Vitelliform macular dystrophy
Encyclopedia
Vitelliform macular dystrophy or vitelliform dystrophy is a genetic eye
disorder that can cause progressive vision loss
. This disorder affects the retina
, specifically cells in a small area near the center of the retina called the macula
. The macula is responsible for sharp central vision, which is needed for detailed tasks such as reading, driving, and recognizing faces.
) to build up in cells underlying the macula. Over time, the abnormal accumulation of this substance can damage cells that are critical for clear central vision. As a result, people with this disorder often lose their central vision and may experience blurry or distorted vision. Vitelliform macular dystrophy does not affect side (peripheral
) vision or the ability to see at night.
Researchers have described two forms of vitelliform macular dystrophy with similar features. The early-onset form (known as Best disease) usually appears in childhood; however, the onset of symptoms and the severity of vision loss vary widely. The adult-onset form begins later, usually in middle age, and tends to cause relatively mild vision loss. The two forms of vitelliform macular dystrophy each have characteristic changes in the macula that can be detected during an eye examination
.
and VMD2 genes cause vitelliform macular dystrophy. Mutations in the VMD2 gene are responsible for Best disease. Changes in either the VMD2 or RDS gene can cause the adult-onset form of vitelliform macular dystrophy; however, fewer than a quarter of cases result from mutations in these two genes. In most cases, the cause of the adult-onset form is unknown.
The VMD2 gene provides instructions for making a protein called bestrophin. Although its exact function is uncertain, this protein likely acts as a channel that controls the movement of negatively charged chlorine
atoms (chloride ions) into or out of cells in the retina. Mutations in the VMD2 gene probably lead to the production of an abnormally shaped channel that cannot regulate the flow of chloride. Researchers have not determined how these malfunctioning channels are related to the buildup of lipofuscin in the macula and progressive vision loss.
The RDS gene provides instructions for making a protein called peripherin. This protein is essential for the normal function of light-sensing (photoreceptor) cells in the retina. Mutations in the RDS gene disrupt the structures in these cells that contain light-sensing pigments, leading to vision loss. It is unclear why RDS mutations affect only central vision in people with adult-onset vitelliform macular dystrophy.
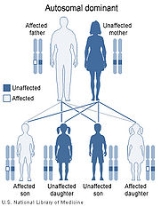
 Best disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, which means one copy of the altered gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the disorder. In most cases, an affected person has one parent with the condition.
Best disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, which means one copy of the altered gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the disorder. In most cases, an affected person has one parent with the condition.
The inheritance pattern of adult-onset vitelliform macular dystrophy is uncertain. Some studies have suggested that it may be inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. Many affected people, however, have no history of the disorder in their family and only a small number of affected families have been reported.
Human eye
The human eye is an organ which reacts to light for several purposes. As a conscious sense organ, the eye allows vision. Rod and cone cells in the retina allow conscious light perception and vision including color differentiation and the perception of depth...
disorder that can cause progressive vision loss
Vision loss
Vision loss or visual loss is the absence of vision where it existed before, which can happen either acutely or chronically .-Ranges of vision loss:...
. This disorder affects the retina
Retina
The vertebrate retina is a light-sensitive tissue lining the inner surface of the eye. The optics of the eye create an image of the visual world on the retina, which serves much the same function as the film in a camera. Light striking the retina initiates a cascade of chemical and electrical...
, specifically cells in a small area near the center of the retina called the macula
Macula
The macula or macula lutea is an oval-shaped highly pigmented yellow spot near the center of the retina of the human eye. It has a diameter of around 5 mm and is often histologically defined as having two or more layers of ganglion cells...
. The macula is responsible for sharp central vision, which is needed for detailed tasks such as reading, driving, and recognizing faces.
Diagnosis
Vitelliform macular dystrophy causes a fatty yellow pigment (lipofuscinLipofuscin
Lipofuscin is the name given to finely granular yellow-brown pigment granules composed of lipid-containing residues of lysosomal digestion. It is considered one of the aging or "wear-and-tear" pigments, found in the liver, kidney, heart muscle, adrenals, nerve cells, and ganglion cells...
) to build up in cells underlying the macula. Over time, the abnormal accumulation of this substance can damage cells that are critical for clear central vision. As a result, people with this disorder often lose their central vision and may experience blurry or distorted vision. Vitelliform macular dystrophy does not affect side (peripheral
Peripheral vision
Peripheral vision is a part of vision that occurs outside the very center of gaze. There is a broad set of non-central points in the field of view that is included in the notion of peripheral vision...
) vision or the ability to see at night.
Researchers have described two forms of vitelliform macular dystrophy with similar features. The early-onset form (known as Best disease) usually appears in childhood; however, the onset of symptoms and the severity of vision loss vary widely. The adult-onset form begins later, usually in middle age, and tends to cause relatively mild vision loss. The two forms of vitelliform macular dystrophy each have characteristic changes in the macula that can be detected during an eye examination
Eye examination
An eye examination is a battery of tests performed by an ophthalmologist, optometrist, or orthoptist assessing vision and ability to focus on and discern objects, as well as other tests and examinations pertaining to the eyes....
.
Pathophysiology
Mutations in the RDSPeripherin 2
Peripherin-2 is a protein, that in humans is encoded by the PRPH2 gene. Peripherin-2 is found in the rod and cone cells of the retina of the eye...
and VMD2 genes cause vitelliform macular dystrophy. Mutations in the VMD2 gene are responsible for Best disease. Changes in either the VMD2 or RDS gene can cause the adult-onset form of vitelliform macular dystrophy; however, fewer than a quarter of cases result from mutations in these two genes. In most cases, the cause of the adult-onset form is unknown.
The VMD2 gene provides instructions for making a protein called bestrophin. Although its exact function is uncertain, this protein likely acts as a channel that controls the movement of negatively charged chlorine
Chlorine
Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine...
atoms (chloride ions) into or out of cells in the retina. Mutations in the VMD2 gene probably lead to the production of an abnormally shaped channel that cannot regulate the flow of chloride. Researchers have not determined how these malfunctioning channels are related to the buildup of lipofuscin in the macula and progressive vision loss.
The RDS gene provides instructions for making a protein called peripherin. This protein is essential for the normal function of light-sensing (photoreceptor) cells in the retina. Mutations in the RDS gene disrupt the structures in these cells that contain light-sensing pigments, leading to vision loss. It is unclear why RDS mutations affect only central vision in people with adult-onset vitelliform macular dystrophy.
Inheritance

The inheritance pattern of adult-onset vitelliform macular dystrophy is uncertain. Some studies have suggested that it may be inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. Many affected people, however, have no history of the disorder in their family and only a small number of affected families have been reported.
External links
- VIDEO - Why Test for Best? Dr. Eric Brinton of the University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Medicine and Public Health.
- www.bestdisease.net
- Best's disease - eMedicine.com
- GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Best Vitelliform Macular Dystrophy

