
Virtual temperature
Encyclopedia
In atmospheric thermodynamics
, the virtual temperature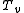 of a moist air parcel
of a moist air parcel
is the temperature
at which a theoretical dry air parcel would have a total pressure
and density
equal to the moist parcel of air.
, and thus approximately ideally
. The gas constant for the standardized mass of one kilogram of a particular gas is dynamic, and described mathematically as:
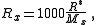
where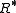 is the universal gas constant and
is the universal gas constant and  is the apparent molecular weight of gas
is the apparent molecular weight of gas  . The apparent molecular weight of a theoretical moist parcel in Earth's atmosphere
. The apparent molecular weight of a theoretical moist parcel in Earth's atmosphere
can be defined in components of dry and moist air as:
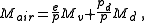
with water vapor pressure,
water vapor pressure, 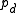 dry air pressure, and
dry air pressure, and 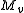 and
and 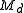 representing the molecular weight of water and dry air respectively. The total pressure
representing the molecular weight of water and dry air respectively. The total pressure 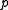 is described by Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures
is described by Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures
:
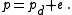
for moist air. Temperature has an inverse proportionality to density. Thus, analytically, a higher vapor pressure would yield a lower density, which should yield a higher virtual temperature in turn.
 and
and 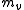 of water vapor in a given volume
of water vapor in a given volume 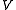 . The density is given by:
. The density is given by:

where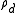 and
and 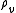 are the densities of dry air and water vapor would respectively have when occupying the volume of the air parcel. Rearranging the standard ideal gas equation with these variables gives:
are the densities of dry air and water vapor would respectively have when occupying the volume of the air parcel. Rearranging the standard ideal gas equation with these variables gives:
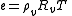 and
and 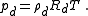
Solving for the densities in each equation and combining with the law of partial pressures yields:
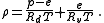
Then, solving for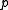 and using
and using 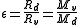 is approximately 0.622 in Earth's atmosphere:
is approximately 0.622 in Earth's atmosphere:
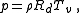
where the virtual temperature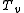 is:
is:

We now have a non-linear scalar
for temperature dependent purely on the unitless value allowing for varying amounts of water vapor in an air parcel. This virtual temperature
allowing for varying amounts of water vapor in an air parcel. This virtual temperature  in units of Kelvin
in units of Kelvin
can be used seamlessly in any thermodynamic equation necessitating it.
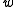 . Through expansion upon the definition of vapor pressure in the law of partial pressures as presented above and the definition of mixing ratio:
. Through expansion upon the definition of vapor pressure in the law of partial pressures as presented above and the definition of mixing ratio:

which allows:
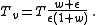
Algebraic expansion of that equation, ignoring higher orders of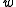 due to its typical order in Earth's atmosphere of
due to its typical order in Earth's atmosphere of  , and substituting
, and substituting  with its constant value yields the linear approximation:
with its constant value yields the linear approximation:
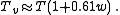
An approximate conversion using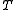 in degrees Celsius
in degrees Celsius
and mixing ratio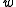 in g/kg is:
in g/kg is:

soundings for assessing available convective potential energy from Skew-T log-P diagram
s. The errors associated with ignoring virtual temperature correction for smaller CAPE values can be quite significant. Thus, in the early stages of convective storm formation, a virtual temperature correction is significant in identifying the potential intensity in tropical cyclogenesis
.
Atmospheric thermodynamics
Atmospheric thermodynamics is the study of heat to work transformations in the earth’s atmospheric system in relation to weather or climate...
, the virtual temperature
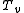 of a moist air parcel
of a moist air parcelAir parcel
In fluid dynamics, within the framework of continuum mechanics, a fluid parcel is a very small amount of fluid, identifiable throughout its dynamic history while moving with the fluid flow. As it moves, the mass of a fluid parcel remains constant, while—in a compressible flow—its volume may...
is the temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
at which a theoretical dry air parcel would have a total pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
and density
Density
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
equal to the moist parcel of air.
Description
In atmospheric thermodynamic processes, it is often useful to assume air parcels behave approximately adiabaticAdiabatic process
In thermodynamics, an adiabatic process or an isocaloric process is a thermodynamic process in which the net heat transfer to or from the working fluid is zero. Such a process can occur if the container of the system has thermally-insulated walls or the process happens in an extremely short time,...
, and thus approximately ideally
Ideal gas law
The ideal gas law is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation to the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stated by Émile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of Boyle's law and Charles's law...
. The gas constant for the standardized mass of one kilogram of a particular gas is dynamic, and described mathematically as:
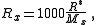
where
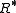 is the universal gas constant and
is the universal gas constant and  is the apparent molecular weight of gas
is the apparent molecular weight of gas  . The apparent molecular weight of a theoretical moist parcel in Earth's atmosphere
. The apparent molecular weight of a theoretical moist parcel in Earth's atmosphereEarth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention , and reducing temperature extremes between day and night...
can be defined in components of dry and moist air as:
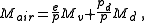
with
 water vapor pressure,
water vapor pressure, 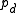 dry air pressure, and
dry air pressure, and 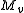 and
and 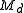 representing the molecular weight of water and dry air respectively. The total pressure
representing the molecular weight of water and dry air respectively. The total pressure 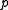 is described by Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures
is described by Dalton's Law of Partial PressuresDalton's law
In chemistry and physics, Dalton's law states that the total pressure exerted by a gaseous mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of each individual component in a gas mixture...
:
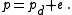
Purpose
Rather than carry out these calculations, it is convenient to scale another quantity within the ideal gas law to equate the pressure and density of a dry parcel to a moist parcel. The only variable quantity of the ideal gas law independent of density and pressure is temperature. This scaled quantity is known as virtual temperature, and it allows for the use of the dry-air equation of stateEquation of state
In physics and thermodynamics, an equation of state is a relation between state variables. More specifically, an equation of state is a thermodynamic equation describing the state of matter under a given set of physical conditions...
for moist air. Temperature has an inverse proportionality to density. Thus, analytically, a higher vapor pressure would yield a lower density, which should yield a higher virtual temperature in turn.
Derivation
Consider an air parcel containing masses and
and 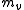 of water vapor in a given volume
of water vapor in a given volume 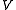 . The density is given by:
. The density is given by:
where
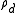 and
and 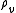 are the densities of dry air and water vapor would respectively have when occupying the volume of the air parcel. Rearranging the standard ideal gas equation with these variables gives:
are the densities of dry air and water vapor would respectively have when occupying the volume of the air parcel. Rearranging the standard ideal gas equation with these variables gives: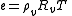 and
and 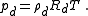
Solving for the densities in each equation and combining with the law of partial pressures yields:
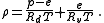
Then, solving for
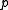 and using
and using 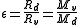 is approximately 0.622 in Earth's atmosphere:
is approximately 0.622 in Earth's atmosphere: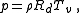
where the virtual temperature
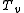 is:
is:
We now have a non-linear scalar
Scalar (mathematics)
In linear algebra, real numbers are called scalars and relate to vectors in a vector space through the operation of scalar multiplication, in which a vector can be multiplied by a number to produce another vector....
for temperature dependent purely on the unitless value
 allowing for varying amounts of water vapor in an air parcel. This virtual temperature
allowing for varying amounts of water vapor in an air parcel. This virtual temperature  in units of Kelvin
in units of KelvinKelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
can be used seamlessly in any thermodynamic equation necessitating it.
Variations
Often the more easily accessible atmospheric parameter is the mixing ratio . Through expansion upon the definition of vapor pressure in the law of partial pressures as presented above and the definition of mixing ratio:
. Through expansion upon the definition of vapor pressure in the law of partial pressures as presented above and the definition of mixing ratio:
which allows:
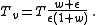
Algebraic expansion of that equation, ignoring higher orders of
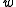 due to its typical order in Earth's atmosphere of
due to its typical order in Earth's atmosphere of  , and substituting
, and substituting  with its constant value yields the linear approximation:
with its constant value yields the linear approximation: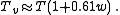
An approximate conversion using
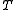 in degrees Celsius
in degrees CelsiusCelsius
Celsius is a scale and unit of measurement for temperature. It is named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius , who developed a similar temperature scale two years before his death...
and mixing ratio
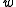 in g/kg is:
in g/kg is:
Uses
Virtual temperature is used in adjusting CAPEConvective available potential energy
In meteorology, convective available potential energy , sometimes, simply, available potential energy , is the amount of energy a parcel of air would have if lifted a certain distance vertically through the atmosphere...
soundings for assessing available convective potential energy from Skew-T log-P diagram
Skew-T log-P diagram
A Skew-T Log-P diagram is one of four thermodynamic diagrams commonly used in weather analysis and forecasting. In 1947, N. Herlofson proposed a modification to the emagram which allows straight, horizontal isobars, and provides for a large angle between isotherms and dry adiabats, similar to that...
s. The errors associated with ignoring virtual temperature correction for smaller CAPE values can be quite significant. Thus, in the early stages of convective storm formation, a virtual temperature correction is significant in identifying the potential intensity in tropical cyclogenesis
Tropical cyclogenesis
Tropical cyclogenesis is the term that describes the development and strengthening of a tropical cyclone in the atmosphere. The mechanisms through which tropical cyclogenesis occurs are distinctly different from those through which mid-latitude cyclogenesis occurs...
.

