
Vertically integrated liquid
Encyclopedia
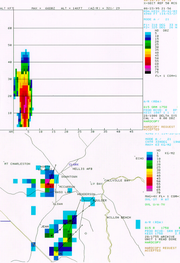
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation...
in the clouds. The measurement is obtained by observing the reflectivity
Reflectivity
In optics and photometry, reflectivity is the fraction of incident radiation reflected by a surface. In general it must be treated as a directional property that is a function of the reflected direction, the incident direction, and the incident wavelength...
of the air which is obtained with weather radar
Weather radar
Weather radar, also called weather surveillance radar and Doppler weather radar, is a type of radar used to locate precipitation, calculate its motion, estimate its type . Modern weather radars are mostly pulse-Doppler radars, capable of detecting the motion of rain droplets in addition to the...
. This measurement is usually used in determining the size of prospective hail
Hail
Hail is a form of solid precipitation. It consists of balls or irregular lumps of ice, each of which is referred to as a hail stone. Hail stones on Earth consist mostly of water ice and measure between and in diameter, with the larger stones coming from severe thunderstorms...
, the potential amount of rain under a thunderstorm and the potential downdraft strength when combined with the height of the echo tops.
When VIL values are high for longer periods of time, the storm may be a supercell.
Multicells usually have alternating VIL values. Multicells can have high VIL values on one radar picture, yet much smaller values in the next radar picture.
When VIL values quickly fall, it may mean that a downburst is imminent. This is the result of the updraft within the cell weakening, thereby losing its ability to hold the copious amounts of moisture (including hail) within the storm's structure. Downbursts of this type are referred to as 'wet microbursts', by the National Weather Service for two reasons; they contain heavy rainfall, hail (usually), as well as damaging winds of greater than 58mph (50knots). Microbursts are classified as being 'a swath of damaging winds not exceeding 2.5 miles in diameter'. Wet microbursts have been mistaken for a tornado by the general public on multiple occasions, as the damage can be quick and hard hitting.

