
Acromegaly
Encyclopedia
Acromegaly is a syndrome
that results when the anterior pituitary
gland produces excess growth hormone
(GH) after epiphyseal plate
closure at puberty. A number of disorders may increase the pituitary's GH output, although most commonly it involves a GH-producing tumor called pituitary adenoma
, derived from a distinct type of cell (somatotrophs).
Acromegaly most commonly affects adults in middle age, and can result in severe disfigurement, serious complicating conditions, and premature death if unchecked. Because of its insidious pathogenesis
and slow progression, the disease is hard to diagnose in the early stages and is frequently missed for many years, until changes in external features, especially of the face, become noticeable.
Acromegaly is often also associated with gigantism
.
 Features that result from high level of GH or expanding tumor include:
Features that result from high level of GH or expanding tumor include:
. These tumors produce excess growth hormones and, as they expand, compress surrounding brain tissues, such as the optic nerves. This expansion causes the headaches and visual disturbances that often accompany acromegaly. In addition, compression of the surrounding normal pituitary tissue can alter production of other hormones, leading to changes in menstruation and breast discharge in women and impotence in men because of reduced testosterone
production.
There is a marked variation in rates of GH production and the aggressiveness of the tumor. Some adenomas grow slowly and symptoms of growth hormone excess are often not noticed for many years. Other adenomas grow rapidly and invade surrounding brain areas or the sinuses, which are located near the pituitary. In general, younger patients tend to have more aggressive tumors.
Most pituitary tumors arise spontaneously and are not genetically inherited. Many pituitary tumors arise from a genetic alteration in a single pituitary cell which leads to increased cell division and tumor formation. This genetic change, or mutation
, is not present at birth, but is acquired during life. The mutation occurs in a gene that regulates the transmission of chemical signals within pituitary cells; it permanently switches on the signal that tells the cell to divide and secrete growth hormones. The events within the cell that cause disordered pituitary cell growth
and growth hormone oversecretion currently are the subject of intensive research.
s of the pancreas
, lung
s, and adrenal gland
s. These tumors also lead to an excess of GH, either because they produce GH themselves or, more frequently, because they produce GHRH (Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone), the hormone that stimulates the pituitary to make GH. In these patients, the excess GHRH can be measured in the blood and establishes that the cause of the acromegaly is not due to a pituitary defect. When these non-pituitary tumors are surgically removed, GH levels fall and the symptoms of acromegaly improve.
In patients with GHRH-producing, non-pituitary tumors, the pituitary still may be enlarged and may be mistaken for a tumor. Therefore, it is important that physicians carefully analyze all "pituitary tumors" removed from patients with acromegaly in order not to overlook the possibility that a tumor elsewhere in the body is causing the disorder.

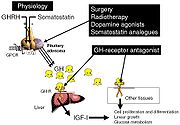 If acromegaly is suspected, medical imaging
If acromegaly is suspected, medical imaging
and medical laboratory
investigations are generally used together to confirm or rule out the presence of this condition.
of the pituitary.
These procedures normally relieve the pressure on the surrounding brain regions and lead to a lowering of GH levels. Surgery is most successful in patients with blood GH levels below 40 ng/ml before the operation and with pituitary tumors no larger than 10 mm in diameter. Success depends on the skill and experience of the surgeon. The success rate also depends on what level of GH is defined as a cure. The best measure of surgical success is normalization of GH and IGF-1 levels. Ideally, GH should be less than 2 ng/ml after an oral glucose load. A review of GH levels in 1,360 patients worldwide immediately after surgery revealed that 60 percent had random GH levels below 5 ng/ml. Complications of surgery may include cerebrospinal fluid
leaks, meningitis
, or damage to the surrounding normal pituitary tissue, requiring lifelong pituitary hormone replacement.
Even when surgery is successful and hormone levels return to normal, patients must be carefully monitored for years for possible recurrence. More commonly, hormone levels may improve, but not return completely to normal. These patients may then require additional treatment, usually with medications.
(Sandostatin) or lanreotide
(Somatuline).
These somatostatin analogues are synthetic forms of a brain hormone, somatostatin, which stops GH production. The long-acting forms of these drugs must be injected every 2 to 4 weeks for effective treatment. Most patients with acromegaly respond to this medication. In many patients, GH levels fall within one hour and headaches improve within minutes after the injection. Octreotide and lanreotide are effective for long-term treatment. Octreotide and lanreotide have also been used successfully to treat patients with acromegaly caused by non-pituitary tumors.
Somatostatin analogues are also sometimes used to shrink large tumors before surgery.
Because octreotide inhibits gastrointestinal and pancreatic function, long-term use causes digestive problems such as loose stools, nausea, and gas in one third of patients. In addition, approximately 25 percent of patients develop gallstone
s, which are usually asymptomatic. In some cases, octreotide treatment can cause diabetes due to the fact that somatosstatin and its analogues can inhibit the release of insulin. On the other hand, scientists have found that in some acromegaly patients who already have diabetes, octreotide can reduce the need for insulin
and improve blood sugar
control.
(Parlodel) or Cabergoline. These have the advantage of being tablets rather than injections, and cost considerably less. These drugs can also be used as an adjunct to somatostatin analogue therapy. They are most effective in those whose pituitary tumours cosecrete prolactin. Side effects of these dopamine agonists include gastrointestinal upset, nausea, vomiting, light-headedness when standing, and nasal congestion. These side effects can be reduced or eliminated if medication is started at a very low dose at bedtime, taken with food, and gradually increased to the full therapeutic dose. However, bromocriptine lowers GH and IGF-1 levels and reduces tumor size in fewer than half of patients with acromegaly. Some patients report improvement in their symptoms although their GH and IGF-1 levels still are elevated.
The latest development in the medical treatment of acromegaly is the use of growth hormone receptor antagonists. The only available member of this family is pegvisomant
(Somavert). By blocking the action of the endogenous growth hormone molecules, this compound is able to control disease activity of acromegaly in virtually all patients. Pegvisomant has to be administered subcutaneously by daily injections. Combinations of long-acting somatostatin analogues and weekly injections of pegvisomant seem to be equally effective as daily injections of pegvisomant.
at an unusually high dose.
, Maurice Tillet
, Wallace Stevens
, and Antonio Silva
) standing in excess of 2.00 metres (6.6 feet):
Syndrome
In medicine and psychology, a syndrome is the association of several clinically recognizable features, signs , symptoms , phenomena or characteristics that often occur together, so that the presence of one or more features alerts the physician to the possible presence of the others...
that results when the anterior pituitary
Anterior pituitary
A major organ of the endocrine system, the anterior pituitary, also called the adenohypophysis, is the glandular, anterior lobe of the pituitary gland...
gland produces excess growth hormone
Growth hormone
Growth hormone is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction and regeneration in humans and other animals. Growth hormone is a 191-amino acid, single-chain polypeptide that is synthesized, stored, and secreted by the somatotroph cells within the lateral wings of the anterior...
(GH) after epiphyseal plate
Epiphyseal plate
The epiphyseal plate is a hyaline cartilage plate in the metaphysis at each end of a long bone...
closure at puberty. A number of disorders may increase the pituitary's GH output, although most commonly it involves a GH-producing tumor called pituitary adenoma
Pituitary adenoma
Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland, and account for about 15% of intracranial neoplasms. Tumors which exceed 10 mm in size are defined as macroadenomas, and those smaller than 10 mm are referred to as microadenomas...
, derived from a distinct type of cell (somatotrophs).
Acromegaly most commonly affects adults in middle age, and can result in severe disfigurement, serious complicating conditions, and premature death if unchecked. Because of its insidious pathogenesis
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis of a disease is the mechanism by which the disease is caused. The term can also be used to describe the origin and development of the disease and whether it is acute, chronic or recurrent...
and slow progression, the disease is hard to diagnose in the early stages and is frequently missed for many years, until changes in external features, especially of the face, become noticeable.
Acromegaly is often also associated with gigantism
Gigantism
Gigantism, also known as giantism , is a condition characterized by excessive growth and height significantly above average...
.
Signs and symptoms



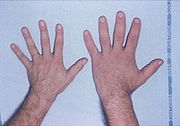
- Soft tissue swelling visibly resulting in enlargement of the hands, feet, nose, lips and ears, and a general thickening of the skin.
- Soft tissue swelling of internal organs, notably the heart with attendant weakening of its muscularity, and the kidneys, also the vocal cords resulting in a characteristic thick, deep voice and slowing of speech
- Generalized expansion of the skull at the fontanelleFontanelleA fontanelle is an anatomical feature on an infant's skull.-Anatomy:Fontanelles are soft spots on a baby's head which, during birth, enable the bony plates of the skull to flex, allowing the child's head to pass through the birth canal. The ossification of the bones of the skull causes the...
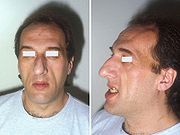
- Pronounced brow protrusion, often with ocular distension
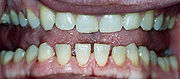
- Pronounced lower jaw protrusion with attendant macroglossiaMacroglossiaMacroglossia is the medical term for unusual enlargement of the tongue. Severe enlargement of the tongue can cause cosmetic and functional difficulties including in speaking, eating, swallowing and sleeping.- Amyloid Disorders :...
(enlargement of the tongue) and teeth gapping - HypertrichosisHypertrichosisHypertrichosis is an abnormal amount of hair growth on the body; extensive cases of hypertrichosis have informally been called werewolf syndrome. There are two distinct types of hypertrichosis: generalized hypertrichosis, which occurs over the entire body, and localized hypertrichosis, which is...
, hyperpigmentationHyperpigmentationIn dermatology, hyperpigmentation is the darkening of an area of skin or nails caused by increased melanin.-Causes:Hyperpigmentation may be caused by sun damage, inflammation, or other skin injuries, including those related to acne vulgaris...
, and hyperhidrosisHyperhidrosisHyperhidrosis is the condition characterized by abnormally increased perspiration, in excess of that required for regulation of body temperature.-Classification:Hyperhidrosis can either be generalized or localized to specific parts of the body...
may occur in these patients. - AcrochordonAcrochordonAn acrochordon An acrochordon An acrochordon (plural acrochorda, and also known as a (cutaneous) skin tag, or fibroepithelial polyp, is a small benign tumour that forms primarily in areas where the skin forms creases, such as the neck, armpit, and groin. They may also occur on the face, usually on...
(skin tags) - Carpal tunnel syndromeCarpal tunnel syndromeCarpal Tunnel Syndrome is an entrapment idiopathic median neuropathy, causing paresthesia, pain, and other symptoms in the distribution of the median nerve due to its compression at the wrist in the carpal tunnel. The pathophysiology is not completely understood but can be considered compression...
Pituitary adenoma
In over 90 percent of acromegaly patients, the overproduction of growth hormones is caused by a benign tumor of the pituitary gland, called an adenomaPituitary adenoma
Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland, and account for about 15% of intracranial neoplasms. Tumors which exceed 10 mm in size are defined as macroadenomas, and those smaller than 10 mm are referred to as microadenomas...
. These tumors produce excess growth hormones and, as they expand, compress surrounding brain tissues, such as the optic nerves. This expansion causes the headaches and visual disturbances that often accompany acromegaly. In addition, compression of the surrounding normal pituitary tissue can alter production of other hormones, leading to changes in menstruation and breast discharge in women and impotence in men because of reduced testosterone
Testosterone
Testosterone is a steroid hormone from the androgen group and is found in mammals, reptiles, birds, and other vertebrates. In mammals, testosterone is primarily secreted in the testes of males and the ovaries of females, although small amounts are also secreted by the adrenal glands...
production.
There is a marked variation in rates of GH production and the aggressiveness of the tumor. Some adenomas grow slowly and symptoms of growth hormone excess are often not noticed for many years. Other adenomas grow rapidly and invade surrounding brain areas or the sinuses, which are located near the pituitary. In general, younger patients tend to have more aggressive tumors.
Most pituitary tumors arise spontaneously and are not genetically inherited. Many pituitary tumors arise from a genetic alteration in a single pituitary cell which leads to increased cell division and tumor formation. This genetic change, or mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
, is not present at birth, but is acquired during life. The mutation occurs in a gene that regulates the transmission of chemical signals within pituitary cells; it permanently switches on the signal that tells the cell to divide and secrete growth hormones. The events within the cell that cause disordered pituitary cell growth
Cell growth
The term cell growth is used in the contexts of cell development and cell division . When used in the context of cell division, it refers to growth of cell populations, where one cell grows and divides to produce two "daughter cells"...
and growth hormone oversecretion currently are the subject of intensive research.
Other tumors
In a few patients, acromegaly is caused not by pituitary tumors but by tumorTumor
A tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
s of the pancreas
Pancreas
The pancreas is a gland organ in the digestive and endocrine system of vertebrates. It is both an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin, as well as a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist...
, lung
Lung
The lung is the essential respiration organ in many air-breathing animals, including most tetrapods, a few fish and a few snails. In mammals and the more complex life forms, the two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart...
s, and adrenal gland
Adrenal gland
In mammals, the adrenal glands are endocrine glands that sit atop the kidneys; in humans, the right suprarenal gland is triangular shaped, while the left suprarenal gland is semilunar shaped...
s. These tumors also lead to an excess of GH, either because they produce GH themselves or, more frequently, because they produce GHRH (Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone), the hormone that stimulates the pituitary to make GH. In these patients, the excess GHRH can be measured in the blood and establishes that the cause of the acromegaly is not due to a pituitary defect. When these non-pituitary tumors are surgically removed, GH levels fall and the symptoms of acromegaly improve.
In patients with GHRH-producing, non-pituitary tumors, the pituitary still may be enlarged and may be mistaken for a tumor. Therefore, it is important that physicians carefully analyze all "pituitary tumors" removed from patients with acromegaly in order not to overlook the possibility that a tumor elsewhere in the body is causing the disorder.
Pituitary gigantism
This condition of growth hormone excess is rare in children and is referred to as pituitary gigantism, because the excessive growth hormone produces excessive growth of bones and the child can achieve excessive height; from 2.1 to 2.7 m (6'11" to 8'11") in stature by adulthood if left untreated. As an affected child becomes an adult, many of the adult problems can gradually develop. The distinction between gigantism (occurring in children) and acromegaly (occurring in adults) can be made by the occurrence of the adenoma in relation to the closure of the epiphyses. If elevated growth hormone levels occur before the closure of the epiphyses (i.e. in prepubertal children), then gigantism ensues. If it occurs after the closure of the epiphyses (i.e., in adults) then acromegaly ensues.Complications
- Severe headacheHeadacheA headache or cephalalgia is pain anywhere in the region of the head or neck. It can be a symptom of a number of different conditions of the head and neck. The brain tissue itself is not sensitive to pain because it lacks pain receptors. Rather, the pain is caused by disturbance of the...
- ArthritisArthritisArthritis is a form of joint disorder that involves inflammation of one or more joints....
and carpal tunnel syndromeCarpal tunnel syndromeCarpal Tunnel Syndrome is an entrapment idiopathic median neuropathy, causing paresthesia, pain, and other symptoms in the distribution of the median nerve due to its compression at the wrist in the carpal tunnel. The pathophysiology is not completely understood but can be considered compression... - Enlarged heart
- HypertensionHypertensionHypertension or high blood pressure is a cardiac chronic medical condition in which the systemic arterial blood pressure is elevated. What that means is that the heart is having to work harder than it should to pump the blood around the body. Blood pressure involves two measurements, systolic and...
- Diabetes mellitusDiabetes mellitusDiabetes mellitus, often simply referred to as diabetes, is a group of metabolic diseases in which a person has high blood sugar, either because the body does not produce enough insulin, or because cells do not respond to the insulin that is produced...
- Heart failure
- Kidney failure
- Compression of the optic chiasmOptic chiasmThe optic chiasm or optic chiasma is the part of the brain where the optic nerves partially cross...
leading to loss of vision in the outer visual fields (typically bitemporal hemianopia) - Increased palmar sweating and sebum production over the face (seborrhea) are clinical indicators of active growth hormone (GH) producing pituitary tumors. These symptoms can also be used to monitor the activity of the tumor after surgery although biochemical monitoring is confirmatory.
Diagnosis



Medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process used to create images of the human body for clinical purposes or medical science...
and medical laboratory
Medical laboratory
A medical laboratory or clinical laboratory is a laboratory where tests are done on clinical specimens in order to get information about the health of a patient as pertaining to the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease.-Departments:...
investigations are generally used together to confirm or rule out the presence of this condition.
- IGF1 provides the most sensitive and useful lab test for the diagnosis of acromegaly. A single value of the growth hormone (GH) is not useful in view of its pulsatality (levels in the blood vary greatly even in healthy individuals). GH levels taken 2 hours after a 75 or 100 gram glucose tolerance testGlucose tolerance testA glucose tolerance test is a medical test in which glucose is given and blood samples taken afterward to determine how quickly it is cleared from the blood. The test is usually used to test for diabetes, insulin resistance, and sometimes reactive hypoglycemia and acromegaly, or rarer disorders of...
are helpful in the diagnosis: GH levels are suppressed below 1 μg/L in normal people, and levels higher than this cutoff are confirmatory of acromegaly. - Other pituitary hormones have to be assessed to address the secretory effects of the tumor as well as the mass effect of the tumor on the normal pituitary gland. They include TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone), gonadotropic hormones (FSH, LH), ACTHAdrenocorticotropic hormoneAdrenocorticotropic hormone , also known as 'corticotropin', 'Adrenocorticotrophic hormone', is a polypeptide tropic hormone produced and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. It is an important component of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and is often produced in response to biological...
(adrenocorticotropic hormone), prolactinProlactinProlactin also known as luteotropic hormone is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRL gene.Prolactin is a peptide hormone discovered by Henry Friesen...
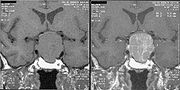
. - An MRIMagnetic resonance imagingMagnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
of the brain focusing on the sella turcicaSella turcica-External links:*...
after gadoliniumGadoliniumGadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. It is a silvery-white, malleable and ductile rare-earth metal. It is found in nature only in combined form. Gadolinium was first detected spectroscopically in 1880 by de Marignac who separated its oxide and is credited with...
administration allows for clear delineation of the pituitary and the hypothalamus and the location of the tumor.
Treatment
The goals of treatment are to reduce GH production to normal levels, to relieve the pressure that the growing pituitary tumor exerts on the surrounding brain areas, to preserve normal pituitary function, and to reverse or ameliorate the symptoms of acromegaly. Currently, treatment options include surgical removal of the tumor, drug therapy, and radiation therapyRadiation therapy
Radiation therapy , radiation oncology, or radiotherapy , sometimes abbreviated to XRT or DXT, is the medical use of ionizing radiation, generally as part of cancer treatment to control malignant cells.Radiation therapy is commonly applied to the cancerous tumor because of its ability to control...
of the pituitary.
Surgery
Surgery is a rapid and effective treatment, of which there are two alternative methods. The first method, a procedure known as Endonasal Transphenoidal surgery, involves the surgeon reaching the pituitary through an incision in the nasal cavity wall. The wall is reached by passing through the nostrils with microsurgical instruments. The second method is Transsphenoidal surgery during which an incision is made into the gum beneath the upper lip. Further incisions are made to cut through the septum to reach the nasal cavity, where the pituitary is located. Endonasal Transphenoidal surgery is a less invasive procedure with a shorter recovery time than the older method of Transphenoidal surgery, and the likelihood of removing the entire tumor is greater with reduced side-effects. Consequently, Endonasal Transphenoidal surgery is often used as a first option, with Transphenoidal and other treatments, such as, medicinal therapy or radiostatic neurosurgery being used to reduce the remaining adverse effects of the remaining tumor.These procedures normally relieve the pressure on the surrounding brain regions and lead to a lowering of GH levels. Surgery is most successful in patients with blood GH levels below 40 ng/ml before the operation and with pituitary tumors no larger than 10 mm in diameter. Success depends on the skill and experience of the surgeon. The success rate also depends on what level of GH is defined as a cure. The best measure of surgical success is normalization of GH and IGF-1 levels. Ideally, GH should be less than 2 ng/ml after an oral glucose load. A review of GH levels in 1,360 patients worldwide immediately after surgery revealed that 60 percent had random GH levels below 5 ng/ml. Complications of surgery may include cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid , Liquor cerebrospinalis, is a clear, colorless, bodily fluid, that occupies the subarachnoid space and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord...
leaks, meningitis
Meningitis
Meningitis is inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, known collectively as the meninges. The inflammation may be caused by infection with viruses, bacteria, or other microorganisms, and less commonly by certain drugs...
, or damage to the surrounding normal pituitary tissue, requiring lifelong pituitary hormone replacement.
Even when surgery is successful and hormone levels return to normal, patients must be carefully monitored for years for possible recurrence. More commonly, hormone levels may improve, but not return completely to normal. These patients may then require additional treatment, usually with medications.
Somatostatin analogues
The primary current medical treatment of acromegaly is to use somatostatin analogues -- octreotideOctreotide
Octreotide is an octapeptide that mimics natural somatostatin pharmacologically, though it is a more potent inhibitor of growth hormone, glucagon, and insulin than the natural hormone...
(Sandostatin) or lanreotide
Lanreotide
Lanreotide is a medication used in the management of acromegaly and symptoms caused by neuroendocrine tumors, most notably carcinoid syndrome. It is a long-acting analogue of somatostatin, like octreotide....
(Somatuline).
These somatostatin analogues are synthetic forms of a brain hormone, somatostatin, which stops GH production. The long-acting forms of these drugs must be injected every 2 to 4 weeks for effective treatment. Most patients with acromegaly respond to this medication. In many patients, GH levels fall within one hour and headaches improve within minutes after the injection. Octreotide and lanreotide are effective for long-term treatment. Octreotide and lanreotide have also been used successfully to treat patients with acromegaly caused by non-pituitary tumors.
Somatostatin analogues are also sometimes used to shrink large tumors before surgery.
Because octreotide inhibits gastrointestinal and pancreatic function, long-term use causes digestive problems such as loose stools, nausea, and gas in one third of patients. In addition, approximately 25 percent of patients develop gallstone
Gallstone
A gallstone is a crystalline concretion formed within the gallbladder by accretion of bile components. These calculi are formed in the gallbladder, but may pass distally into other parts of the biliary tract such as the cystic duct, common bile duct, pancreatic duct, or the ampulla of...
s, which are usually asymptomatic. In some cases, octreotide treatment can cause diabetes due to the fact that somatosstatin and its analogues can inhibit the release of insulin. On the other hand, scientists have found that in some acromegaly patients who already have diabetes, octreotide can reduce the need for insulin
Insulin
Insulin is a hormone central to regulating carbohydrate and fat metabolism in the body. Insulin causes cells in the liver, muscle, and fat tissue to take up glucose from the blood, storing it as glycogen in the liver and muscle....
and improve blood sugar
Blood sugar
The blood sugar concentration or blood glucose level is the amount of glucose present in the blood of a human or animal. Normally in mammals, the body maintains the blood glucose level at a reference range between about 3.6 and 5.8 mM , or 64.8 and 104.4 mg/dL...
control.
Dopamine agonists
For those who are unresponsive to somatostatin analogues, or for whom they are otherwise contraindicated, it is possible to treat using one of the dopamine agonists, BromocriptineBromocriptine
Bromocriptine , an ergoline derivative, is a dopamine agonist that is used in the treatment of pituitary tumors, Parkinson's disease , hyperprolactinaemia, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, and type 2 diabetes.- Indications :Amenorrhea, female infertility, galactorrhea, hypogonadism, and acromegaly...
(Parlodel) or Cabergoline. These have the advantage of being tablets rather than injections, and cost considerably less. These drugs can also be used as an adjunct to somatostatin analogue therapy. They are most effective in those whose pituitary tumours cosecrete prolactin. Side effects of these dopamine agonists include gastrointestinal upset, nausea, vomiting, light-headedness when standing, and nasal congestion. These side effects can be reduced or eliminated if medication is started at a very low dose at bedtime, taken with food, and gradually increased to the full therapeutic dose. However, bromocriptine lowers GH and IGF-1 levels and reduces tumor size in fewer than half of patients with acromegaly. Some patients report improvement in their symptoms although their GH and IGF-1 levels still are elevated.
The latest development in the medical treatment of acromegaly is the use of growth hormone receptor antagonists. The only available member of this family is pegvisomant
Pegvisomant
Pegvisomant is a growth hormone receptor antagonist used in the treatment of acromegaly. It is used if the tumor of the pituitary gland causing the acromegaly cannot be controlled with surgery or radiation, and the use of somatostatin analogues is unsuccessful...
(Somavert). By blocking the action of the endogenous growth hormone molecules, this compound is able to control disease activity of acromegaly in virtually all patients. Pegvisomant has to be administered subcutaneously by daily injections. Combinations of long-acting somatostatin analogues and weekly injections of pegvisomant seem to be equally effective as daily injections of pegvisomant.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy has been used both as a primary treatment and combined with surgery or drugs. It is usually reserved for patients who have tumor remaining after surgery. These patients often also receive medication to lower GH levels. Radiation therapy is given in divided doses over four to six weeks. This treatment lowers GH levels by about 50 percent over 2 to 5 years. Patients monitored for more than 5 years show significant further improvement. Radiation therapy causes a gradual loss of production of other pituitary hormones with time. Loss of vision and brain injury, which have been reported, are very rare complications of radiation treatments.Choice of treatment
No single treatment is effective for all patients. Treatment should be individualized depending on patient characteristics, such as age and tumor size. If the tumor has not yet invaded surrounding brain tissues, removal of the pituitary adenoma by an experienced neurosurgeon is usually the first choice. After surgery, a patient must be monitored for a long time for increasing GH levels. If surgery does not normalize hormone levels or a relapse occurs, a doctor will usually begin additional drug therapy. The current first choice is generally octreotide or lanreotide. However, bromocriptine or cabergoline are much cheaper and easier to administer. With both types of medication, long-term therapy is necessary because their withdrawal can lead to rising GH levels and tumor re-expansion. Radiation therapy is generally used for patients whose tumors are not completely removed by surgery; for patients who are not good candidates for surgery because of other health problems; and for patients who do not respond adequately to surgery and medication.Prognosis upon treatment
Upon successful treatment, symptoms and complications generally improve substantially or disappear, including headaches, visual disturbances, excess sweating and diabetes. Soft tissue swellings generally decrease and acromegaly-associated facial features gradually return towards normal although this may take some time. Life expectancy after the successful treatment of early acromegaly is equal to that of the normal population.Pseudoacromegaly
Pseudoacromegaly is a condition with the usual acromegaloid features but without an increase in growth hormone and IGF-1. It is frequently associated with insulin resistance. Cases have been reported due to minoxidilMinoxidil
Minoxidil is an antihypertensive vasodilator medication which also slows or stops hair loss and promotes hair regrowth. Now off-patent, it is available over-the-counter for the treatment of androgenic alopecia. Minoxidil must be used indefinitely for continued support of existing hair follicles and...
at an unusually high dose.
Notable cases
Famous patients, all but four (Abraham LincolnAbraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln was the 16th President of the United States, serving from March 1861 until his assassination in April 1865. He successfully led his country through a great constitutional, military and moral crisis – the American Civil War – preserving the Union, while ending slavery, and...
, Maurice Tillet
Maurice Tillet
Maurice Tillet was a French professional wrestler known as The French Angel who was a leading box office draw in the early 1940s and was recognized as world heavyweight champion by the American Wrestling Association run by Paul Bowser in Boston...
, Wallace Stevens
Wallace Stevens
Wallace Stevens was an American Modernist poet. He was born in Reading, Pennsylvania, educated at Harvard and then New York Law School, and spent most of his life working as a lawyer for the Hartford insurance company in Connecticut.His best-known poems include "Anecdote of the Jar",...
, and Antonio Silva
Antonio Silva (fighter)
Antonio Silva is a Brazilian mixed martial artist. He initially fought in the super heavyweight division, but currently competes in the heavyweight weight class. He is the first and last EliteXC heavyweight champion...
) standing in excess of 2.00 metres (6.6 feet):
- Abraham LincolnAbraham LincolnAbraham Lincoln was the 16th President of the United States, serving from March 1861 until his assassination in April 1865. He successfully led his country through a great constitutional, military and moral crisis – the American Civil War – preserving the Union, while ending slavery, and...
, the 16th President of the United States, was debated at several occasions to have Marfan's syndrome and also Acromegaly. He grew to 1.93 m (6 ft. 4 in) in height and generally weighed less than 82 kg (180 lb). Lincoln's body growth and energic constitution show gross evidence of pituitary hyperactivity and gonadal hypoactivity. He was a long, thin baby at birth, with unusually long, thin arms and legs. - André the GiantAndré the GiantAndré René Roussimoff , best known as André the Giant, was a French professional wrestler and actor. His best remembered acting role was that of Fezzik, the giant in the film The Princess Bride...
, wrestler and actor 2.13 m (7') tall after back surgery; his original wrestling stats listed him at 2.23 m (7'4"). He died at the age of 46. (He chose not to be treated and died from cardiac complications of the disease.) - Antonio SilvaAntonio Silva (fighter)Antonio Silva is a Brazilian mixed martial artist. He initially fought in the super heavyweight division, but currently competes in the heavyweight weight class. He is the first and last EliteXC heavyweight champion...
, Mixed Martial Artist, currently competing at heavyweight in the American promotion StrikeforceStrikeforceStrikeforce is a U.S.-based mixed martial arts and kickboxing organization based in San Jose, California. It is headed by CEO Scott Coker and owned by Zuffa, LLC...
. Silva has a professional record of 16-3, with 11 of his 17 wins coming by way of Knockout. Silva stands at 6'4 and weighs in for fights at 264 lbs. - Richard KielRichard KielRichard Dawson Kiel is an American actor best known for his role as the steel-toothed Jaws in the James Bond movies The Spy Who Loved Me and Moonraker as well as the video game Everything or Nothing, and Mr. Larson in Happy Gilmore...
, Jaws from the James Bond Movies and Mr. Larson in Happy GilmoreHappy GilmoreHappy Gilmore is a 1996 sports comedy film directed by Dennis Dugan and produced by Robert Simonds for Universal Studios. It stars Adam Sandler as the title character, an unsuccessful ice hockey player who discovers a talent for golf. The screenplay was written by Sandler and Tim Herlihy...
. He grew up to 7ft 1 1/2 but is now slightly under 7ft due to age and injury - Rondo HattonRondo HattonRondo Hatton was an American actor who had a brief, but prolific career playing thuggish bit parts in many Hollywood B-movies. He was known for his brutish facial features which were the result of acromegaly, a disorder of the pituitary gland.-Biography:Hatton was born Rondo K...
, character horror actor in the 1930s and 1940s - Pío PicoPío PicoPío de Jesús Pico was the last Governor of Alta California under Mexican rule.-Origins:...
, the last Mexican Governor of California (1801–1894), manifested acromegaly without gigantism between at least 1847 and 1858. Some time after 1858 signs of the growth hormone-producing tumor disappeared along with all the secondary effects the tumor had caused in him. He looked normal in his 90's. His remarkable recovery is likely an example of spontaneous selective pituitary tumor apoplexyApoplexyApoplexy is a medical term, which can be used to describe 'bleeding' in a stroke . Without further specification, it is rather outdated in use. Today it is used only for specific conditions, such as pituitary apoplexy and ovarian apoplexy. In common speech, it is used non-medically to mean a state...
. - Sir Archibald Levin Smith, British judge,
- Paul "The Big Show" Wight, wrestler, also known as "The Big Show" or "The Giant".
- James McLeay, professional SANFL player, suffers from low grade acromegaly, 2.1 m, 120 kilograms.
- Carel StruyckenCarel StruyckenCarel Struycken is a Dutch film, television, and stage actor. He is best known for playing Mr. Homn on the television series Star Trek: The Next Generation and Lurch in the films The Addams Family and Addams Family Values...
, Actor, 2.13m (7'0"). - Primo CarneraPrimo CarneraPrimo Carnera was an Italian boxer, nicknamed the Ambling Alp, who became the world heavyweight champion.-Biography:...
, professional boxer and World Heavyweight champion, 200 cm (6'7").
Fictional
- It has been suggested that the character 'Punch' from Punch and JudyPunch and JudyPunch and Judy is a traditional, popular puppet show featuring the characters of Mr. Punch and his wife, Judy. The performance consists of a sequence of short scenes, each depicting an interaction between two characters, most typically the anarchic Punch and one other character...
was originally a caricature of an Acromegaly sufferer.
External links
- Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases Information Service
- AcromegalyAnswersWebinar.com A webinar series
- acromegaly.org A satellite site of the Pituitary Network Association
- Acromegaly and Gigantism (a very comprehensive article)
- Acromegaly and Gigantism (Image of a patient with macroglossia - enlargement of the tongue)

