
Vircator
Encyclopedia
A vircator is a microwave
generator that is capable of generating brief pulses of tunable, narrow band microwaves at very high power levels.
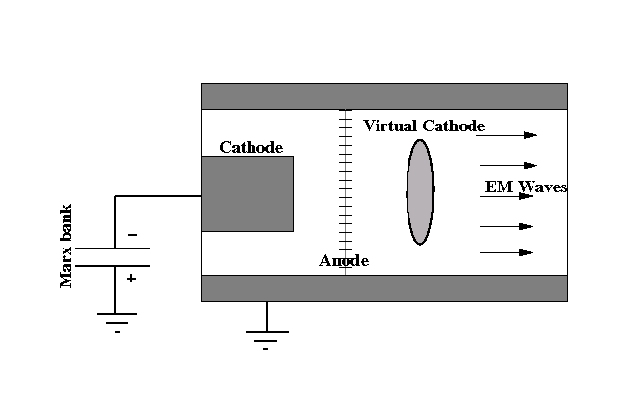
A typical vircator is built inside an evacuated
resonant cavity or waveguide
. An electrode at one end injects an intense electron beam, such as from a Marx generator
or a flux compression generator. The electrons are attracted to a thin anode
, such as an aluminized PET film
, that is connected to the grounded waveguide body. The unit is surrounded by a magnet
. Due to the intensity of the electron beam, many electrons pass through the anode into the region beyond it, forming a virtual cathode
. The electron beam must be so intense as to exceed the space charge limiting current
in that region, causing oscillations that generate microwaves. The frequency, efficiency and other characteristics of the emitted beam depend on the precise physical configuration and operating parameters.
Vircators have been used as electromagnetic pulse
generators and for generating X-ray
s. Power levels on the order of 1010 to 1012 watts are possible.
Microwave
Microwaves, a subset of radio waves, have wavelengths ranging from as long as one meter to as short as one millimeter, or equivalently, with frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. This broad definition includes both UHF and EHF , and various sources use different boundaries...
generator that is capable of generating brief pulses of tunable, narrow band microwaves at very high power levels.

A typical vircator is built inside an evacuated
Vacuum
In everyday usage, vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter, such that its gaseous pressure is much less than atmospheric pressure. The word comes from the Latin term for "empty". A perfect vacuum would be one with no particles in it at all, which is impossible to achieve in...
resonant cavity or waveguide
Waveguide
A waveguide is a structure which guides waves, such as electromagnetic waves or sound waves. There are different types of waveguides for each type of wave...
. An electrode at one end injects an intense electron beam, such as from a Marx generator
Marx generator
A Marx generator is an electrical circuit first described by Erwin Otto Marx in 1924. Its purpose is to generate a high-voltage pulse. Marx generators are often used to simulate the effects of lightning on power line gear and aviation equipment....
or a flux compression generator. The electrons are attracted to a thin anode
Anode
An anode is an electrode through which electric current flows into a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: ACID ....
, such as an aluminized PET film
PET film (biaxially oriented)
BoPET is a polyester film made from stretched polyethylene terephthalate and is used for its high tensile strength, chemical and dimensional stability, transparency, reflectivity, gas and aroma barrier properties and electrical insulation.A variety of companies manufacture boPET and other...
, that is connected to the grounded waveguide body. The unit is surrounded by a magnet
Magnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets.A permanent magnet is an object...
. Due to the intensity of the electron beam, many electrons pass through the anode into the region beyond it, forming a virtual cathode
Cathode
A cathode is an electrode through which electric current flows out of a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: CCD .Cathode polarity is not always negative...
. The electron beam must be so intense as to exceed the space charge limiting current
Space charge
Space charge is a concept in which excess electric charge is treated as a continuum of charge distributed over a region of space rather than distinct point-like charges...
in that region, causing oscillations that generate microwaves. The frequency, efficiency and other characteristics of the emitted beam depend on the precise physical configuration and operating parameters.
Vircators have been used as electromagnetic pulse
Electromagnetic pulse
An electromagnetic pulse is a burst of electromagnetic radiation. The abrupt pulse of electromagnetic radiation usually results from certain types of high energy explosions, especially a nuclear explosion, or from a suddenly fluctuating magnetic field...
generators and for generating X-ray
X-ray
X-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
s. Power levels on the order of 1010 to 1012 watts are possible.
Sources
, High power microwave generator using relativistic electron beam in waveguide drift tube, to Donald J. Sullivan, 1982, "Virtual cathode microwave generator having annular anode slit," Thomas J. T. Kwan, 1988- Donald J. Sullivan, "High Power Microwave Generation From a Virtual Cathode scillator (Vircator)," IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., vol. NS-30, No. 4, 3426-3428 (Aug. 1983) http://epaper.kek.jp/p83/PDF/PAC1983_3426.PDF
- Thomas J. T. Kwan, "High-Power Coherent Microwave Generation from Oscillating Virtual Cathodes," Phys. Fluids 27 (1), 228-232 (Jan. 1984)

