XXTEA
Encyclopedia
In cryptography
, Corrected Block TEA (often referred to as XXTEA) is a block cipher
designed to correct weaknesses in the original Block TEA.
XXTEA is vulnerable to a chosen-plaintext attack
requiring 259 queries and negligible work. See cryptanalysis below.
The cipher
's designers were Roger Needham
and David Wheeler of the Cambridge Computer Laboratory
, and the algorithm was presented in an unpublished technical report in October 1998 (Wheeler and Needham, 1998). It is not subject to any patent
s.
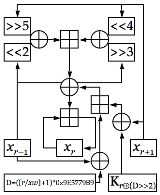
Formally speaking, XXTEA is a consistent incomplete source-heavy heterogeneous UFN (unbalanced Feistel network) block cipher. XXTEA operates on variable-length blocks that are some arbitrary multiple of 32 bits in size (minimum 64 bits). The number of full cycles depends on the block size, but there are at least six (rising to 32 for small block sizes). The original Block TEA applies the XTEA
round function to each word in the block and combines it additively with its leftmost neighbour. Slow diffusion rate of the decryption process was immediately exploited to break the cipher. Corrected Block TEA uses a more involved round function which makes use of both immediate neighbours in processing each word in the block.
XXTEA is likely to be more efficient than XTEA for longer messages.
Needham & Wheeler make the following comments on the use of Block TEA:
However, due to the incomplete nature of the round function, two large ciphertexts of 53 or more 32-bit words identical in all but 12 words can be found by a simple brute-force collision search requiring 296−N memory, 2N time and 2N+296−N chosen plaintexts, in other words with a total time*memory complexity of 296, which is actually 2wordsize*fullcycles/2 for any such cipher. It is currently unknown if such partial collisions pose any threat to the security of the cipher. Eight full cycles would raise the bar for such collision search above complexity of parallel brute-force attacks.
The unusually small size of the XXTEA algorithm would make it a viable option in situations where there are extreme constraints e.g. legacy hardware systems (perhaps embedded) where the amount of available RAM
is minimal.
against full-round XXTEA, requiring 259 queries and negligible work. It is based on differential cryptanalysis
.
#define MX (z>>5^y<<2) + (y>>3^z<<4)^(sum^y) + (k[p&3^e]^z);
long btea(long* v, long n, long* k) {
unsigned long z=v[n-1], y=v[0], sum=0, e, DELTA=0x9e3779b9;
long p, q ;
if (n > 1) { /* Coding Part */
q = 6 + 52/n;
while (q-- > 0) {
sum += DELTA;
e = (sum >> 2) & 3;
for (p=0; p
z = v[n-1] += MX;
}
return 0 ;
} else if (n < -1) { /* Decoding Part */
n = -n;
q = 6 + 52/n;
sum = q*DELTA ;
while (sum != 0) {
e = (sum >> 2) & 3;
for (p=n-1; p>0; p--) z = v[p-1], y = v[p] -= MX;
z = v[n-1];
y = v[0] -= MX;
sum -= DELTA;
}
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
According to Needham and Wheeler:
Note that the initialization of z will cause a segmentation fault
in some languages – it would be better placed inside the 'Coding Part' block. Also, in the definition of MX some programmers would prefer to use bracketing to clarify operator precedence.
A clarified version including those improvements is as follows:
#include
#define DELTA 0x9e3779b9
#define MX (((z>>5^y<<2) + (y>>3^z<<4)) ^ ((sum^y) + (key[(p&3)^e] ^ z)))
void btea(uint32_t *v, int n, uint32_t const key[4]) {
uint32_t y, z, sum;
unsigned p, rounds, e;
if (n > 1) { /* Coding Part */
rounds = 6 + 52/n;
sum = 0;
z = v[n-1];
do {
sum += DELTA;
e = (sum >> 2) & 3;
for (p=0; p
z = v[p] += MX;
}
y = v[0];
z = v[n-1] += MX;
} while (--rounds);
} else if (n < -1) { /* Decoding Part */
n = -n;
rounds = 6 + 52/n;
sum = rounds*DELTA;
y = v[0];
do {
e = (sum >> 2) & 3;
for (p=n-1; p>0; p--) {
z = v[p-1];
y = v[p] -= MX;
}
z = v[n-1];
y = v[0] -= MX;
} while ((sum -= DELTA) != 0);
}
}
Cryptography
Cryptography is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of third parties...
, Corrected Block TEA (often referred to as XXTEA) is a block cipher
Block cipher
In cryptography, a block cipher is a symmetric key cipher operating on fixed-length groups of bits, called blocks, with an unvarying transformation. A block cipher encryption algorithm might take a 128-bit block of plaintext as input, and output a corresponding 128-bit block of ciphertext...
designed to correct weaknesses in the original Block TEA.
XXTEA is vulnerable to a chosen-plaintext attack
Chosen-plaintext attack
A chosen-plaintext attack is an attack model for cryptanalysis which presumes that the attacker has the capability to choose arbitrary plaintexts to be encrypted and obtain the corresponding ciphertexts. The goal of the attack is to gain some further information which reduces the security of the...
requiring 259 queries and negligible work. See cryptanalysis below.
The cipher
Cipher
In cryptography, a cipher is an algorithm for performing encryption or decryption — a series of well-defined steps that can be followed as a procedure. An alternative, less common term is encipherment. In non-technical usage, a “cipher” is the same thing as a “code”; however, the concepts...
's designers were Roger Needham
Roger Needham
Roger Michael Needham, CBE, FRS, FREng was a British computer scientist.-Early life:He attended Doncaster Grammar School for Boys in Doncaster ....
and David Wheeler of the Cambridge Computer Laboratory
University of Cambridge Computer Laboratory
The Computer Laboratory is the computer science department of the University of Cambridge. As of 2007, it employs 35 academic staff, 25 support staff, 35 affiliated research staff, and about 155 research students...
, and the algorithm was presented in an unpublished technical report in October 1998 (Wheeler and Needham, 1998). It is not subject to any patent
Patent
A patent is a form of intellectual property. It consists of a set of exclusive rights granted by a sovereign state to an inventor or their assignee for a limited period of time in exchange for the public disclosure of an invention....
s.
Formally speaking, XXTEA is a consistent incomplete source-heavy heterogeneous UFN (unbalanced Feistel network) block cipher. XXTEA operates on variable-length blocks that are some arbitrary multiple of 32 bits in size (minimum 64 bits). The number of full cycles depends on the block size, but there are at least six (rising to 32 for small block sizes). The original Block TEA applies the XTEA
XTEA
In cryptography, XTEA is a block cipher designed to correct weaknesses in TEA. The cipher's designers were David Wheeler and Roger Needham of the Cambridge Computer Laboratory, and the algorithm was presented in an unpublished technical report in 1997...
round function to each word in the block and combines it additively with its leftmost neighbour. Slow diffusion rate of the decryption process was immediately exploited to break the cipher. Corrected Block TEA uses a more involved round function which makes use of both immediate neighbours in processing each word in the block.
XXTEA is likely to be more efficient than XTEA for longer messages.
Needham & Wheeler make the following comments on the use of Block TEA:
For ease of use and general security the large block version is to be preferred when applicable for the following reasons.
- A single bit change will change about one half of the bits of the entire block, leaving no place where the changes start.
- There is no choice of mode involved.
- Even if the correct usage of always changing the data sent (possibly by a message number) is employed, only identical messages give the same result and the information leakage is minimal.
- The message number should always be checked as this redundancy is the check against a random message being accepted.
- Cut and join attacks do not appear to be possible.
- If it is not acceptable to have very long messages, they can be broken into chunks say of 60 words and chained
Block cipher modes of operationIn cryptography, modes of operation is the procedure of enabling the repeated and secure use of a block cipher under a single key.A block cipher by itself allows encryption only of a single data block of the cipher's block length. When targeting a variable-length message, the data must first be...
analogously to the methods used for DESData Encryption StandardThe Data Encryption Standard is a block cipher that uses shared secret encryption. It was selected by the National Bureau of Standards as an official Federal Information Processing Standard for the United States in 1976 and which has subsequently enjoyed widespread use internationally. It is...
.
However, due to the incomplete nature of the round function, two large ciphertexts of 53 or more 32-bit words identical in all but 12 words can be found by a simple brute-force collision search requiring 296−N memory, 2N time and 2N+296−N chosen plaintexts, in other words with a total time*memory complexity of 296, which is actually 2wordsize*fullcycles/2 for any such cipher. It is currently unknown if such partial collisions pose any threat to the security of the cipher. Eight full cycles would raise the bar for such collision search above complexity of parallel brute-force attacks.
The unusually small size of the XXTEA algorithm would make it a viable option in situations where there are extreme constraints e.g. legacy hardware systems (perhaps embedded) where the amount of available RAM
Ram
-Animals:*Ram, an uncastrated male sheep*Ram cichlid, a species of freshwater fish endemic to Colombia and Venezuela-Military:*Battering ram*Ramming, a military tactic in which one vehicle runs into another...
is minimal.
Cryptanalysis
An attack published in 2010 by E. Yarrkov presents an a chosen-plaintext attackChosen-plaintext attack
A chosen-plaintext attack is an attack model for cryptanalysis which presumes that the attacker has the capability to choose arbitrary plaintexts to be encrypted and obtain the corresponding ciphertexts. The goal of the attack is to gain some further information which reduces the security of the...
against full-round XXTEA, requiring 259 queries and negligible work. It is based on differential cryptanalysis
Differential cryptanalysis
Differential cryptanalysis is a general form of cryptanalysis applicable primarily to block ciphers, but also to stream ciphers and cryptographic hash functions. In the broadest sense, it is the study of how differences in an input can affect the resultant difference at the output...
.
Reference code
The original formulation of the Corrected Block TEA algorithm, published by David Wheeler and Roger Needham, is as follows:#define MX (z>>5^y<<2) + (y>>3^z<<4)^(sum^y) + (k[p&3^e]^z);
long btea(long* v, long n, long* k) {
unsigned long z=v[n-1], y=v[0], sum=0, e, DELTA=0x9e3779b9;
long p, q ;
if (n > 1) { /* Coding Part */
q = 6 + 52/n;
while (q-- > 0) {
sum += DELTA;
e = (sum >> 2) & 3;
for (p=0; p
z = v[n-1] += MX;
}
return 0 ;
} else if (n < -1) { /* Decoding Part */
n = -n;
q = 6 + 52/n;
sum = q*DELTA ;
while (sum != 0) {
e = (sum >> 2) & 3;
for (p=n-1; p>0; p--) z = v[p-1], y = v[p] -= MX;
z = v[n-1];
y = v[0] -= MX;
sum -= DELTA;
}
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
According to Needham and Wheeler:
Note that the initialization of z will cause a segmentation fault
Segmentation fault
A segmentation fault , bus error or access violation is generally an attempt to access memory that the CPU cannot physically address. It occurs when the hardware notifies an operating system about a memory access violation. The OS kernel then sends a signal to the process which caused the exception...
in some languages – it would be better placed inside the 'Coding Part' block. Also, in the definition of MX some programmers would prefer to use bracketing to clarify operator precedence.
A clarified version including those improvements is as follows:
#include
#define DELTA 0x9e3779b9
#define MX (((z>>5^y<<2) + (y>>3^z<<4)) ^ ((sum^y) + (key[(p&3)^e] ^ z)))
void btea(uint32_t *v, int n, uint32_t const key[4]) {
uint32_t y, z, sum;
unsigned p, rounds, e;
if (n > 1) { /* Coding Part */
rounds = 6 + 52/n;
sum = 0;
z = v[n-1];
do {
sum += DELTA;
e = (sum >> 2) & 3;
for (p=0; p
z = v[p] += MX;
}
y = v[0];
z = v[n-1] += MX;
} while (--rounds);
} else if (n < -1) { /* Decoding Part */
n = -n;
rounds = 6 + 52/n;
sum = rounds*DELTA;
y = v[0];
do {
e = (sum >> 2) & 3;
for (p=n-1; p>0; p--) {
z = v[p-1];
y = v[p] -= MX;
}
z = v[n-1];
y = v[0] -= MX;
} while ((sum -= DELTA) != 0);
}
}
See also
- RC4RC4In cryptography, RC4 is the most widely used software stream cipher and is used in popular protocols such as Secure Sockets Layer and WEP...
: A stream cipherStream cipherIn cryptography, a stream cipher is a symmetric key cipher where plaintext digits are combined with a pseudorandom cipher digit stream . In a stream cipher the plaintext digits are encrypted one at a time, and the transformation of successive digits varies during the encryption...
that, just like XXTEA, is designed to be very simple to implement. - XTEAXTEAIn cryptography, XTEA is a block cipher designed to correct weaknesses in TEA. The cipher's designers were David Wheeler and Roger Needham of the Cambridge Computer Laboratory, and the algorithm was presented in an unpublished technical report in 1997...
: Block TEA's precursor. - TEATiny Encryption AlgorithmIn cryptography, the Tiny Encryption Algorithm is a block cipher notable for its simplicity of description and implementation, typically a few lines of code...
: XTEA's precursor.

