
AA postulate
Encyclopedia
The AA Postulate in Euclidean geometry
Euclidean geometry
Euclidean geometry is a mathematical system attributed to the Alexandrian Greek mathematician Euclid, which he described in his textbook on geometry: the Elements. Euclid's method consists in assuming a small set of intuitively appealing axioms, and deducing many other propositions from these...
states that two triangle
Triangle
A triangle is one of the basic shapes of geometry: a polygon with three corners or vertices and three sides or edges which are line segments. A triangle with vertices A, B, and C is denoted ....
s are similar if they have two corresponding angle
Angle
In geometry, an angle is the figure formed by two rays sharing a common endpoint, called the vertex of the angle.Angles are usually presumed to be in a Euclidean plane with the circle taken for standard with regard to direction. In fact, an angle is frequently viewed as a measure of an circular arc...
s congruent
Congruence (geometry)
In geometry, two figures are congruent if they have the same shape and size. This means that either object can be repositioned so as to coincide precisely with the other object...
.
The AA Postulate works because the interior angles of a triangle
Triangle
A triangle is one of the basic shapes of geometry: a polygon with three corners or vertices and three sides or edges which are line segments. A triangle with vertices A, B, and C is denoted ....
are always equal to 180°. By knowing two angles, such as 32° and 64° degrees, we know that the next angle is 84°, because 180-(32+64)=84. (This is sometimes referred to as the AAA Postulate—which is true in all respects, but two angles are entirely sufficient.)
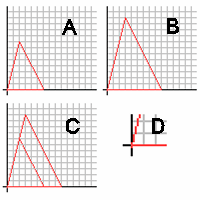
The postulate can be better understood by working in reverse order. The two triangles on grids A and B are similar
Similarity (geometry)
Two geometrical objects are called similar if they both have the same shape. More precisely, either one is congruent to the result of a uniform scaling of the other...
, by a 1.5 dilation
Dilation
Dilation refers to an enlargement or expansion in bulk or extent, the opposite of contraction. It derives from the Latin dilatare, "to spread wide".In physiology:* Pupillary dilation, dilation of the pupil of the eye...
from A to B. If they are aligned, as in grid C, it is apparent find that the angle on the origin is congruent with the other (D). We also know that the pair of sides opposite the origin are parallel. We know this because the pairs of sides around them are similar, stem from the same point, and line up with each other. We can then look at the sides around the parallels as transversal
Transversal
In geometry , when two coplanar lines exist such that a third coplanar line passes thru both lines. This third line is named the Transversal....
s, and therefore the corresponding angles are congruent. Using this reasoning we can tell that similar triangles have congruent angles.

