
Value (mathematics)
Encyclopedia
In mathematics, value commonly refers to the 'output' of a function
. In the most basic case, that of unary
, single-valued functions, there is one input (the argument
) and one output (the value of the function).
The function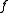 of the example is real-valued, since each and every possible function value is real. On the other hand, it is not injective, since different inputs may yield the same value; e.g.,
of the example is real-valued, since each and every possible function value is real. On the other hand, it is not injective, since different inputs may yield the same value; e.g., 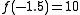 , too.
, too.
In some contexts, for convenience, functions may be considered to have several arguments
and/or several values
; also cf. the discussion in the article function. However, strictly seen, this is not an extension, since such functions may be considered as having single families and/or sets as input or output.
Value is also used in other senses, e.g., to specify a certain instance of a variable
.
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function associates one quantity, the argument of the function, also known as the input, with another quantity, the value of the function, also known as the output. A function assigns exactly one output to each input. The argument and the value may be real numbers, but they can...
. In the most basic case, that of unary
Unary function
A unary function is a function that takes one argument. In computer science, a unary operator is a subset of unary function.Many of the elementary functions are unary functions, in particular the trigonometric functions and hyperbolic function are unary....
, single-valued functions, there is one input (the argument
Argument of a function
In mathematics, an argument of a function is a specific input in the function, also known as an independent variable. When it is clear from the context which argument is meant, the argument is often denoted by arg....
) and one output (the value of the function).
- Example: If the function
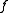 is defined by prescribing that
is defined by prescribing that 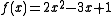 for each real number
for each real number  , then the input 3 will yield the function value 10 (since indeed ).
, then the input 3 will yield the function value 10 (since indeed ).
The function
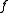 of the example is real-valued, since each and every possible function value is real. On the other hand, it is not injective, since different inputs may yield the same value; e.g.,
of the example is real-valued, since each and every possible function value is real. On the other hand, it is not injective, since different inputs may yield the same value; e.g., 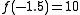 , too.
, too.In some contexts, for convenience, functions may be considered to have several arguments
Arity
In logic, mathematics, and computer science, the arity of a function or operation is the number of arguments or operands that the function takes. The arity of a relation is the dimension of the domain in the corresponding Cartesian product...
and/or several values
Multivalued function
In mathematics, a multivalued function is a left-total relation; i.e. every input is associated with one or more outputs...
; also cf. the discussion in the article function. However, strictly seen, this is not an extension, since such functions may be considered as having single families and/or sets as input or output.
Value is also used in other senses, e.g., to specify a certain instance of a variable
Variable (mathematics)
In mathematics, a variable is a value that may change within the scope of a given problem or set of operations. In contrast, a constant is a value that remains unchanged, though often unknown or undetermined. The concepts of constants and variables are fundamental to many areas of mathematics and...
.
- Example:
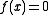 for two separate values of
for two separate values of  , namely, for
, namely, for 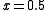 and for
and for 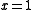 .
.
See also
- Absolute valueAbsolute valueIn mathematics, the absolute value |a| of a real number a is the numerical value of a without regard to its sign. So, for example, the absolute value of 3 is 3, and the absolute value of -3 is also 3...
- Valuation (mathematics)Valuation (mathematics)In algebra , a valuation is a function on a field that provides a measure of size or multiplicity of elements of the field...
- Value distribution theory of holomorphic functionsValue distribution theory of holomorphic functionsIn mathematics, the value distribution theory of holomorphic functions is a division of mathematical analysis. It tries to get quantitative measures of the number of times a function f assumes a value a, as z grows in size, refining the Picard theorem on behaviour close to an essential singularity...

