Alemannic German
Overview
Dialect
The term dialect is used in two distinct ways, even by linguists. One usage refers to a variety of a language that is a characteristic of a particular group of the language's speakers. The term is applied most often to regional speech patterns, but a dialect may also be defined by other factors,...
s of the Upper German
Upper German
Upper German is a family of High German dialects spoken primarily in southern Germany, Austria, Switzerland and Northern Italy.-Family tree:Upper German can be generally classified as Alemannic or Austro-Bavarian...
branch of the Germanic language family. It is spoken by approximately ten million people in six countries: Switzerland
Switzerland
Switzerland name of one of the Swiss cantons. ; ; ; or ), in its full name the Swiss Confederation , is a federal republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities. The country is situated in Western Europe,Or Central Europe depending on the definition....
, Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
, Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein
The Principality of Liechtenstein is a doubly landlocked alpine country in Central Europe, bordered by Switzerland to the west and south and by Austria to the east. Its area is just over , and it has an estimated population of 35,000. Its capital is Vaduz. The biggest town is Schaan...
, France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
and Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
. The name derives from the ancient Germanic alliance of tribes known as the Alamanni
Alamanni
The Alamanni, Allemanni, or Alemanni were originally an alliance of Germanic tribes located around the upper Rhine river . One of the earliest references to them is the cognomen Alamannicus assumed by Roman Emperor Caracalla, who ruled the Roman Empire from 211 to 217 and claimed thereby to be...
.
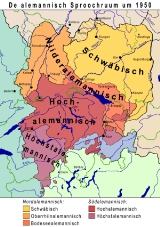
Alemannic itself comprises a dialect continuum
Dialect continuum
A dialect continuum, or dialect area, was defined by Leonard Bloomfield as a range of dialects spoken across some geographical area that differ only slightly between neighboring areas, but as one travels in any direction, these differences accumulate such that speakers from opposite ends of the...
, from the Highest Alemannic spoken in the mountainous south to Swabian
Swabian German
Swabian is one of the Alemannic dialects of High German. It is spoken in Swabia, a region which covers much of Germany's southwestern state Baden-Württemberg, including its capital Stuttgart, the rural area known as the Swabian Alb, and Bavaria...
in the relatively flat north, with more of the characteristics of Standard German
Standard German
Standard German is the standard variety of the German language used as a written language, in formal contexts, and for communication between different dialect areas...
the farther north one goes.
Some linguist
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. Linguistics can be broadly broken into three categories or subfields of study: language form, language meaning, and language in context....
s and organisations that differentiate between languages and dialects primarily on the grounds of mutual intelligibility, such as SIL International
SIL International
SIL International is a U.S.-based, worldwide, Christian non-profit organization, whose main purpose is to study, develop and document languages, especially those that are lesser-known, in order to expand linguistic knowledge, promote literacy, translate the Christian Bible into local languages,...
and UNESCO
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations...
, describe Alemannic as one or several independent languages.

