2000s in economics
Encyclopedia
- GlobalizationGlobalizationGlobalization refers to the increasingly global relationships of culture, people and economic activity. Most often, it refers to economics: the global distribution of the production of goods and services, through reduction of barriers to international trade such as tariffs, export fees, and import...
: Multinational corporationMultinational corporationA multi national corporation or enterprise , is a corporation or an enterprise that manages production or delivers services in more than one country. It can also be referred to as an international corporation...
s become more pervasive, and anti-globalizationAnti-globalizationCriticism of globalization is skepticism of the claimed benefits of the globalization of capitalism. Many of these views are held by the anti-globalization movement however other groups also are critical of the policies of globalization....
protests occur frequently during meetings of International Monetary FundInternational Monetary FundThe International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
(IMF) and World Trade OrganizationWorld Trade OrganizationThe World Trade Organization is an organization that intends to supervise and liberalize international trade. The organization officially commenced on January 1, 1995 under the Marrakech Agreement, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade , which commenced in 1948...
(WTO), especially in the early 2000s. - The euroEuroThe euro is the official currency of the eurozone: 17 of the 27 member states of the European Union. It is also the currency used by the Institutions of the European Union. The eurozone consists of Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg,...
becomes legal tender in twelve European UnionEuropean UnionThe European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
countries in 2002. It is the largest monetary union in history. The euro eases trade in the EurozoneEurozoneThe eurozone , officially called the euro area, is an economic and monetary union of seventeen European Union member states that have adopted the euro as their common currency and sole legal tender...
. By 2009, four more countries join the euro, SloveniaSloveniaSlovenia , officially the Republic of Slovenia , is a country in Central and Southeastern Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean. Slovenia borders Italy to the west, Croatia to the south and east, Hungary to the northeast, and Austria to the north, and also has a small portion of...
in 2007, MaltaMaltaMalta , officially known as the Republic of Malta , is a Southern European country consisting of an archipelago situated in the centre of the Mediterranean, south of Sicily, east of Tunisia and north of Libya, with Gibraltar to the west and Alexandria to the east.Malta covers just over in...
and CyprusCyprusCyprus , officially the Republic of Cyprus , is a Eurasian island country, member of the European Union, in the Eastern Mediterranean, east of Greece, south of Turkey, west of Syria and north of Egypt. It is the third largest island in the Mediterranean Sea.The earliest known human activity on the...
in 2008 and SlovakiaSlovakiaThe Slovak Republic is a landlocked state in Central Europe. It has a population of over five million and an area of about . Slovakia is bordered by the Czech Republic and Austria to the west, Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east and Hungary to the south...
in 2009. - The NASDAQNASDAQThe NASDAQ Stock Market, also known as the NASDAQ, is an American stock exchange. "NASDAQ" originally stood for "National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations". It is the second-largest stock exchange by market capitalization in the world, after the New York Stock Exchange. As of...
, the American Stock ExchangeAmerican Stock ExchangeNYSE Amex Equities, formerly known as the American Stock Exchange is an American stock exchange situated in New York. AMEX was a mutual organization, owned by its members. Until 1953, it was known as the New York Curb Exchange. On January 17, 2008, NYSE Euronext announced it would acquire the...
and the New York Stock ExchangeNew York Stock ExchangeThe New York Stock Exchange is a stock exchange located at 11 Wall Street in Lower Manhattan, New York City, USA. It is by far the world's largest stock exchange by market capitalization of its listed companies at 13.39 trillion as of Dec 2010...
closed for six days after the September 11th, 2001 attacks, the longest close since the Great DepressionGreat DepressionThe Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression in the decade preceding World War II. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations, but in most countries it started in about 1929 and lasted until the late 1930s or early 1940s...
in 1929. - The 2000s contained two recessions, according to the U.S. National Bureau of Economic Resarch. The firstEarly 2000s recessionThe early 2000s recession was a decline in economic activity which occurred mainly in developed countries. The recession affected the European Union mostly during 2000 and 2001 and the United States mostly in 2002 and 2003. The UK, Canada and Australia avoided the recession for the most part, while...
occurred from 2001 to 2003, and the second began in December 2007. - Major downturn in the value of dot-comDot-com companyA dot-com company, or simply a dot-com , is a company that does most of its business on the Internet, usually through a website that uses the popular top-level domain, ".com" .While the term can refer to present-day companies, it is also used specifically to refer to companies with...
shares, with occasional exceptions (GoogleGoogleGoogle Inc. is an American multinational public corporation invested in Internet search, cloud computing, and advertising technologies. Google hosts and develops a number of Internet-based services and products, and generates profit primarily from advertising through its AdWords program...
's IPO on August 13, 2004). The Internet continues to grow as a business and advertising medium, with steady increases in online shopping and banking activities. Other successful firms include Amazon.comAmazon.comAmazon.com, Inc. is a multinational electronic commerce company headquartered in Seattle, Washington, United States. It is the world's largest online retailer. Amazon has separate websites for the following countries: United States, Canada, United Kingdom, Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Japan, and...
and eBayEBayeBay Inc. is an American internet consumer-to-consumer corporation that manages eBay.com, an online auction and shopping website in which people and businesses buy and sell a broad variety of goods and services worldwide...
. - The US dominance over the world economy continues, but economically rising nations and organizations like ChinaPeople's Republic of ChinaChina , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
and IndiaIndiaIndia , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
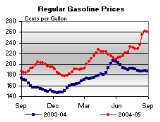
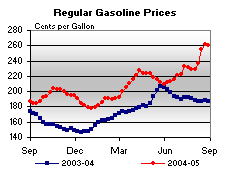
show signs of becoming contending world powers. - Oil price rises. Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan pipelineBaku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan pipelineThe Baku–Tbilisi–Ceyhan pipeline is a long crude oil pipeline from the Azeri-Chirag-Guneshli oil field in the Caspian Sea to the Mediterranean Sea. It connects Baku, the capital of Azerbaijan; Tbilisi, the capital of Georgia; and Ceyhan, a port on the south-eastern Mediterranean coast of Turkey,...
opens on May 25, 2005, potentially removing the dependence of the United States and other Western nations on Middle Eastern oil. - EnronEnronEnron Corporation was an American energy, commodities, and services company based in Houston, Texas. Before its bankruptcy on December 2, 2001, Enron employed approximately 22,000 staff and was one of the world's leading electricity, natural gas, communications, and pulp and paper companies, with...
and other major accounting and corporate governanceCorporate governanceCorporate governance is a number of processes, customs, policies, laws, and institutions which have impact on the way a company is controlled...
scandals prompt reviews of corporate government legislation worldwide (e.g., Sarbanes-Oxley ActSarbanes-Oxley ActThe Sarbanes–Oxley Act of 2002 , also known as the 'Public Company Accounting Reform and Investor Protection Act' and 'Corporate and Auditing Accountability and Responsibility Act' and commonly called Sarbanes–Oxley, Sarbox or SOX, is a United States federal law enacted on July 30, 2002, which...
) - The 1990s1990sFile:1990s decade montage.png|From left, clockwise: The Hubble Space Telescope floats in space after it was taken up in 1990; American F-16s and F-15s fly over burning oil fields and the USA Lexie in Operation Desert Storm, also known as the 1991 Gulf War; The signing of the Oslo Accords on...
stock market boom ends in mid-March to early September 2000-2001. - Post-9/11 Recession from 2001 to 2002. The Dow Jones average would sink to the 7000 level during July 2002. Continuing stagnation in US and global monthly jobs growth afterwards. A recovery in US GDP growth begins after May 2003, but with continuing weakness on many indicators as of 2006.
- American automobile companies General MotorsGeneral MotorsGeneral Motors Company , commonly known as GM, formerly incorporated as General Motors Corporation, is an American multinational automotive corporation headquartered in Detroit, Michigan and the world's second-largest automaker in 2010...
and FordFord Motor CompanyFord Motor Company is an American multinational automaker based in Dearborn, Michigan, a suburb of Detroit. The automaker was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. In addition to the Ford and Lincoln brands, Ford also owns a small stake in Mazda in Japan and Aston Martin in the UK...
lose market share to Japanese Makes such as Toyota and HondaHondais a Japanese public multinational corporation primarily known as a manufacturer of automobiles and motorcycles.Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, as well as the world's largest manufacturer of internal combustion engines measured by volume, producing more than...
in the US. This trend of General Motors and Ford losing market share to Honda and Toyota started around 1998 in the US and still continues in 2006. - By 2006, the U.S. economy had reached new heights, with the stock market increasing in value, home prices rising, and interest rates curbed. Gas prices lowered out by September 2006, further fueling economic prospects.
- The Dow Jones surpasses 12,000 for the first time in history, in mid-2006, and hits levels above 14,000 in 2007; however levels have dropped to around 8,000.
- In 2006-2007, the United States housing market made a sharp downturn, with home sales falling to levels not seen in a decade. Median home prices began slipping. The effects of the housing downturn on the overall economy are still being determined as of 2007, though by July–August 2007, worries over a "credit crunch" emerged and increasing numbers of economists and CEOs feared the economy would slip into a recession. The gross domestic product in the United States continued slowing in 2007.
- A barrel of oil peaked at $140 in mid 2008, and banks became less willing to lend money to each other. Inflation is already rising across many industrialized countries.
- The American housing market caused difficulty for the two mortgage brokers Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, which have been subject to fears of collapse.

