Western Yugur
Encyclopedia
Western Yugur and Eastern Yugur
are terms coined by Chinese linguists to distinguish between the Turkic
and Mongolic
Yugur language, both spoken within the Yugur
nationality
. The terms may also indicate the speakers of these languages. Traditionally, both languages are indicated by the term Yellow Uygur, from the endonym of the Yugur.
The Turkic speaking Yugur number about 4,600 and denote their own language by the terms yoğïr lar (Yugur speech) or yoğïr śoz (Yugur word).
s, with several of the Northeastern Turkic languages, but it is not closer to any one of them in particular.
province's Sunan Yugur Autonomous County
.
, corresponding to the so-called pharyngealised
or low vowel
s in Tuva
and Tofa, and short vowels in Yakut and Turkmen
. Examples of this phenomenon include oʰtɯs "thirty", jaʰʂ "good", and iʰt "meat".
The vowel harmonical system
, typical of Turkic languages, has largely collapsed. Voice
as a distinguishing feature
in plosives and affricates was replaced by aspiration
, as in Chinese
.
For centuries, the Western Yugur language has been in contact
with Mongolic languages, Tibetan
, and Chinese, and as a result has adopted a large amount of loanword
s from these languages, as well as grammatical features. Chinese dialects neighboring the areas where Yugur is spoken have influenced the Yugur language, giving it loanwords.
s as well as in verb
s were largely lost. In the verbal system, the notion of evidentiality
has been grammaticalised
, seemingly under the influence of Tibetan.
Eastern Yugur language
Eastern Yugur and Western Yugur are terms coined by Chinese linguists to distinguish between the Mongolic and Turkic Yugur language, both spoken within the Yugur nationality. The terms may also indicate the speakers of these languages. Traditionally, both languages are indicated by the term Yellow...
are terms coined by Chinese linguists to distinguish between the Turkic
Turkic languages
The Turkic languages constitute a language family of at least thirty five languages, spoken by Turkic peoples across a vast area from Eastern Europe and the Mediterranean to Siberia and Western China, and are considered to be part of the proposed Altaic language family.Turkic languages are spoken...
and Mongolic
Mongolic languages
The Mongolic languages are a group of languages spoken in East-Central Asia, mostly in Mongolia and surrounding areas plus in Kalmykia. The best-known member of this language family, Mongolian, is the primary language of most of the residents of Mongolia and the Mongolian residents of Inner...
Yugur language, both spoken within the Yugur
Yugur
The Yugurs ,or Yellow Uyghurs as they are traditionally known,are one of China's 56 officially recognized nationalities, consisting of 13,719 persons according to the 2000 census. The Yugur live primarily in Sunan Yugur Autonomous County in Gānsù Province. They are Buddhists, unlike the Xinjiang...
nationality
Nationality
Nationality is membership of a nation or sovereign state, usually determined by their citizenship, but sometimes by ethnicity or place of residence, or based on their sense of national identity....
. The terms may also indicate the speakers of these languages. Traditionally, both languages are indicated by the term Yellow Uygur, from the endonym of the Yugur.
The Turkic speaking Yugur number about 4,600 and denote their own language by the terms yoğïr lar (Yugur speech) or yoğïr śoz (Yugur word).
Classification
Western Yugur shares a number of features, mainly archaismArchaism
In language, an archaism is the use of a form of speech or writing that is no longer current. This can either be done deliberately or as part of a specific jargon or formula...
s, with several of the Northeastern Turkic languages, but it is not closer to any one of them in particular.
Geographic distribution
Speakers of Western Yugur reside primarily in the western part of GansuGansu
' is a province located in the northwest of the People's Republic of China.It lies between the Tibetan and Huangtu plateaus, and borders Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Ningxia to the north, Xinjiang and Qinghai to the west, Sichuan to the south, and Shaanxi to the east...
province's Sunan Yugur Autonomous County
Sunan Yugur Autonomous County
Sunan Yugur Autonomous County is an autonomous county in Zhangye City, Gansu Province, China. It is home to the majority of the Yugur ethnic group...
.
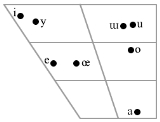
Sounds
A special feature in Western Yugur is the occurrence of preaspirationPreaspiration
In phonetics, preaspiration is a period of voicelessness or aspiration preceding the closure of a voiceless obstruent, basically equivalent to an -like sound preceding the obstruent. In other words, when an obstruent is preaspirated, the glottis is opened for some time before the obstruent closure...
, corresponding to the so-called pharyngealised
Pharyngealisation
-Further reading:*Ian Maddieson, -See also:*Velarization*Creaky voice *Pharyngeal consonant*Epiglottal consonant*Pharynx...
or low vowel
Vowel
In phonetics, a vowel is a sound in spoken language, such as English ah! or oh! , pronounced with an open vocal tract so that there is no build-up of air pressure at any point above the glottis. This contrasts with consonants, such as English sh! , where there is a constriction or closure at some...
s in Tuva
Tuvan language
Tuvan , also known as Tuvinian, Tyvan or Tuvin, is a Turkic language spoken in the Republic of Tuva in south-central Siberia in Russia. The language has borrowed a great number of roots from the Mongolian language and more recently from the Russian language...
and Tofa, and short vowels in Yakut and Turkmen
Turkmen language
Turkmen is the national language of Turkmenistan...
. Examples of this phenomenon include oʰtɯs "thirty", jaʰʂ "good", and iʰt "meat".
The vowel harmonical system
Vowel harmony
Vowel harmony is a type of long-distance assimilatory phonological process involving vowels that occurs in some languages. In languages with vowel harmony, there are constraints on which vowels may be found near each other....
, typical of Turkic languages, has largely collapsed. Voice
Voice (phonetics)
Voice or voicing is a term used in phonetics and phonology to characterize speech sounds, with sounds described as either voiceless or voiced. The term, however, is used to refer to two separate concepts. Voicing can refer to the articulatory process in which the vocal cords vibrate...
as a distinguishing feature
Distinctive feature
In linguistics, a distinctive feature is the most basic unit of phonological structure that may be analyzed in phonological theory.Distinctive features are grouped into categories according to the natural classes of segments they describe: major class features, laryngeal features, manner features,...
in plosives and affricates was replaced by aspiration
Aspiration (phonetics)
In phonetics, aspiration is the strong burst of air that accompanies either the release or, in the case of preaspiration, the closure of some obstruents. To feel or see the difference between aspirated and unaspirated sounds, one can put a hand or a lit candle in front of one's mouth, and say pin ...
, as in Chinese
Chinese language
The Chinese language is a language or language family consisting of varieties which are mutually intelligible to varying degrees. Originally the indigenous languages spoken by the Han Chinese in China, it forms one of the branches of Sino-Tibetan family of languages...
.
Consonants
West Yugur has 28 native consonants and two more (indicated in paretheses) found only in loan words.| Labial Labial consonant Labial consonants are consonants in which one or both lips are the active articulator. This precludes linguolabials, in which the tip of the tongue reaches for the posterior side of the upper lip and which are considered coronals... |
Alveolar Alveolar consonant Alveolar consonants are articulated with the tongue against or close to the superior alveolar ridge, which is called that because it contains the alveoli of the superior teeth... |
Retroflex Retroflex consonant A retroflex consonant is a coronal consonant where the tongue has a flat, concave, or even curled shape, and is articulated between the alveolar ridge and the hard palate. They are sometimes referred to as cerebral consonants, especially in Indology... |
Palatal Palatal consonant Palatal consonants are consonants articulated with the body of the tongue raised against the hard palate... |
Velar Velar consonant Velars are consonants articulated with the back part of the tongue against the soft palate, the back part of the roof of the mouth, known also as the velum).... |
Uvular Uvular consonant Uvulars are consonants articulated with the back of the tongue against or near the uvula, that is, further back in the mouth than velar consonants. Uvulars may be plosives, fricatives, nasal stops, trills, or approximants, though the IPA does not provide a separate symbol for the approximant, and... |
Glottal Glottal consonant Glottal consonants, also called laryngeal consonants, are consonants articulated with the glottis. Many phoneticians consider them, or at least the so-called fricative, to be transitional states of the glottis without a point of articulation as other consonants have; in fact, some do not consider... |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal Nasal consonant A nasal consonant is a type of consonant produced with a lowered velum in the mouth, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. Examples of nasal consonants in English are and , in words such as nose and mouth.- Definition :... |
m | n | ŋ | |||||||||||
| Plosive | pʰ | p | tʰ | t | kʰ | k | qʰ | q | ||||||
| Affricate Affricate consonant Affricates are consonants that begin as stops but release as a fricative rather than directly into the following vowel.- Samples :... |
(tsʰ) | ts | tʂʰ | tʂ | tɕʰ | tɕ | ||||||||
| Fricative Fricative consonant Fricatives are consonants produced by forcing air through a narrow channel made by placing two articulators close together. These may be the lower lip against the upper teeth, in the case of ; the back of the tongue against the soft palate, in the case of German , the final consonant of Bach; or... |
(f) | s | z | ʂ | ʐ | ɕ | x | ɣ | h | |||||
| Rhotic Rhotic consonant In phonetics, rhotic consonants, also called tremulants or "R-like" sounds, are liquid consonants that are traditionally represented orthographically by symbols derived from the Greek letter rho, including "R, r" from the Roman alphabet and "Р, p" from the Cyrillic alphabet... |
r | |||||||||||||
| Approximant Approximant consonant Approximants are speech sounds that involve the articulators approaching each other but not narrowly enough or with enough articulatory precision to create turbulent airflow. Therefore, approximants fall between fricatives, which do produce a turbulent airstream, and vowels, which produce no... |
l | j | w | |||||||||||
Vocabulary
Western Yugur is the only Turkic language that preserved the anticipating counting system, known from Old Turkic.For centuries, the Western Yugur language has been in contact
Language contact
Language contact occurs when two or more languages or varieties interact. The study of language contact is called contact linguistics.Multilingualism has likely been common throughout much of human history, and today most people in the world are multilingual...
with Mongolic languages, Tibetan
Tibetan language
The Tibetan languages are a cluster of mutually-unintelligible Tibeto-Burman languages spoken primarily by Tibetan peoples who live across a wide area of eastern Central Asia bordering the Indian subcontinent, including the Tibetan Plateau and the northern Indian subcontinent in Baltistan, Ladakh,...
, and Chinese, and as a result has adopted a large amount of loanword
Loanword
A loanword is a word borrowed from a donor language and incorporated into a recipient language. By contrast, a calque or loan translation is a related concept where the meaning or idiom is borrowed rather than the lexical item itself. The word loanword is itself a calque of the German Lehnwort,...
s from these languages, as well as grammatical features. Chinese dialects neighboring the areas where Yugur is spoken have influenced the Yugur language, giving it loanwords.
Grammar
Personal markers in nounNoun
In linguistics, a noun is a member of a large, open lexical category whose members can occur as the main word in the subject of a clause, the object of a verb, or the object of a preposition .Lexical categories are defined in terms of how their members combine with other kinds of...
s as well as in verb
Verb
A verb, from the Latin verbum meaning word, is a word that in syntax conveys an action , or a state of being . In the usual description of English, the basic form, with or without the particle to, is the infinitive...
s were largely lost. In the verbal system, the notion of evidentiality
Evidentiality
In linguistics, evidentiality is, broadly, the indication of the nature of evidence for a given statement; that is, whether evidence exists for the statement and/or what kind of evidence exists. An evidential is the particular grammatical element that indicates evidentiality...
has been grammaticalised
Grammaticalisation
In linguistics, grammaticalization is a process by which words representing objects and actions transform through sound change and language migration to become grammatical objects...
, seemingly under the influence of Tibetan.

