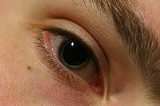
Adie syndrome
Encyclopedia
Adie syndrome, sometimes known as Holmes-Adie's syndrome or Adie's Tonic Pupil, is a neurological disorder
characterized by a tonic
ally dilated
pupil. It is named after the British neurologist William John Adie
. It is caused by damage to the postganglionic fibers of the parasympathetic innervation
of the eye, usually by a viral
or bacterial infection which causes inflammation
, and affects the pupil
of the eye and the autonomic nervous system
.
) which does not constrict in response to light, loss of deep tendon reflexes and diaphoresis
(excessive sweating). Other signs may include hyperopia
due to accommodative paresis
, photophobia
and difficulty reading.
, an area of the brain that controls eye movements, and the spinal ganglion, an area of the brain involved in the response of the autonomic nervous system
.
may constrict the tonic pupil due to cholinergic
denervation supersensitivity. A normal pupil will not constrict with the dilute
dose of pilocarpine. CT scans and MRI scans may be useful in the diagnostic testing of focal
hypoactive reflexes.
drops may be administered as a treatment as well as a diagnostic measure. Thoracic sympathectomy is the definitive treatment of diaphoresis
, if the condition is not treatable by drug therapy.
Neurological disorder
A neurological disorder is a disorder of the body's nervous system. Structural, biochemical or electrical abnormalities in the brain, spinal cord, or in the nerves leading to or from them, can result in symptoms such as paralysis, muscle weakness, poor coordination, loss of sensation, seizures,...
characterized by a tonic
Tonic (physiology)
Tonic in physiology refers to a physiological response which is slow, and may be graded. This term is typically used in opposition to a fast response...
ally dilated
Mydriasis
Mydriasis is a dilation of the pupil due to disease, trauma or the use of drugs. Normally, the pupil dilates in the dark and constricts in the light to respectively improve vividity at night and to protect the retina from sunlight damage during the day...
pupil. It is named after the British neurologist William John Adie
William John Adie
William John Adie MD Ed., FRCP was a British physician and neurologist known for describing the Adie syndrome and narcolepsy.-Biography:...
. It is caused by damage to the postganglionic fibers of the parasympathetic innervation
Parasympathetic nervous system
The parasympathetic nervous system is one of the two main divisions of the autonomic nervous system . The ANS is responsible for regulation of internal organs and glands, which occurs unconsciously...
of the eye, usually by a viral
Virus
A virus is a small infectious agent that can replicate only inside the living cells of organisms. Viruses infect all types of organisms, from animals and plants to bacteria and archaea...
or bacterial infection which causes inflammation
Inflammation
Inflammation is part of the complex biological response of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. Inflammation is a protective attempt by the organism to remove the injurious stimuli and to initiate the healing process...
, and affects the pupil
Pupil
The pupil is a hole located in the center of the iris of the eye that allows light to enter the retina. It appears black because most of the light entering the pupil is absorbed by the tissues inside the eye. In humans the pupil is round, but other species, such as some cats, have slit pupils. In...
of the eye and the autonomic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
.
Signs and symptoms
Adie syndrome presents with three hallmark symptoms, namely at least one abnormally dilated pupil (mydriasisMydriasis
Mydriasis is a dilation of the pupil due to disease, trauma or the use of drugs. Normally, the pupil dilates in the dark and constricts in the light to respectively improve vividity at night and to protect the retina from sunlight damage during the day...
) which does not constrict in response to light, loss of deep tendon reflexes and diaphoresis
Diaphoresis
Diaphoresis is excessive sweating commonly associated with shock and other medical emergency conditions.Diaphoretic is the state of perspiring profusely, or something that has the power to cause increased perspiration....
(excessive sweating). Other signs may include hyperopia
Hyperopia
Hyperopia, also known as farsightedness, longsightedness or hypermetropia, is a defect of vision caused by an imperfection in the eye , causing difficulty focusing on near objects, and in extreme cases causing a sufferer to be unable to focus on objects at any distance...
due to accommodative paresis
Paresis
Paresis is a condition typified by partial loss of voluntary movement or by impaired movement. When used without qualifiers, it usually refers to the limbs, but it also can be used to describe the muscles of the eyes , the stomach , and also the vocal cords...
, photophobia
Photophobia
Photophobia is a symptom of abnormal intolerance to visual perception of light. As a medical symptom photophobia is not a morbid fear or phobia, but an experience of discomfort or pain to the eyes due to light exposure or by presence of actual physical photosensitivity of the eyes, though the term...
and difficulty reading.
Causes
Holmes-Adie syndrome is thought to be the result of a viral or bacterial infection that causes inflammation and damage to neurons in the ciliary ganglionCiliary ganglion
The ciliary ganglion is a parasympathetic ganglion located in the posterior orbit. It measures 1–2 millimeters in diameter and contains approximately 2,500 neurons. Preganglionic axons from the Edinger-Westphal nucleus travel along the oculomotor nerve and form synapses with these cells...
, an area of the brain that controls eye movements, and the spinal ganglion, an area of the brain involved in the response of the autonomic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
.
Diagnosis
Clinical exam may reveal sectoral paresis of the iris sphincter or vermiform iris movements. The tonic pupil may become smaller (miotic) over time which is referred to as "little old Adie's". Testing with low dose (1/8%) pilocarpinePilocarpine
Pilocarpine is a parasympathomimetic alkaloid obtained from the leaves of tropical American shrubs from the genus Pilocarpus. It is a non-selective muscarinic receptor agonist in the parasympathetic nervous system, which acts therapeutically at the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M3 due to its...
may constrict the tonic pupil due to cholinergic
Cholinergic
The word choline generally refers to the various quaternary ammonium salts containing the N,N,N-trimethylethanolammonium cation. Found in most animal tissues, choline is a primary component of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine and functions with inositol as a basic constituent of lecithin...
denervation supersensitivity. A normal pupil will not constrict with the dilute
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
dose of pilocarpine. CT scans and MRI scans may be useful in the diagnostic testing of focal
Focal dystonia
Focal dystonia is a neurological condition that affects a muscle or group of muscles in a part of the body and causes an involuntary muscular contraction or twisting...
hypoactive reflexes.
Treatment
The usual treatment of a standardised Adie syndrome is to prescribe reading glasses to correct for impairment of the eye(s). PilocarpinePilocarpine
Pilocarpine is a parasympathomimetic alkaloid obtained from the leaves of tropical American shrubs from the genus Pilocarpus. It is a non-selective muscarinic receptor agonist in the parasympathetic nervous system, which acts therapeutically at the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M3 due to its...
drops may be administered as a treatment as well as a diagnostic measure. Thoracic sympathectomy is the definitive treatment of diaphoresis
Diaphoresis
Diaphoresis is excessive sweating commonly associated with shock and other medical emergency conditions.Diaphoretic is the state of perspiring profusely, or something that has the power to cause increased perspiration....
, if the condition is not treatable by drug therapy.
Prognosis
Adie's syndrome is not life threatening or disabling. As such, there is no mortality rate relating to the condition; however, loss of deep tendon reflexes is permanent and may progress over time.Epidemiology
It most commonly affects younger women (2.6:1 female preponderance) and is unilateral in 80% of cases. Average age of onset is 32 years.External links
- Personal experience
- Animation at mrcophth.com

