was quaestor of Hispania Baetica in AD 68. On the death of Nero, he attached himself to Galba, who appointed him to the command of Legio IV Macedonica at Mogontiacum in Germania Superior...
and the other by Fabius Valens
Fabius Valens
Fabius Valens of Anagnia was a Roman commander favoured by Nero. In 69 he was commander of Legio I Germanica based in Germania Inferior...
. The Vitellian forces included legions XXI Rapax
Legio XXI Rapax
Legio vigesima prima rapax was a Roman legion levied in 31 BC by Augustus, probably from men previously enlisted in other legions. The XXI Rapax was destroyed in 92 by the Dacians and Sarmatians...
, V Alaudae
Legio V Alaudae
Legio quinta Alaudae sometimes known as Gallica, was levied by Julius Caesar in 52 BC from native Gauls. Their emblem was an elephant, and their cognomen Alaudae came from the high crest on their helmets, typical of the Gauls, which made them look like larks...
and powerful vexillatio
Vexillatio
A vexillatio was a detachment of a Roman legion formed as a temporary task force created by the Roman Army of the Principate. It was named from the standards carried by legionary detachments, vexillum , which bore the emblem and name of the parent legion...
nes from all the other legions stationed on the Rhine, together with a strong force of Batavian
Batavians
The Batavi were an ancient Germanic tribe, originally part of the Chatti, reported by Tacitus to have lived around the Rhine delta, in the area that is currently the Netherlands, "an uninhabited district on the extremity of the coast of Gaul, and also of a neighbouring island, surrounded by the...
auxiliaries, a force of around 70,000 in total. The forces commanded by Caecina crossed the Alps by the Great St. Bernard Pass
Great St. Bernard Pass
Great St. Bernard Pass is the third highest road pass in Switzerland. It connects Martigny in the Canton of Valais in Switzerland to Aosta in Italy. It is the lowest pass lying on the ridge between the two highest summits of the Alps, Mont Blanc and Monte Rosa...
to reach northern Italy. They attacked Placentia
Placentia
Placentia may refer to:* Palace of Placentia, an English Royal Palace* Placentia, California, United States* Placentia, Italy* Placentia, Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada* Battle of Placentia* Placentia Bay, the name of two ships of the Royal Navy...
but were repulsed by the Othonian garrison and fell back on Cremona to await the arrival of Valens' army.
Otho left Rome on the March 14, and marched north to meet the challenge, leaving his brother Titianus in charge of Rome. He made his base at Brixellum
Brescello
Brescello is a comune in the Province of Reggio Emilia in the Italian region Emilia-Romagna, located about 80 km northwest of Bologna and about 25 km northwest of Reggio Emilia...
. His forces included legions I Adiutrix
Legio I Adiutrix
Legio prima Adiutrix , was a Roman legion formed in 68, possibly by Galba under orders of Nero. The last record mentioning the Adiutrix is in 344, when it was stationed at Brigetio , in the Roman province of Pannonia...
, XIII Gemina
Legio XIII Gemina
Legio tertia decima Gemina was one of the most prominent Roman legions. It was one of Julius Caesar's key units in Gaul and in the civil war, and was the legion with which he famously crossed the Rubicon on January 10, 49 BC. The legion appears to have still been in existence in the fifth century...
, a forward detachment of XIIII Gemina, the Praetorian Guard and a force of gladiator
Gladiator
A gladiator was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gladiators were volunteers who risked their legal and social standing and their lives by appearing in the...
s. His general staff included generals such as Gaius Suetonius Paulinus
Gaius Suetonius Paulinus
Gaius Suetonius Paulinus, also spelled Paullinus, was a Roman general best known as the commander who defeated the rebellion of Boudica.-Career:...
, who, as governor of Britain, had defeated Boudica
Boudica
Boudica , also known as Boadicea and known in Welsh as "Buddug" was queen of the British Iceni tribe who led an uprising against the occupying forces of the Roman Empire....
eight years before, but Otho decided to call his brother Titianus from Rome to act as his commander in chief.
Before Titianus arrived, one engagement had already been fought. Caecina tried to set up an ambush at a village called Locus Castrorum, about half way between Bedriacum and Cremona on the Via Postumia
Via Postumia
The Via Postumia was an ancient Roman road of northern Italy constructed in 148 BC by the consul Spurius Postumius Albinus Magnus.It ran from the coast at Genua through the mountains to Dertona, Placentia and Cremona, just east of the point where it crossed the Po River...
. However the Othonians were informed of this, and their army marched for Locus Castrorum, led by Suetonius Paulinus. The Othonians had the better of the fighting which followed, and Caecina's troops retreated to Cremona. Here they were joined by Valens' army, which had followed a longer route through Gaul
Gaul
Gaul was a region of Western Europe during the Iron Age and Roman era, encompassing present day France, Luxembourg and Belgium, most of Switzerland, the western part of Northern Italy, as well as the parts of the Netherlands and Germany on the left bank of the Rhine. The Gauls were the speakers of...
.
Titanius had now joined the Othonian armies and took command. It was decided to march on Cremona to give battle, against the advice of Paulinus and other generals, who wished to wait until other legions, known to be on the way, had arrived. Otho himself remained at Brixellum to await the outcome. On 14 April the two armies met on the Via Postumia, nearer Cremona than Bedriacum, with the Othonian troops already tired after a long march. Some of the heaviest fighting was where Otho's 1st Adiutrix legion, recently raised from the marines at Ravenna
Ravenna
Ravenna is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna in the Emilia-Romagna region of Italy and the second largest comune in Italy by land area, although, at , it is little more than half the size of the largest comune, Rome...
, clashed with Vitellius' veteran Rapax. The Adiutrix acquitted itself well, capturing the eagle of the 21st, though its commanding officer was killed as the 21st strove to recover it. Elsewhere on the battlefield, however, Otho's 13th legion was defeated by Vitellius' Alaudae, and the Adiutrix eventually gave way when a force of Batavian auxiliaries took them in the flank. According to Dio Cassius
Dio Cassius
Lucius Cassius Dio Cocceianus , known in English as Cassius Dio, Dio Cassius, or Dio was a Roman consul and a noted historian writing in Greek...
about 40,000 men were killed in the fighting. The Othonian troops fled back to their camp in Bedriacum, and the next day surrendered to the Vitellian forces and took the oath of allegiance to Vitellius.
When news of the defeat was brought to Brixellum, many of Otho's troops urged him to fight on, pointing out that more troops were on the way. Otho however decided to commit suicide rather than cause more deaths. He had been emperor for less than three months. Vitellius continued his march on Rome, where he made a triumphal entry and was recognized as emperor by the Senate.
Second Battle of Bedriacum
Meanwhile, the legions stationed in the Middle East provinces of Judaea and SyriaSyria (Roman province)
Syria was a Roman province, annexed in 64 BC by Pompey, as a consequence of his military presence after pursuing victory in the Third Mithridatic War. It remained under Roman, and subsequently Byzantine, rule for seven centuries, until 637 when it fell to the Islamic conquests.- Principate :The...
had acclaimed Vespasian
Vespasian
Vespasian , was Roman Emperor from 69 AD to 79 AD. Vespasian was the founder of the Flavian dynasty, which ruled the Empire for a quarter century. Vespasian was descended from a family of equestrians, who rose into the senatorial rank under the Emperors of the Julio-Claudian dynasty...
as emperor. Vespasian had been given a special command in Iudaea by Nero
Nero
Nero , was Roman Emperor from 54 to 68, and the last in the Julio-Claudian dynasty. Nero was adopted by his great-uncle Claudius to become his heir and successor, and succeeded to the throne in 54 following Claudius' death....
in 67 with the task of putting down the Great Jewish Revolt. He gained the support of the governor of Syria, Gaius Licinius Mucianus and a strong force drawn from the Judaean and Syrian legions marched on Rome under the command of Mucianus.
Before the eastern legions could reach Rome, the Danubian legions of the provinces of Raetia
Raetia
Raetia was a province of the Roman Empire, named after the Rhaetian people. It was bounded on the west by the country of the Helvetii, on the east by Noricum, on the north by Vindelicia, on the west by Cisalpine Gaul and on south by Venetia et Histria...
and Moesia
Moesia
Moesia was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans, along the south bank of the Danube River. It included territories of modern-day Southern Serbia , Northern Republic of Macedonia, Northern Bulgaria, Romanian Dobrudja, Southern Moldova, and Budjak .-History:In ancient...
also acclaimed Vespasian as Emperor in August. Three of these legions, III Gallica
Legio III Gallica
Legio tertia Gallica was a Roman legion levied by Julius Caesar around 49 BC, for his civil war against the conservative republicans led by Pompey. The cognomen Gallica suggests that recruits were originally from the Gallic Roman provinces. The legion was still active in Egypt in the early 4th...
, VIII Augusta
Legio VIII Augusta
Legio octava Augusta was a Roman legion created by Pompey in 65 BC, along with the 6th, 7th & 9th, and continuing in service to Rome for at least 400 years thereafter....
and VII Claudia
Legio VII Claudia
Legio septima Claudia Pia Fidelis was a Roman legion. Its emblem, like that of all Caesar's legions, was the bull, together with the lion....
had been on their way to support Otho when they heard of his defeat at the first battle of Bedriacum. They had been made to swear allegiance to Vitellius, but when they heard of Vespasian's bid for power they switched their support to him. They persuaded the other two legions, VII Galbiana
Legio VII Gemina
Legio septima Gemina was a Roman legion; its full name was Legio VII Gemina Felix. VII Gemina dates back to the Year of the four emperors , when the governor of Hispania Tarraconensis, Galba, levied a legion to march on Rome...
and XIII Gemina to join them, which the thirteenth Gemina did all the more readily as they were one of the legions which had been defeated at First Bedriacum, and had been made to build amphitheatres for Valens and Caecina as punishment. Led by the commanding officer of the seventh Galbiana, Marcus Antonius Primus
Marcus Antonius Primus
Marcus Antonius Primus was a Roman Empire general.Primus was born at Tolosa in Gaul. During the reign of Nero, he was resident in Rome and a member of the Senate, from which he was expelled for conspiring to forge a will with Valerius Fabianus, and was banished from the city...
, they marched on Rome, and having a shorter distance to march reached Italy before Mucianus' troops.
When Vitellius heard of Antonius' approach, he dispatched Caecina with a powerful army composed of XXI Rapax, V Alaudae, I Italica
Legio I Italica
Legio prima Italica was a Roman legion levied by emperor Nero on September 22, 66 . There are still records of the I Italica in the Danube border in the beginning of the 5th century...
and XXII Primigenia
Legio XXII Primigenia
Legio XXII Primigenia was a Roman legion levied by Roman Emperor Caligula in 39, for his campaigns in Germania. There are still records of the XXII Primigenia in Mogontiacum from the end of 3rd century...
together with detachments from seven other legions and a force of auxiliaries. The first of Antonius' legions had arrived at Verona
Verona
Verona ; German Bern, Dietrichsbern or Welschbern) is a city in the Veneto, northern Italy, with approx. 265,000 inhabitants and one of the seven chef-lieus of the region. It is the second largest city municipality in the region and the third of North-Eastern Italy. The metropolitan area of Verona...
, but though urged to attack them before the remainder of the army arrived, Caecina declined to do so. Caecina had been plotting with Lucilius Bassus, commander of the fleet
Roman Navy
The Roman Navy comprised the naval forces of the Ancient Roman state. Although the navy was instrumental in the Roman conquest of the Mediterranean basin, it never enjoyed the prestige of the Roman legions...
at Ravenna, to switch their support to Vespasian. His troops refused to follow his lead however, and put him in chains. Valens, who had been delayed by illness, had by now set out from Rome.
Caecina's army, now without their general, advanced on Cremona. Antonius was now based at Bedriacum, and advanced towards Cremona with a force of cavalry. They encountered the vanguard of the Vitellian army between Bedriacum and Cremona on the 24 October and a battle followed, with Antonius sending back to Bedriacum for the legions. Antonius' troops had the better of the fighting, and the Vitellian troops retreated to their camp outside Cremona.
Antonius' forces advanced along the Via Postuma towards Cremona. They were opposed by a powerful Vitellian army, who had been reinforced by other legions including legion IIII Macedonica, but were still without a commander as Valens had not yet arrived. By now night had fallen and the battle continued through the hours of darkness. The seventh Galbiana, Antonius' own legion, suffered heavy casualties and lost its eagle for a while, though one of its centurions later sacrificed his own life to win it back. Eventually Antonius' forces began to gain the upper hand, and the turning point came when dawn broke. Antonius' third Gallica had served in Syria for many years and while there had adopted a local custom. As the sun rose they turned to the east to salute it, and this was misinterpreted by the Vitellian forces who thought that they were greeting reinforcements from the east and lost heart. The Vitellian forces were driven back into their camp, which was taken by Antonius' forces. Antonius then attacked Cremona itself, which surrendered. Cremona was burned by the victorious troops.
Antonius continued to Rome, where Vitellius was taken prisoner and shortly afterwards killed. The way was thus cleared for Vespasian to ascend the throne near the end of this bloody year of crisis.

