
Weakly o-minimal structure
Encyclopedia
In model theory
, a weakly o-minimal structure is a model theoretic structure
whose definable sets in the domain are just finite unions of convex sets.
structure, M, with language L including an ordering relation <, is called weakly o-minimal if every parametrically definable subset of M is a finite union of convex (definable) subsets. A theory is weakly o-minimal if all its models are weakly o-minimal.
Note that, in contrast to o-minimality, it is possible for a theory to have models which are weakly o-minimal and to have other models which are not weakly o-minimal.
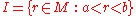
for some (possibly infinite) constants a and b in M. For weakly o-minimal structures (m,<,...) this is relaxed so that the definable sets in m are finite unions of convex sets. A set C is convex if whenever a and b are in C with a < b and c ∈ m satisfies a < c < b, then c is in C.
On the face of it, convex sets are just intervals, in which case weakly o-minimal structures would just be o-minimal structures. And indeed, if we have a weakly o-minimal structure expanding (R,<), the real ordered field, then this structure will be o-minimal. The two notions are different in other settings though. For example, let R be the ordered field of real algebraic number
s with the usual ordering < inherited from R. Take a transcendental number, say π
, and add a unary relation S to the structure given by the subset (−π,π) ∩ R. Now consider the subset A of R defined by the formula
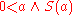
so that the set consists of all strictly positive real algebraic numbers that are less than π. The set is clearly convex, but cannot be written as a finite union of points and intervals whose endpoints are in R. To write it as an interval one would either have to include the endpoint π, which isn't in R, or one would require infinitely many intervals, such as the union
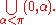
Since we have a definable set that isn't a finite union of points and intervals, this structure is not o-minimal. However, it is known that the structure is weakly o-minimal, and in fact the theory of this structure is weakly o-minimal.
Model theory
In mathematics, model theory is the study of mathematical structures using tools from mathematical logic....
, a weakly o-minimal structure is a model theoretic structure
Structure (mathematical logic)
In universal algebra and in model theory, a structure consists of a set along with a collection of finitary operations and relations which are defined on it....
whose definable sets in the domain are just finite unions of convex sets.
Definition
A linearly orderedTotal order
In set theory, a total order, linear order, simple order, or ordering is a binary relation on some set X. The relation is transitive, antisymmetric, and total...
structure, M, with language L including an ordering relation <, is called weakly o-minimal if every parametrically definable subset of M is a finite union of convex (definable) subsets. A theory is weakly o-minimal if all its models are weakly o-minimal.
Note that, in contrast to o-minimality, it is possible for a theory to have models which are weakly o-minimal and to have other models which are not weakly o-minimal.
Difference from o-minimality
In an o-minimal structure (M,<,...) the definable sets in M are finite unions of points and intervals, an interval here being a set of the form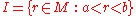
for some (possibly infinite) constants a and b in M. For weakly o-minimal structures (m,<,...) this is relaxed so that the definable sets in m are finite unions of convex sets. A set C is convex if whenever a and b are in C with a < b and c ∈ m satisfies a < c < b, then c is in C.
On the face of it, convex sets are just intervals, in which case weakly o-minimal structures would just be o-minimal structures. And indeed, if we have a weakly o-minimal structure expanding (R,<), the real ordered field, then this structure will be o-minimal. The two notions are different in other settings though. For example, let R be the ordered field of real algebraic number
Algebraic number
In mathematics, an algebraic number is a number that is a root of a non-zero polynomial in one variable with rational coefficients. Numbers such as π that are not algebraic are said to be transcendental; almost all real numbers are transcendental...
s with the usual ordering < inherited from R. Take a transcendental number, say π
Pi
' is a mathematical constant that is the ratio of any circle's circumference to its diameter. is approximately equal to 3.14. Many formulae in mathematics, science, and engineering involve , which makes it one of the most important mathematical constants...
, and add a unary relation S to the structure given by the subset (−π,π) ∩ R. Now consider the subset A of R defined by the formula

so that the set consists of all strictly positive real algebraic numbers that are less than π. The set is clearly convex, but cannot be written as a finite union of points and intervals whose endpoints are in R. To write it as an interval one would either have to include the endpoint π, which isn't in R, or one would require infinitely many intervals, such as the union
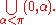
Since we have a definable set that isn't a finite union of points and intervals, this structure is not o-minimal. However, it is known that the structure is weakly o-minimal, and in fact the theory of this structure is weakly o-minimal.

