
Yamaguchi esterification
Encyclopedia
The Yamaguchi esterification is the chemical reaction
of an aliphatic carboxylic acid
and 2,4,6-trichlorobenzoyl chloride (Yamaguchi reagent) to form a mixed anhydride which, upon reaction with an alcohol
in the presence of stoichiometric amount of DMAP, produces the desired ester
. It was first reported by M. Yamaguchi et al. in 1979.
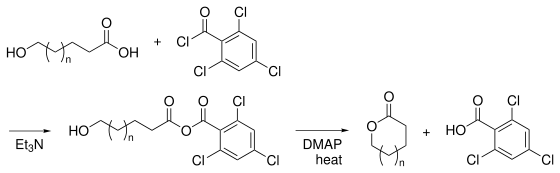 It is especially useful in the synthesis of macro-lactone
It is especially useful in the synthesis of macro-lactone
s and highly functionalised esters.
at the less hindered carbon, producing acyl-substituted DMAP. It reacts with the alcohol to form the product ester.
The in situ formation of the symmetric aliphatic anhydride is proposed to explain the regioselectivity observed in the reactions of aliphatic acids, based on the fact that aliphatic carboxylates are more nucleophilic, and aliphatic anhydrides are more eletrophilic towards DMAP and alcohol than their counterparts.
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
of an aliphatic carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by the presence of at least one carboxyl group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R-COOH, where R is some monovalent functional group...
and 2,4,6-trichlorobenzoyl chloride (Yamaguchi reagent) to form a mixed anhydride which, upon reaction with an alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
in the presence of stoichiometric amount of DMAP, produces the desired ester
Ester
Esters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and...
. It was first reported by M. Yamaguchi et al. in 1979.

Lactone
In chemistry, a lactone is a cyclic ester which can be seen as the condensation product of an alcohol group -OH and a carboxylic acid group -COOH in the same molecule...
s and highly functionalised esters.
Reaction mechanism
The aliphatic carboxylate adds to the carbonyl carbon of Yamaguchi reagent, forming a mixed anhydride, which is then attacked by DMAP regioselectivelyRegioselectivity
In chemistry, regioselectivity is the preference of one direction of chemical bond making or breaking over all other possible directions. It can often apply to which of many possible positions a reagent will affect, such as which proton a strong base will abstract from an organic molecule, or where...
at the less hindered carbon, producing acyl-substituted DMAP. It reacts with the alcohol to form the product ester.
The in situ formation of the symmetric aliphatic anhydride is proposed to explain the regioselectivity observed in the reactions of aliphatic acids, based on the fact that aliphatic carboxylates are more nucleophilic, and aliphatic anhydrides are more eletrophilic towards DMAP and alcohol than their counterparts.
External links
- Yamaguchi esterification—organic-chemistry.org
- Investigation of the Yamaguchi Esterification Mechanism. Synthesis of a Lux-S Enzyme Inhibitor Using an Improved Esterification Method. I. Dhimitruka, J. SantaLucia, Org. Lett., 2006, 8, 47-50. Article

