Array data type
Encyclopedia
In computer science
, an array type is a data type
that is meant to describe a collection of elements (values
or variables), each selected by one or more indices
that can be computed at run time by the program. Such a collection is usually called an array variable, array value, or simply array. By analogy with the mathematical concepts of vector and matrix
, an array type with one or two indices is often called a vector type or matrix type, respectively.
Language support for array types may include certain built-in array data types, some syntactic constructions (array type constructors) that the programmer
may use to define such types and declare array variables, and special notation for indexing array elements. For example, in the Pascal programming language, the declaration
.
Array types are distinguished from record
types mainly because they allow the element indices to be computed at run time, as in the Pascal assignment
In more theoretical contexts, especially in type theory
and in the description of abstract algorithm
s, the terms "array" and "array type" sometimes refer to an abstract data type
(ADT) also called abstract array or may refer to an associative array
, a mathematical
model with the basic operations and behavior of a typical array type in most languages — basically, a collection of elements that are selected by indices computed at run-time.
Depending on the language, array types may overlap (or be identified with) other data types that describe aggregates of values, such as lists and strings
. Array types are often implemented by array data structures, but sometimes by other means, such as hash table
s, linked list
s, or search tree
s.
Because of the importance of array structures for efficient computation, the earliest high-level programming languages, including FORTRAN
(1957), COBOL
(1960), and Algol 60
(1960), provided support for multi-dimensional arrays.
These operations are required to satisfy the axiom
s
for any array state A, any value V, and any tuples I, J for which the operations are defined.
The first axiom means that each element behaves like a variable. The second axiom means that elements with distinct indices behave as disjoint
variables, so that storing a value in one element does not affect the value of any other element.
These axioms do not place any constraints on the set of valid index tuples I, therefore this abstract model can be used for triangular matrices
and other oddly-shaped arrays.
data types (or other types that can be interpreted as integers, such as byte
s and enumerated type
s), and require that all elements have the same data type and storage size. Most of those languages also restrict each index to a finite interval
of integers, that remains fixed throughout the lifetime of the array variable. In some compiled
languages, in fact, the index ranges may have to be known at compile time
.
On the other hand, some programming languages provide more liberal array types, that allow indexing by arbitrary values, such as floating-point numbers
, strings
, objects
, references
, etc.. Such index values cannot be restricted to an interval, much less a fixed interval. So, these languages usually allow arbitrary new elements to be created at any time. This choice precludes the implementation of array types as array data structures. That is, those languages use array-like syntax to implement a more general associative array
semantics, and must therefore be implemented by a hash table
or some other search data structure.
of the array type. (This nomenclature conflicts with the concept of dimension in linear algebra, where it is the number of elements. Thus, an array of numbers with 5 rows and 4 columns (hence 20 elements) is said to have dimension 2 in computing contexts, but 20 in mathematics. Also, the computer science meaning of "rank" is similar to its meaning in tensor algebra but not to the linear algebra concept of rank of a matrix.)
 Many languages support only one-dimensional arrays. In those languages, a multi-dimensional array is typically represented by an Iliffe vector
Many languages support only one-dimensional arrays. In those languages, a multi-dimensional array is typically represented by an Iliffe vector
, a one-dimensional array of references
to arrays of one dimension less. A two-dimensional array, in particular, would be implemented as a vector of pointers to its rows. Thus an element in row i and column j of an array A would be accessed by double indexing (A[i][j] in typical notation). This way of emulating multi-dimensional arrays allows the creation of ragged or jagged arrays, where each row may have a different size — or, in general, where the valid range of each index depends on the values of all preceding indices.
This representation for multi-dimensional arrays is quite prevalent in C and C++ software. However, C and C++ will use a linear indexing formula for multi-dimensional arrays that are declared as such, e.g. by
languages, and is still the case of most systems programming languages such as Ada
, C, and C++
. In some languages, however, array data types have the semantics of associative arrays, with indices of arbitrary type and dynamic element creation. This is the case in some scripting languages such as Awk and Lua, and of some array types provided by standard C++
libraries.
on every access, raising an exception or aborting the program when any index is out of its valid range. Compilers may allow these checks to be turned off to trade safety for speed. Other languages (like FORTRAN and C) trust the programmer and perform no checks. Good compilers may also analyze the program to determine the range of possible values that the index may have, and this analysis may lead to bounds-checking elimination
.
Other languages provide only one-based array types, where each index starts at 1; this is the traditional convention in mathematics for matrices and mathematical sequence
s. A few languages, such as Pascal, support n-based array types, whose minimum legal indices are chosen by the programmer. The relative merits of each choice have been the subject of heated debate. Zero-based indexing has a natural advantage to one-based indexing in avoiding off-by-one
or fencepost errors.
See comparison of programming languages (array)
for the base indices used by various languages.
The 0-based/1-based debate is not limited to just programming languages. For example, the elevator button for the ground-floor of a building is labeled "0" in France
and many other countries, but "1" in the USA.
) one should specify the numeric value of the index of the last element. Needless to say, this distinction is immaterial in languages where the indices start at 1.
, Matlab
, and newer versions of Fortran
) directly support array programming
, where operations and functions defined for certain data types are implicitly extended to arrays of elements of those types. Thus one can write A+B to add corresponding elements of two arrays A and B. The multiplication operation may be merely distributed over corresponding elements of the operands (APL) or may be interpreted as the matrix product of linear algebra
(Matlab).
data type, with specialized notation ("string literals") to build values of that type. In some languages (such as C), a string is just an array of characters, or is handled in much the same way. Other languages, like Pascal, may provide vastly different operations for strings and arrays.
and C++
arrays do not support the size function, so programmers often have to declare separate variable to hold the size, and pass it to procedures as a separate parameter.
Elements of a newly created array may have undefined values (as in C), or may be defined to have a specific "default" value such as 0 or a null pointer (as in Java).
In C++
a std::vector object supports the store, select, and append operations with the performance characteristics discussed above. Vectors can be queried for their size and can be resized. Slower operations like inserting an element in the middle are also supported.
operation takes a subset of the elements of an array-typed entity (value or variable) and then assembles them as another array-typed entity, possibly with other indices. If array types are implemented as array structures, many useful slicing operations (such as selecting a sub-array, swapping indices, or reversing the direction of the indices) can be performed very efficiently by manipulating the dope vector
of the structure. The possible slicings depend on the implementation details: for example, FORTRAN allows slicing off one column of a matrix variable, but not a row, and treat it as a vector; whereas C allow slicing off a row from a matrix, but not a column.
On the other hand, other slicing operations are possible when array types are implemented in other ways.
s (also called resizable, growable, or extensible): array variables whose index ranges may be expanded at any time after creation, without changing the values of its current elements.
For one-dimensional arrays, this facility may be provided as an operation "
An exensible array can be implemented as a fixed-size array, with a counter that records how many elements are actually in use. The
with a fixed capacity, as in the string type of Pascal. Alternatively, the
Computer science
Computer science or computing science is the study of the theoretical foundations of information and computation and of practical techniques for their implementation and application in computer systems...
, an array type is a data type
Data type
In computer programming, a data type is a classification identifying one of various types of data, such as floating-point, integer, or Boolean, that determines the possible values for that type; the operations that can be done on values of that type; the meaning of the data; and the way values of...
that is meant to describe a collection of elements (values
Value (computer science)
In computer science, a value is an expression which cannot be evaluated any further . The members of a type are the values of that type. For example, the expression "1 + 2" is not a value as it can be reduced to the expression "3"...
or variables), each selected by one or more indices
Index (information technology)
In computer science, an index can be:# an integer that identifies an array element# a data structure that enables sublinear-time lookup -Array element identifier:...
that can be computed at run time by the program. Such a collection is usually called an array variable, array value, or simply array. By analogy with the mathematical concepts of vector and matrix
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, symbols, or expressions. The individual items in a matrix are called its elements or entries. An example of a matrix with six elements isMatrices of the same size can be added or subtracted element by element...
, an array type with one or two indices is often called a vector type or matrix type, respectively.
Language support for array types may include certain built-in array data types, some syntactic constructions (array type constructors) that the programmer
Programmer
A programmer, computer programmer or coder is someone who writes computer software. The term computer programmer can refer to a specialist in one area of computer programming or to a generalist who writes code for many kinds of software. One who practices or professes a formal approach to...
may use to define such types and declare array variables, and special notation for indexing array elements. For example, in the Pascal programming language, the declaration
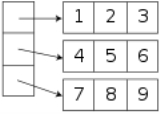
type MyTable = array [1..4,1..2] of integer, defines a new array data type called MyTable. The declaration var A: MyTable then defines a variable A of that type, which is an aggregate of eight elements, each being an integer variable identified by two indices. In the Pascal program, those elements are denoted A[1,1], A[1,2], A[2,1],… A[4,2]. Special array types are often defined by the language's standard librariesLibrary (computer science)
In computer science, a library is a collection of resources used to develop software. These may include pre-written code and subroutines, classes, values or type specifications....
.
Array types are distinguished from record
Record (computer science)
In computer science, a record is an instance of a product of primitive data types called a tuple. In C it is the compound data in a struct. Records are among the simplest data structures. A record is a value that contains other values, typically in fixed number and sequence and typically indexed...
types mainly because they allow the element indices to be computed at run time, as in the Pascal assignment
A[I,J] := A[N-I,2*J]. Among other things, this feature allows a single iterative statement to process arbitrarily many elements of an array variable.In more theoretical contexts, especially in type theory
Type theory
In mathematics, logic and computer science, type theory is any of several formal systems that can serve as alternatives to naive set theory, or the study of such formalisms in general...
and in the description of abstract algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
s, the terms "array" and "array type" sometimes refer to an abstract data type
Abstract data type
In computing, an abstract data type is a mathematical model for a certain class of data structures that have similar behavior; or for certain data types of one or more programming languages that have similar semantics...
(ADT) also called abstract array or may refer to an associative array
Associative array
In computer science, an associative array is an abstract data type composed of a collection of pairs, such that each possible key appears at most once in the collection....
, a mathematical
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
model with the basic operations and behavior of a typical array type in most languages — basically, a collection of elements that are selected by indices computed at run-time.
Depending on the language, array types may overlap (or be identified with) other data types that describe aggregates of values, such as lists and strings
String (computer science)
In formal languages, which are used in mathematical logic and theoretical computer science, a string is a finite sequence of symbols that are chosen from a set or alphabet....
. Array types are often implemented by array data structures, but sometimes by other means, such as hash table
Hash table
In computer science, a hash table or hash map is a data structure that uses a hash function to map identifying values, known as keys , to their associated values . Thus, a hash table implements an associative array...
s, linked list
Linked list
In computer science, a linked list is a data structure consisting of a group of nodes which together represent a sequence. Under the simplest form, each node is composed of a datum and a reference to the next node in the sequence; more complex variants add additional links...
s, or search tree
Search tree
In computer science, a search tree is a binary tree data structure in whose nodes data values are stored from some ordered set, in such a way that in-order traversal of the tree visits the nodes in ascending order of the stored values...
s.
History
Assembly languages and low-level languages like BCPL generally have no syntactic support for arrays.Because of the importance of array structures for efficient computation, the earliest high-level programming languages, including FORTRAN
Fortran
Fortran is a general-purpose, procedural, imperative programming language that is especially suited to numeric computation and scientific computing...
(1957), COBOL
COBOL
COBOL is one of the oldest programming languages. Its name is an acronym for COmmon Business-Oriented Language, defining its primary domain in business, finance, and administrative systems for companies and governments....
(1960), and Algol 60
ALGOL 60
ALGOL 60 is a member of the ALGOL family of computer programming languages. It gave rise to many other programming languages, including BCPL, B, Pascal, Simula, C, and many others. ALGOL 58 introduced code blocks and the begin and end pairs for delimiting them...
(1960), provided support for multi-dimensional arrays.
Abstract arrays
An array data structure can be mathematically modeled as an abstract data structure (an abstract array) with two operations- get(A, I): the data stored in the element of the array A whose indices are the integer tupleTupleIn mathematics and computer science, a tuple is an ordered list of elements. In set theory, an n-tuple is a sequence of n elements, where n is a positive integer. There is also one 0-tuple, an empty sequence. An n-tuple is defined inductively using the construction of an ordered pair...
I. - set(A,I,V): the array that results by setting the value of that element to V.
These operations are required to satisfy the axiom
Axiom
In traditional logic, an axiom or postulate is a proposition that is not proven or demonstrated but considered either to be self-evident or to define and delimit the realm of analysis. In other words, an axiom is a logical statement that is assumed to be true...
s
- get(set(A,I, V), I) = V
- get(set(A,I, V), J) = get(A, J) if I ≠ J
for any array state A, any value V, and any tuples I, J for which the operations are defined.
The first axiom means that each element behaves like a variable. The second axiom means that elements with distinct indices behave as disjoint
Aliasing (computing)
In computing, aliasing describes a situation in which a data location in memory can be accessed through different symbolic names in the program. Thus, modifying the data through one name implicitly modifies the values associated to all aliased names, which may not be expected by the programmer...
variables, so that storing a value in one element does not affect the value of any other element.
These axioms do not place any constraints on the set of valid index tuples I, therefore this abstract model can be used for triangular matrices
Triangular array
In mathematics and computing, a triangular array of numbers, polynomials, or the like, is a doubly indexed sequence in which each row is only as long as the row's own index.Notable particular examples include these:...
and other oddly-shaped arrays.
Implementations
In order to effectively implement variables of such types as array structures (with indexing done by pointer arithmetic), many languages restrict the indices to integerInteger (computer science)
In computer science, an integer is a datum of integral data type, a data type which represents some finite subset of the mathematical integers. Integral data types may be of different sizes and may or may not be allowed to contain negative values....
data types (or other types that can be interpreted as integers, such as byte
Byte
The byte is a unit of digital information in computing and telecommunications that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, a byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the basic addressable element in many computer...
s and enumerated type
Enumerated type
In computer programming, an enumerated type is a data type consisting of a set of named values called elements, members or enumerators of the type. The enumerator names are usually identifiers that behave as constants in the language...
s), and require that all elements have the same data type and storage size. Most of those languages also restrict each index to a finite interval
Interval (mathematics)
In mathematics, a interval is a set of real numbers with the property that any number that lies between two numbers in the set is also included in the set. For example, the set of all numbers satisfying is an interval which contains and , as well as all numbers between them...
of integers, that remains fixed throughout the lifetime of the array variable. In some compiled
Compiler
A compiler is a computer program that transforms source code written in a programming language into another computer language...
languages, in fact, the index ranges may have to be known at compile time
Compile time
In computer science, compile time refers to either the operations performed by a compiler , programming language requirements that must be met by source code for it to be successfully compiled , or properties of the program that can be reasoned about at compile time.The operations performed at...
.
On the other hand, some programming languages provide more liberal array types, that allow indexing by arbitrary values, such as floating-point numbers
Floating point
In computing, floating point describes a method of representing real numbers in a way that can support a wide range of values. Numbers are, in general, represented approximately to a fixed number of significant digits and scaled using an exponent. The base for the scaling is normally 2, 10 or 16...
, strings
String (computer science)
In formal languages, which are used in mathematical logic and theoretical computer science, a string is a finite sequence of symbols that are chosen from a set or alphabet....
, objects
Object-oriented programming
Object-oriented programming is a programming paradigm using "objects" – data structures consisting of data fields and methods together with their interactions – to design applications and computer programs. Programming techniques may include features such as data abstraction,...
, references
Reference (computer science)
In computer science, a reference is a value that enables a program to indirectly access a particular data item, such as a variable or a record, in the computer's memory or in some other storage device. The reference is said to refer to the data item, and accessing those data is called...
, etc.. Such index values cannot be restricted to an interval, much less a fixed interval. So, these languages usually allow arbitrary new elements to be created at any time. This choice precludes the implementation of array types as array data structures. That is, those languages use array-like syntax to implement a more general associative array
Associative array
In computer science, an associative array is an abstract data type composed of a collection of pairs, such that each possible key appears at most once in the collection....
semantics, and must therefore be implemented by a hash table
Hash table
In computer science, a hash table or hash map is a data structure that uses a hash function to map identifying values, known as keys , to their associated values . Thus, a hash table implements an associative array...
or some other search data structure.
Multi-dimensional arrays
The number of indices needed to specify an element is called the dimension, dimensionality, or rankRank (computer programming)
In computer programming, rank with no further specifications is usually a synonym for "number of dimensions"; thus, a bi-dimensional array has rank two, a three-dimensional array has rank three and so on....
of the array type. (This nomenclature conflicts with the concept of dimension in linear algebra, where it is the number of elements. Thus, an array of numbers with 5 rows and 4 columns (hence 20 elements) is said to have dimension 2 in computing contexts, but 20 in mathematics. Also, the computer science meaning of "rank" is similar to its meaning in tensor algebra but not to the linear algebra concept of rank of a matrix.)

Iliffe vector
In computer programming, an Iliffe vector, also known as a display, is a data structure used to implement multi-dimensional arrays. An Iliffe vector for an n-dimensional array consists of a vector of pointers to an -dimensional array...
, a one-dimensional array of references
Reference (computer science)
In computer science, a reference is a value that enables a program to indirectly access a particular data item, such as a variable or a record, in the computer's memory or in some other storage device. The reference is said to refer to the data item, and accessing those data is called...
to arrays of one dimension less. A two-dimensional array, in particular, would be implemented as a vector of pointers to its rows. Thus an element in row i and column j of an array A would be accessed by double indexing (A[i][j] in typical notation). This way of emulating multi-dimensional arrays allows the creation of ragged or jagged arrays, where each row may have a different size — or, in general, where the valid range of each index depends on the values of all preceding indices.
This representation for multi-dimensional arrays is quite prevalent in C and C++ software. However, C and C++ will use a linear indexing formula for multi-dimensional arrays that are declared as such, e.g. by
int A[10][20] or int A[m][n], instead of the traditional int **A.Indexing notation
Most programming languages that support arrays support the store and select operations, and have special syntax for indexing. Early languages used parentheses, e.g.A(i,j), as in FORTRAN; others choose square brackets, e.g. A[i,j] or A[i][j], as in Algol 60 and Pascal.Index types
Array data types are most often implemented as array structures: with the indices restricted to integer (or totally ordered) values, index ranges fixed at array creation time, and multilinear element addressing. This was the case in most "third generation"Third-generation programming language
A third-generation programming language is a refinement of a second-generation programming language. The second generation of programming languages brought logical structure to software. The third generation brought refinements to make the languages more programmer-friendly...
languages, and is still the case of most systems programming languages such as Ada
Ada (programming language)
Ada is a structured, statically typed, imperative, wide-spectrum, and object-oriented high-level computer programming language, extended from Pascal and other languages...
, C, and C++
C++
C++ is a statically typed, free-form, multi-paradigm, compiled, general-purpose programming language. It is regarded as an intermediate-level language, as it comprises a combination of both high-level and low-level language features. It was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup starting in 1979 at Bell...
. In some languages, however, array data types have the semantics of associative arrays, with indices of arbitrary type and dynamic element creation. This is the case in some scripting languages such as Awk and Lua, and of some array types provided by standard C++
C++
C++ is a statically typed, free-form, multi-paradigm, compiled, general-purpose programming language. It is regarded as an intermediate-level language, as it comprises a combination of both high-level and low-level language features. It was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup starting in 1979 at Bell...
libraries.
Bounds checking
Some languages (like Pascal and Modula) perform bounds checkingBounds checking
In computer programming, bounds checking is any method of detecting whether a variable is within some bounds before its use. It is particularly relevant to a variable used as an index into an array to ensure its value lies within the bounds of the array...
on every access, raising an exception or aborting the program when any index is out of its valid range. Compilers may allow these checks to be turned off to trade safety for speed. Other languages (like FORTRAN and C) trust the programmer and perform no checks. Good compilers may also analyze the program to determine the range of possible values that the index may have, and this analysis may lead to bounds-checking elimination
Bounds-checking elimination
In computer science, bounds-checking elimination is a compiler optimization useful in programming languages or runtimes that enforce bounds checking, the practice of consistently checking every index into an array to verify that the index is within the defined valid range of indexes...
.
Index origin
Some languages, such as C, provide only zero-based array types, for which the minimum valid value for any index is 0. This choice is convenient for array implementation and address computations. With a language such as C, a pointer to the interior of any array can be defined that will symbolically act as a pseudo-array that accommodates negative indices. This works only because C does not check an index against bounds when used.Other languages provide only one-based array types, where each index starts at 1; this is the traditional convention in mathematics for matrices and mathematical sequence
Sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an ordered list of objects . Like a set, it contains members , and the number of terms is called the length of the sequence. Unlike a set, order matters, and exactly the same elements can appear multiple times at different positions in the sequence...
s. A few languages, such as Pascal, support n-based array types, whose minimum legal indices are chosen by the programmer. The relative merits of each choice have been the subject of heated debate. Zero-based indexing has a natural advantage to one-based indexing in avoiding off-by-one
Off-by-one error
An off-by-one error is a logical error involving the discrete equivalent of a boundary condition. It often occurs in computer programming when an iterative loop iterates one time too many or too few...
or fencepost errors.
See comparison of programming languages (array)
Comparison of programming languages (array)
- Array dimensions :The following list contains Syntax examples on how to determine the dimensions :- Indexing :...
for the base indices used by various languages.
The 0-based/1-based debate is not limited to just programming languages. For example, the elevator button for the ground-floor of a building is labeled "0" in France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
and many other countries, but "1" in the USA.
Highest index
The relation between numbers appearing in an array declaration and the index of that array's last element also varies by language. In many languages (such as C), languages one should specify the number of elements contained in the array; whereas in others (such as Pascal and Visual Basic .NETVisual Basic .NET
Visual Basic .NET , is an object-oriented computer programming language that can be viewed as an evolution of the classic Visual Basic , which is implemented on the .NET Framework...
) one should specify the numeric value of the index of the last element. Needless to say, this distinction is immaterial in languages where the indices start at 1.
Array algebra
Some programming languages (including APLAPL programming language
APL is an interactive array-oriented language and integrated development environment, which is available from a number of commercial and noncommercial vendors and for most computer platforms. It is based on a mathematical notation developed by Kenneth E...
, Matlab
MATLAB
MATLAB is a numerical computing environment and fourth-generation programming language. Developed by MathWorks, MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs written in other languages,...
, and newer versions of Fortran
Fortran
Fortran is a general-purpose, procedural, imperative programming language that is especially suited to numeric computation and scientific computing...
) directly support array programming
Array programming
In computer science, array programming languages generalize operations on scalars to apply transparently to vectors, matrices, and higher dimensional arrays....
, where operations and functions defined for certain data types are implicitly extended to arrays of elements of those types. Thus one can write A+B to add corresponding elements of two arrays A and B. The multiplication operation may be merely distributed over corresponding elements of the operands (APL) or may be interpreted as the matrix product of linear algebra
Linear algebra
Linear algebra is a branch of mathematics that studies vector spaces, also called linear spaces, along with linear functions that input one vector and output another. Such functions are called linear maps and can be represented by matrices if a basis is given. Thus matrix theory is often...
(Matlab).
String types and arrays
Many languages provide a built-in stringString (computer science)
In formal languages, which are used in mathematical logic and theoretical computer science, a string is a finite sequence of symbols that are chosen from a set or alphabet....
data type, with specialized notation ("string literals") to build values of that type. In some languages (such as C), a string is just an array of characters, or is handled in much the same way. Other languages, like Pascal, may provide vastly different operations for strings and arrays.
Array index range queries
Some programming languages provide operations that return the size (number of elements) of a vector, or, more generally, range of each index of an array. In CC (programming language)
C is a general-purpose computer programming language developed between 1969 and 1973 by Dennis Ritchie at the Bell Telephone Laboratories for use with the Unix operating system....
and C++
C++
C++ is a statically typed, free-form, multi-paradigm, compiled, general-purpose programming language. It is regarded as an intermediate-level language, as it comprises a combination of both high-level and low-level language features. It was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup starting in 1979 at Bell...
arrays do not support the size function, so programmers often have to declare separate variable to hold the size, and pass it to procedures as a separate parameter.
Elements of a newly created array may have undefined values (as in C), or may be defined to have a specific "default" value such as 0 or a null pointer (as in Java).
In C++
C++
C++ is a statically typed, free-form, multi-paradigm, compiled, general-purpose programming language. It is regarded as an intermediate-level language, as it comprises a combination of both high-level and low-level language features. It was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup starting in 1979 at Bell...
a std::vector object supports the store, select, and append operations with the performance characteristics discussed above. Vectors can be queried for their size and can be resized. Slower operations like inserting an element in the middle are also supported.
Slicing
An array slicingArray slicing
In computer programming, array slicing is an operation that extracts certain elements from an array and packages them as another array, possibly with different number of indices and different index ranges. Two common examples are extracting a substring from a string of characters In computer...
operation takes a subset of the elements of an array-typed entity (value or variable) and then assembles them as another array-typed entity, possibly with other indices. If array types are implemented as array structures, many useful slicing operations (such as selecting a sub-array, swapping indices, or reversing the direction of the indices) can be performed very efficiently by manipulating the dope vector
Dope vector
In computer programming, a dope vector is a data structure used to hold information about a data object, e.g. an array, especially its memory layout....
of the structure. The possible slicings depend on the implementation details: for example, FORTRAN allows slicing off one column of a matrix variable, but not a row, and treat it as a vector; whereas C allow slicing off a row from a matrix, but not a column.
On the other hand, other slicing operations are possible when array types are implemented in other ways.
Resizing
Some languages allow dynamic arrayDynamic array
In computer science, a dynamic array, growable array, resizable array, dynamic table, or array list is a random access, variable-size list data structure that allows elements to be added or removed...
s (also called resizable, growable, or extensible): array variables whose index ranges may be expanded at any time after creation, without changing the values of its current elements.
For one-dimensional arrays, this facility may be provided as an operation "
append(A,x)" that increases the size of the array A by one and then sets the value of the last element to x. Other array types (such as Pascal strings) provide a concatenation operator, which can be used together with slicing to achieve that effect and more. In some languages, assigning a value to an element of an array automatically extends the array, if necessary, to include that element. In other array types, a slice can be replaced by an array of different size" with subsequent elements being renumbered accordingly — as in Python's list assignment "A[5:5] = [10,20,30]", that inserts three new elements (10,20, and 30) before element "A[5]". Resizable arrays are conceptually similar to lists, and the two concepts are synonymous in some languages.An exensible array can be implemented as a fixed-size array, with a counter that records how many elements are actually in use. The
append operation merely increments the counter; until the whole array is used, when the append operation may be defined to fail. This is an implementation of a dynamic arrayDynamic array
In computer science, a dynamic array, growable array, resizable array, dynamic table, or array list is a random access, variable-size list data structure that allows elements to be added or removed...
with a fixed capacity, as in the string type of Pascal. Alternatively, the
append operation may re-allocate the underlying array with a larger size, and copy the old elements to the new area.See also
- Array access analysisArray access analysisIn computer science, array access analysis is a compiler analysis used to decide the read and write access patterns to elements or portions of arrays....
- Array programmingArray programmingIn computer science, array programming languages generalize operations on scalars to apply transparently to vectors, matrices, and higher dimensional arrays....
- Array slicingArray slicingIn computer programming, array slicing is an operation that extracts certain elements from an array and packages them as another array, possibly with different number of indices and different index ranges. Two common examples are extracting a substring from a string of characters In computer...
- Bounds checkingBounds checkingIn computer programming, bounds checking is any method of detecting whether a variable is within some bounds before its use. It is particularly relevant to a variable used as an index into an array to ensure its value lies within the bounds of the array...
and index checking - Bounds checking elimination
- Delimiter-separated values
- Comparison of programming languages (array)Comparison of programming languages (array)- Array dimensions :The following list contains Syntax examples on how to determine the dimensions :- Indexing :...
- List comprehension
- Off-by-one errorOff-by-one errorAn off-by-one error is a logical error involving the discrete equivalent of a boundary condition. It often occurs in computer programming when an iterative loop iterates one time too many or too few...
- Parallel arrayParallel arrayIn computing, a parallel array is a data structure for representing arrays of records. It keeps a separate, homogeneous array for each field of the record, each having the same number of elements. Then, objects located at the same index in each array are implicitly the fields of a single record....
- Range check
- ReDimRedimReDim, short for re-dimension, is a Visual Basic function that is used to resize arrays. By using this function you can add or remove space from an array. This function can only be used on arrays that are declared without dimensions....
- a Visual Basic function to resize arrays
Related types
- StringString (computer science)In formal languages, which are used in mathematical logic and theoretical computer science, a string is a finite sequence of symbols that are chosen from a set or alphabet....
- Collection class
- Variable-length arrayVariable-length arrayIn programming, a variable-length array is an array data structure of automatic storage duration whose length is determined at run time ....
- Dynamic arrayDynamic arrayIn computer science, a dynamic array, growable array, resizable array, dynamic table, or array list is a random access, variable-size list data structure that allows elements to be added or removed...
- Sparse arraySparse arrayIn computer science, a sparse array is an array in which most of the elements have the same value . The occurrence of zero elements in a large array is inconvenient for both computation and storage...
- Vector (C++)

