
Water potential
Encyclopedia
Water potential is the potential energy
of water
per unit volume relative to pure water in reference conditions. Water potential quantifies the tendency of water to move from one area to another due to osmosis
, gravity, mechanical pressure
, or matrix effects such as surface tension
. Water potential has proved especially useful in understanding water movement within plant
s, animal
s, and soil
. Water potential is typically expressed in potential energy per unit volume and very often is represented by the Greek letter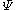 .
.
Water potential integrates a variety of different potential drivers of water movement, which may operate in the same or different directions. Within complex biological systems, it is common for many potential factors to be important. For example, the addition of solutes to water lowers the water's potential (makes it more negative), just as the increase in pressure increases its potential (makes it more positive). If possible, water will move from an area of higher water potential to an area that has a lower water potential. One very common example is water that contains a dissolved salt, like sea water or the solution within living cells. These solutions typically have negative water potentials, relative to the pure water reference. If there is no restriction on flow, water molecules will proceed from the locus of pure water to the more negative water potential of the solution; flow proceeds until the difference in solute potential is balanced by another force, for example, pressure potential.
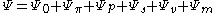
where:
All of these factors are quantified as potential energies per unit volume, and different subsets of these terms may be used for particular applications (e.g., plants or soils). Different conditions are also defined as reference depending on the application: for example, in soils, the reference condition is typically defined as pure water at the soil surface.
Pressure potential is based on mechanical pressure, and is an important component of the total water potential within plant cell
s. Pressure potential increases as water enters a cell. As water passes through the cell wall
and cell membrane
, it increases the total amount of water present inside the cell, which exerts an outward pressure that is retained by the structural rigidity of the cell wall. By creating this pressure, the plant can maintain turgor
, which allows the plant to keep its rigidity. Without turgor, plants lose structure and wilt
.
The pressure potential in a living plant cell is usually positive. In plasmolysed cells
, pressure potential is almost zero. Negative pressure potentials occur when water is pulled through an open system such as a plant xylem
vessel. Withstanding negative pressure potentials (frequently called tension) is an important adaptation of xylem vessels.
Pure water is usually defined as having a osmotic potential ( ) of zero, and in this case, solute potential can never be positive. The relationship of solute concentration (in molarity) to solute potential is given by the van 't Hoff equation:
) of zero, and in this case, solute potential can never be positive. The relationship of solute concentration (in molarity) to solute potential is given by the van 't Hoff equation:
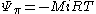
where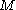 is the concentration in molarity of the solute,
is the concentration in molarity of the solute, 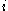 is the van 't Hoff factor
is the van 't Hoff factor
, the ratio of amount of particles in solution to amount of formula units dissolved,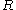 is the ideal gas constant, and
is the ideal gas constant, and  is the absolute
is the absolute
temperature.
For example, when a solute
is dissolved in water, water molecules are less likely to diffuse
away via osmosis
than when there is no solute. A solution will have a lower and hence more negative water potential than that of pure water. Furthermore, the more solute molecules present, the more negative the solute potential is.
Osmotic potential has important implication for many living organisms. If a living cell with a smaller solute concentration is surrounded by a more concentrated solution, the cell will tend to lose water to the more negative water potential ( ) of the surrounding environment. This is often the case for marine
) of the surrounding environment. This is often the case for marine
organisms living in sea water and halophytic plants growing in saline environments. In the case of a plant cell, the flow of water out of the cell may eventually cause the plasma membrane to pull away from the cell wall, leading to plasmolysis
. It can be measured in plant cells using the Pressure bomb
. Most plants, however, have the ability to increase solute inside the cell to drive the flow of water into the cell and maintain turgor.
This effect can be used to power an osmotic power plant.
or sand
particles within soil
), adhesive
intermolecular force
s between the water and the solid
can be large and important. The forces between the water molecules and the solid particles in combination with attraction among water molecules promote surface tension
and the formation of menisci within the solid matrix. Force is then required to break these menisci. The magnitude of matrix potential depends on the distances between solid particles—the width of the menisci (see also capillary action
)--and the chemical composition of the solid matrix. In many cases, matrix potential can be quite large and comparable to the other components of water potential discussed above.
It is worth noting that matrix potentials are very important for plant water relations. Strong (very negative) matrix potentials bind water to soil particles within very dry soils. Plants then create even more negative matrix potentials within tiny pores in the cell walls of their leaves to extract water from the soil and allow physiological activity to continue through dry periods. Germinating seeds
have a very negative matric potential. This causes water uptake in even somewhat dry soils and hydrates the dry seed. In terms of negative water potential, creosote bush
es can tolerate extreme drought stress by operating fully at -50 bars of water potential and have been found living down to -120 bars.
Potential energy
In physics, potential energy is the energy stored in a body or in a system due to its position in a force field or due to its configuration. The SI unit of measure for energy and work is the Joule...
of water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
per unit volume relative to pure water in reference conditions. Water potential quantifies the tendency of water to move from one area to another due to osmosis
Osmosis
Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, aiming to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides...
, gravity, mechanical pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
, or matrix effects such as surface tension
Surface tension
Surface tension is a property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force. It is revealed, for example, in floating of some objects on the surface of water, even though they are denser than water, and in the ability of some insects to run on the water surface...
. Water potential has proved especially useful in understanding water movement within plant
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
s, animal
Animal
Animals are a major group of multicellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. Their body plan eventually becomes fixed as they develop, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on in their life. Most animals are motile, meaning they can move spontaneously and...
s, and soil
Soil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
. Water potential is typically expressed in potential energy per unit volume and very often is represented by the Greek letter
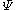 .
.Water potential integrates a variety of different potential drivers of water movement, which may operate in the same or different directions. Within complex biological systems, it is common for many potential factors to be important. For example, the addition of solutes to water lowers the water's potential (makes it more negative), just as the increase in pressure increases its potential (makes it more positive). If possible, water will move from an area of higher water potential to an area that has a lower water potential. One very common example is water that contains a dissolved salt, like sea water or the solution within living cells. These solutions typically have negative water potentials, relative to the pure water reference. If there is no restriction on flow, water molecules will proceed from the locus of pure water to the more negative water potential of the solution; flow proceeds until the difference in solute potential is balanced by another force, for example, pressure potential.
Components of water potential
Many different factors may affect the total water potential, and the sum of these potentials determines the overall water potential and the direction of water flow: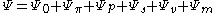
where:
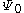 is the reference correction,
is the reference correction,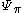 is the soluteSolutionIn chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
is the soluteSolutionIn chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
potential,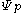 is the pressurePressurePressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
is the pressurePressurePressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
component, is the gravimetric component,
is the gravimetric component,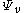 is the potential due to humidityHumidityHumidity is a term for the amount of water vapor in the air, and can refer to any one of several measurements of humidity. Formally, humid air is not "moist air" but a mixture of water vapor and other constituents of air, and humidity is defined in terms of the water content of this mixture,...
is the potential due to humidityHumidityHumidity is a term for the amount of water vapor in the air, and can refer to any one of several measurements of humidity. Formally, humid air is not "moist air" but a mixture of water vapor and other constituents of air, and humidity is defined in terms of the water content of this mixture,...
, and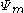 is the potential due to matrix effects (e.g., fluid cohesion and surface tension.)
is the potential due to matrix effects (e.g., fluid cohesion and surface tension.)
All of these factors are quantified as potential energies per unit volume, and different subsets of these terms may be used for particular applications (e.g., plants or soils). Different conditions are also defined as reference depending on the application: for example, in soils, the reference condition is typically defined as pure water at the soil surface.
Pressure Potential
Pressure potential is based on mechanical pressure, and is an important component of the total water potential within plant cell
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
s. Pressure potential increases as water enters a cell. As water passes through the cell wall
Cell wall
The cell wall is the tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to...
and cell membrane
Cell membrane
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell...
, it increases the total amount of water present inside the cell, which exerts an outward pressure that is retained by the structural rigidity of the cell wall. By creating this pressure, the plant can maintain turgor
Turgor pressure
Turgor Pressure or turgidity is the main pressure of the cell contents against the cell wall in plant cells and bacteria cells, determined by the water content of the vacuole, resulting from osmotic pressure, i.e...
, which allows the plant to keep its rigidity. Without turgor, plants lose structure and wilt
Wilting
Wilting refers to the loss of rigidity of non-woody parts of plants. This occurs when the turgor pressure in non-lignified plant cells falls towards zero, as a result of diminished water in the cells...
.
The pressure potential in a living plant cell is usually positive. In plasmolysed cells
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the process in plant cells where the cytoplasm pulls away from the cell wall due to the loss of water through osmosis. The reverse process, cytolysis, can occur if the cell is in a hypotonic solution resulting in a higher external osmotic pressure and a net flow of water into the cell...
, pressure potential is almost zero. Negative pressure potentials occur when water is pulled through an open system such as a plant xylem
Xylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue in vascular plants. . The word xylem is derived from the Classical Greek word ξυλον , meaning "wood"; the best-known xylem tissue is wood, though it is found throughout the plant...
vessel. Withstanding negative pressure potentials (frequently called tension) is an important adaptation of xylem vessels.
Osmotic potential
Pure water is usually defined as having a osmotic potential (
 ) of zero, and in this case, solute potential can never be positive. The relationship of solute concentration (in molarity) to solute potential is given by the van 't Hoff equation:
) of zero, and in this case, solute potential can never be positive. The relationship of solute concentration (in molarity) to solute potential is given by the van 't Hoff equation: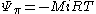
where
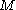 is the concentration in molarity of the solute,
is the concentration in molarity of the solute, 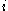 is the van 't Hoff factor
is the van 't Hoff factorVan 't Hoff factor
The van 't Hoff factor i is a measure of the effect of a solute upon colligative properties, such as vapor pressure, osmotic pressure and freezing point depression. The van 't Hoff factor is the ratio between the actual concentration of particles produced when the substance is dissolved, and the...
, the ratio of amount of particles in solution to amount of formula units dissolved,
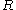 is the ideal gas constant, and
is the ideal gas constant, and  is the absolute
is the absolutetemperature.
For example, when a solute
Solution
In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
is dissolved in water, water molecules are less likely to diffuse
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
away via osmosis
Osmosis
Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, aiming to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides...
than when there is no solute. A solution will have a lower and hence more negative water potential than that of pure water. Furthermore, the more solute molecules present, the more negative the solute potential is.
Osmotic potential has important implication for many living organisms. If a living cell with a smaller solute concentration is surrounded by a more concentrated solution, the cell will tend to lose water to the more negative water potential (
 ) of the surrounding environment. This is often the case for marine
) of the surrounding environment. This is often the case for marineMarine (ocean)
Marine is an umbrella term. As an adjective it is usually applicable to things relating to the sea or ocean, such as marine biology, marine ecology and marine geology...
organisms living in sea water and halophytic plants growing in saline environments. In the case of a plant cell, the flow of water out of the cell may eventually cause the plasma membrane to pull away from the cell wall, leading to plasmolysis
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the process in plant cells where the cytoplasm pulls away from the cell wall due to the loss of water through osmosis. The reverse process, cytolysis, can occur if the cell is in a hypotonic solution resulting in a higher external osmotic pressure and a net flow of water into the cell...
. It can be measured in plant cells using the Pressure bomb
Pressure bomb
A pressure bomb or pressure chamber or Scholander bomb is an instrument with which it is possible to measure the approximate water potential of plant tissues. A leaf attached to a stem is placed inside a sealed chamber and pressurised gas is added to the chamber slowly...
. Most plants, however, have the ability to increase solute inside the cell to drive the flow of water into the cell and maintain turgor.
This effect can be used to power an osmotic power plant.
Matrix potential (Matric potential)
When water is in contact with solid particles (e.g., clayClay
Clay is a general term including many combinations of one or more clay minerals with traces of metal oxides and organic matter. Geologic clay deposits are mostly composed of phyllosilicate minerals containing variable amounts of water trapped in the mineral structure.- Formation :Clay minerals...
or sand
Sand
Sand is a naturally occurring granular material composed of finely divided rock and mineral particles.The composition of sand is highly variable, depending on the local rock sources and conditions, but the most common constituent of sand in inland continental settings and non-tropical coastal...
particles within soil
Soil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
), adhesive
Adhesion
Adhesion is any attraction process between dissimilar molecular species that can potentially bring them in close contact. By contrast, cohesion takes place between similar molecules....
intermolecular force
Intermolecular force
Intermolecular forces are forces of attraction or repulsion which act between neighboring particles: atoms, molecules or ions. They are weak compared to the intramolecular forces, the forces which keep a molecule together...
s between the water and the solid
Solid
Solid is one of the three classical states of matter . It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire volume available to it like a...
can be large and important. The forces between the water molecules and the solid particles in combination with attraction among water molecules promote surface tension
Surface tension
Surface tension is a property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force. It is revealed, for example, in floating of some objects on the surface of water, even though they are denser than water, and in the ability of some insects to run on the water surface...
and the formation of menisci within the solid matrix. Force is then required to break these menisci. The magnitude of matrix potential depends on the distances between solid particles—the width of the menisci (see also capillary action
Capillary action
Capillary action, or capilarity, is the ability of a liquid to flow against gravity where liquid spontanously rise in a narrow space such as between the hair of a paint-brush, in a thin tube, or in porous material such as paper or in some non-porous material such as liquified carbon fiber, or in a...
)--and the chemical composition of the solid matrix. In many cases, matrix potential can be quite large and comparable to the other components of water potential discussed above.
It is worth noting that matrix potentials are very important for plant water relations. Strong (very negative) matrix potentials bind water to soil particles within very dry soils. Plants then create even more negative matrix potentials within tiny pores in the cell walls of their leaves to extract water from the soil and allow physiological activity to continue through dry periods. Germinating seeds
Germination
Germination is the process in which a plant or fungus emerges from a seed or spore, respectively, and begins growth. The most common example of germination is the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm. However the growth of a sporeling from a spore, for example the...
have a very negative matric potential. This causes water uptake in even somewhat dry soils and hydrates the dry seed. In terms of negative water potential, creosote bush
Creosote bush
Larrea tridentata is known as Creosote bush as a plant, chaparral as a medicinal herb, and as "gobernadora" in Mexico, Spanish for "governess," due to its ability for inhibiting the growth of nearby plants to have more water. In Sonora, it is more commonly called "hediondilla." It is a flowering...
es can tolerate extreme drought stress by operating fully at -50 bars of water potential and have been found living down to -120 bars.
External links
- http://lawr.ucdavis.edu/classes/ssc107/SSC107Syllabus/chapter2-00.pdf

