
Absolute neutrophil count
Encyclopedia
Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) is a measure of the number of neutrophil granulocytes (also known as polymorphonuclear cells, PMN's, polys, granulocytes, segmented neutrophils or segs) present in the blood
. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell
that fights against infection
.
The ANC is calculated from measurements of the total number of white blood cells (WBC), usually based on the combined percentage of mature neutrophils (sometimes called "segs," or segmented cells) and band
s, which are immature neutrophils.
is the condition of a low ANC, and the most common condition where an ANC would be measured is in the setting of chemotherapy for cancer.
Neutrophilia
indicates an elevated count.
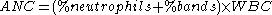
The unit of ANC is cells per microlitre (abbreviated µL; a microlitre is equal to one cubic millimetre) of blood.
Source: NCI CTC Toxicity scale Version 2.0 http://ctep.cancer.gov/forms/CTCv20_4-30-992.pdf
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell
White blood cell
White blood cells, or leukocytes , are cells of the immune system involved in defending the body against both infectious disease and foreign materials. Five different and diverse types of leukocytes exist, but they are all produced and derived from a multipotent cell in the bone marrow known as a...
that fights against infection
Infection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
.
The ANC is calculated from measurements of the total number of white blood cells (WBC), usually based on the combined percentage of mature neutrophils (sometimes called "segs," or segmented cells) and band
Band cell
A band cell is a cell undergoing granulopoiesis, derived from a metamyelocyte, and leading to a mature granulocyte.It is characterized by having a nucleus which is curved, but not lobar....
s, which are immature neutrophils.
Clinical significance
A normal ANC is above 1,500 cells per microliter. An ANC less than 500 cells/µL is defined as neutropenia and significantly increases the risk of infection. NeutropeniaNeutropenia
Neutropenia, from Latin prefix neutro- and Greek suffix -πενία , is a granulocyte disorder characterized by an abnormally low number of neutrophils, the most important type of white blood cell...
is the condition of a low ANC, and the most common condition where an ANC would be measured is in the setting of chemotherapy for cancer.
Neutrophilia
Neutrophilia
Neutrophilia is a condition where a person has a high number of neutrophil granulocytes in their blood.-Causes:...
indicates an elevated count.
Calculation
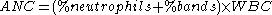
The unit of ANC is cells per microlitre (abbreviated µL; a microlitre is equal to one cubic millimetre) of blood.
Ranges
| NCI Risk Category | ANC |
|---|---|
| 0 | Within normal limits |
| 1 | ≥1500 - <2000/mm³ |
| 2 | ≥1000 - <1500/mm³ |
| 3 | ≥500 - <1000/mm³ |
| 4 | < 500/mm³ |
Source: NCI CTC Toxicity scale Version 2.0 http://ctep.cancer.gov/forms/CTCv20_4-30-992.pdf

