
World file
Encyclopedia
A world file is a plain text
computer data file
used by geographic information system
s to georeference
raster
map images. The file specification was introduced by ESRI
.
Small-scale rectangular raster image maps can have an associated world file for GIS map software which describes the location, scale and rotation of the map. These world files are six-line files with decimal numbers on each line.
This description is however misleading in that the D and B rotation parameters are not really rotations (in degrees or gradients) and in that as soon as D or B are not zero, the A and E parameters do not correspond to the pixel size any more. The A, D, B and E parameters are sometimes named "x-scale", "y-skew", "x-skew" and "y-scale". A better description of the A, D, B and E parameters would be:
All four parameters are expressed in the map units depending on the coordinate system associated with the raster.
When D or B are different than zero the pixel width is given by:

and the pixel height by

World files describing a map on the Universal Transverse Mercator coordinate system
(UTM) use these conventions:
The above description applies also to a rectangular, non-rotated image which might be, for example, overlaid on an orthogonally projected map. If the world file describes an image that is rotated from the axis of the target projection, however, then A, D, B and E must be derived from the required affine transformation (see below). Specifically, A and E will no longer be the meter/pixel measurement on their respective axes.
These values are used in a six-parameter affine transformation
:
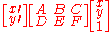
which can be written as this set of equations:
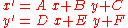
where:
The y-scale (E) is negative because the origins of an image and the UTM coordinate system are different. The origin of an image is located in the upper-left corner, whereas the origin of the map coordinate system is located in the lower-left corner. Row values in the image increase from the origin downward, while y-coordinate values in the map increase from the origin upward. Many mapping programs are unable to handle "upside down" images (i.e. those with a positive y-scale).
Example:
Original
Its world file is
32.0
0.0
0.0
-32.0
691200.0
4576000.0
The position of Falkner Island
light on the map image is:
x = 171 pixels from left
y = 343 pixels from top
This gives:
x1 = 696672 meters Easting
y1 = 4565024 meters Northing
Note that the UTM (grid) zone is not given so the coordinates are ambiguous — they can represent a position in any of the approximately 120 UTM grid zones. In this case, approximate latitude and longitude (41.2, −072.7) were looked up in a gazetteer and the UTM (grid) zone was found to be 18 using a Web-based converter.
One convention is to append the letter "w" to the end of the raster filename:
falknermap.jpg → falknermap.jpgw.
An alternative naming convention is also honored, and in fact is more widespread.
The second letter of the original filename extension is removed, and the letter "w"
is added at the end. For example,
falknermap.jpg → falknermap.jgw or
falknermap.tif → falknermap.tfw.
This convention was developed for filenames that need to conform to the 8.3 file naming convention.
Plain text
In computing, plain text is the contents of an ordinary sequential file readable as textual material without much processing, usually opposed to formatted text....
computer data file
Data file
A data file is a computer file which stores data to use by a computer application or system. It generally does not refer to files that contain instructions or code to be executed , or to files which define the operation or structure of an application or system ; but specifically to information...
used by geographic information system
Geographic Information System
A geographic information system, geographical information science, or geospatial information studies is a system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage, and present all types of geographically referenced data...
s to georeference
Georeference
To georeference something means to define its existence in physical space. That is, establishing its location in terms of map projections or coordinate systems. The term is used both when establishing the relation between raster or vector images and coordinates, and when determining the spatial...
raster
Raster graphics
In computer graphics, a raster graphics image, or bitmap, is a data structure representing a generally rectangular grid of pixels, or points of color, viewable via a monitor, paper, or other display medium...
map images. The file specification was introduced by ESRI
ESRI
Esri is a software development and services company providing Geographic Information System software and geodatabase management applications. The headquarters of Esri is in Redlands, California....
.
Small-scale rectangular raster image maps can have an associated world file for GIS map software which describes the location, scale and rotation of the map. These world files are six-line files with decimal numbers on each line.
Definition
World files do not specify a coordinate system; this information is generally stored somewhere else in the raster file itself or in another companion file. The generic meaning of world file parameters are:- Line 1: A: pixel size in the x-direction in map units/pixel
- Line 2: D: rotation about y-axis
- Line 3: B: rotation about x-axis
- Line 4: E: pixel size in the y-direction in map units, almost always negative
- Line 5: C: x-coordinate of the center of the upper left pixel
- Line 6: F: y-coordinate of the center of the upper left pixel
This description is however misleading in that the D and B rotation parameters are not really rotations (in degrees or gradients) and in that as soon as D or B are not zero, the A and E parameters do not correspond to the pixel size any more. The A, D, B and E parameters are sometimes named "x-scale", "y-skew", "x-skew" and "y-scale". A better description of the A, D, B and E parameters would be:
- Line 1: A: x component of the pixel width (x-scale)
- Line 2: D: y component of the pixel width (y-skew)
- Line 3: B: x component of the pixel height (x-skew)
- Line 4: E: y component of the pixel height (y-scale), almost always negative
All four parameters are expressed in the map units depending on the coordinate system associated with the raster.
When D or B are different than zero the pixel width is given by:

and the pixel height by

World files describing a map on the Universal Transverse Mercator coordinate system
Universal Transverse Mercator coordinate system
The Universal Transverse Mercator geographic coordinate system uses a 2-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system to give locations on the surface of the Earth. It is a horizontal position representation, i.e...
(UTM) use these conventions:
- D and B are usually 0, since the image pixels are usually made to align with the UTM grid
- C is the UTM easting
- F is the UTM northing
- Units are always meters per pixel
The above description applies also to a rectangular, non-rotated image which might be, for example, overlaid on an orthogonally projected map. If the world file describes an image that is rotated from the axis of the target projection, however, then A, D, B and E must be derived from the required affine transformation (see below). Specifically, A and E will no longer be the meter/pixel measurement on their respective axes.
These values are used in a six-parameter affine transformation
Affine transformation
In geometry, an affine transformation or affine map or an affinity is a transformation which preserves straight lines. It is the most general class of transformations with this property...
:
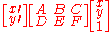
which can be written as this set of equations:
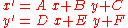
where:
- x is the calculated UTM easting of the pixel on the map
- y is the calculated UTM northing of the pixel on the map
- x is the column number of the pixel in the image counting from left
- y is the row number of the pixel in the image counting from top
- A or x-scale; dimension of a pixel in map units in x-direction
- B, D are rotation terms
- C, F are translation terms: x, y map coordinates of the center of the upper-left pixel
- E is negative of y-scale: dimension of a pixel in map units in y-direction
The y-scale (E) is negative because the origins of an image and the UTM coordinate system are different. The origin of an image is located in the upper-left corner, whereas the origin of the map coordinate system is located in the lower-left corner. Row values in the image increase from the origin downward, while y-coordinate values in the map increase from the origin upward. Many mapping programs are unable to handle "upside down" images (i.e. those with a positive y-scale).
Example:
Original
falknermap.jpg is 800×600 pixels (map not shown).Its world file is
falknermap.jgw and contains:32.0
0.0
0.0
-32.0
691200.0
4576000.0
The position of Falkner Island
Falkner Island
Falkner Island is a 4.5 acre crescent-shaped island located in Long Island Sound 3 miles off the coast of Guilford, Connecticut, USA....
light on the map image is:
x = 171 pixels from left
y = 343 pixels from top
This gives:
x1 = 696672 meters Easting
y1 = 4565024 meters Northing
Note that the UTM (grid) zone is not given so the coordinates are ambiguous — they can represent a position in any of the approximately 120 UTM grid zones. In this case, approximate latitude and longitude (41.2, −072.7) were looked up in a gazetteer and the UTM (grid) zone was found to be 18 using a Web-based converter.
The filename
The name of the world file is based on the raster file's name.One convention is to append the letter "w" to the end of the raster filename:
falknermap.jpg → falknermap.jpgw.
An alternative naming convention is also honored, and in fact is more widespread.
The second letter of the original filename extension is removed, and the letter "w"
is added at the end. For example,
falknermap.jpg → falknermap.jgw or
falknermap.tif → falknermap.tfw.
This convention was developed for filenames that need to conform to the 8.3 file naming convention.
Localization
When writing World Files it is advisable to ignore localization settings and always use '.' as the decimal separator. Also, negative numbers should be specified with the '-' character exclusively. This ensures maximum portability of the images.See also
- ESRI gridESRI gridAn Esri grid is a raster GIS file format developed by Esri, which has two formats:#A proprietary binary format, also known as an ARC/INFO GRID, ARC GRID and many other variations...
– embeds a similar georeferencing context within a single raster file - MapInfo TAB formatMapInfo TAB formatThe MapInfo TAB format is a popular geospatial vector data format for geographic information systems software. It is developed and regulated by MapInfo as a proprietary format.-File components:...
- a popular geospatial vector data format for GIS software

