
Alkyl cycloalkane
Encyclopedia
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
s with an alkyl group with a single ring of carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
s to which hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
s are attached according to the formula
- CnH2n.
They are named analogously to their normal alkane
Alkane
Alkanes are chemical compounds that consist only of hydrogen and carbon atoms and are bonded exclusively by single bonds without any cycles...
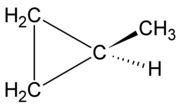
counterpart of the same carbon count: methylcyclopropane
Methylcyclopropane
Methylcyclopropane is an organic compound with the structural formula C3H5CH3. This colorless gas is the monomethyl derivative of cyclopropane.- Reactions :...
, methylcyclobutane, methylcyclopentane
Methylcyclopentane
Methylcyclopentane is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3C5H9. It is one of the important benzene precursors that can react in refinery processes to form benzene....
, methylcyclohexane
Methylcyclohexane
Methylcyclohexane is a colourless liquid with a faint benzene-like odour. Its molecular formula is C7H14. Methylcyclohexane is used in organic synthesis and as a solvent for cellulose ethers. It is a component of jet fuel and is also a component of correction fluids.-Structure:Monosubstituted...
, etc.
Methylcycloalkanes are classed into compounds with small, normal and bigger cycloalcanes, where cyclopropane and cyclopbutane are the small ones, cyclopentane
Cyclopentane
Cyclopentane is a highly flammable alicyclic hydrocarbon with chemical formula 510 and CAS number 287-92-3, consisting of a ring of five carbon atoms each bonded with two hydrogen atoms above and below the plane. It occurs as a colorless liquid with a petrol-like odor. Its melting point is −94 °C...
, cyclohexane
Cyclohexane
Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula C6H12. Cyclohexane is used as a nonpolar solvent for the chemical industry, and also as a raw material for the industrial production of adipic acid and caprolactam, both of which being intermediates used in the production of nylon...
, cycloheptane
Cycloheptane
Cycloheptane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula C7H14. Cycloheptane is used as a nonpolar solvent for the chemical industry and as an intermediate in the manufacture of chemicals and pharmaceutical drugs. It may be derived by Clemmensen reduction from cycloheptanone. Cycloheptane vapour is...
are the normal ones and the rest are the bigger ones.
Nomenclature
The naming of polycyclic alkanes is more complex, with the base name indicating the number of carbons in the ring system, a prefix indicating the number of rings (e.g., "bicyclo"), and a numeric prefix before that indicating the number of carbons in each part of each ring, exclusive of vertices. For instance, a bicyclooctane which consists of a six-member ring and a four member ring, which share two adjacent carbon atoms which form a shared edge, is [4.2.0]-bicyclooctane. That part of the six-member ring, exclusive of the shared edge has 4 carbons. That part of the four-member ring, exclusive of the shared edge, has 2 carbons. The edge itself, exclusive of the two vertices that define it, has 0 carbons.Reactions
The normal and the bigger alkylcycloalkanes are very stable like alkanes and their reactions (cf. radicalic chain reactions) are like alkanes.The small alkylcycloalkanes - particularly alkylcyclopropane - has a lower stability due to the Baeyer-tension. They react similar to alkenes, though they don't react with the EA (cf. electrophilic addition
Electrophilic addition
In organic chemistry, an electrophilic addition reaction is an addition reaction where, in a chemical compound, a π bond is broken and two new σ bonds are formed...
), but with the SN2 (cf. nucleophilic substitution
Nucleophilic substitution
In organic and inorganic chemistry, nucleophilic substitution is a fundamental class of reactions in which an electron nucleophile selectively bonds with or attacks the positive or partially positive charge of an atom or a group of atoms called the leaving group; the positive or partially positive...
) reaction mechanism. These reactions are both ring opening reactions and cleavage
Cleavage (crystal)
Cleavage, in mineralogy, is the tendency of crystalline materials to split along definite crystallographic structural planes. These planes of relative weakness are a result of the regular locations of atoms and ions in the crystal, which create smooth repeating surfaces that are visible both in the...
reactions.
Typical compound
The typical compound of the group alkyl cycloalkanes is methylcyclopropaneMethylcyclopropane
Methylcyclopropane is an organic compound with the structural formula C3H5CH3. This colorless gas is the monomethyl derivative of cyclopropane.- Reactions :...
.

