
Vacuum evaporation
Encyclopedia
Vacuum evaporation is the process of causing the pressure
in a liquid-filled container to be reduced below the vapor pressure
of the liquid, causing the liquid to evaporate at a lower temperature than normal. Although the process can be applied to any type of liquid at any vapor pressure, it is generally used to describe the boiling of water
by lowering the container's internal pressure below standard atmospheric pressure
and causing the water to boil at room temperature
.
When the process is applied to food
and the water is evaporated and removed, the food can be stored for long periods of time without spoiling. It is also used when boiling a substance at normal temperatures would chemically change the consistency of the product, such as egg whites coagulating when attempting to dehydrate the albumen into a powder.
This process was invented by Henri Nestlé
in 1866, of Nestlé
Chocolate fame, although the Shakers
were already using a vacuum pan earlier than that (see condensed milk
).
This process is used industrially to make such food products as evaporated milk
for milk chocolate, and tomato paste
for ketchup
.
In the sugar industry the vacuum evaporation is used in the crystallization
of sucrose
solutions. Traditionally, this process was performed in batch mode, but nowadays also continuous vacuum pans are available
Vacuum evaporation is also a form of physical vapor deposition
used in the semiconductor
, microelectronics
, and optic
al industries and in this context is a process of depositing thin films of material onto surfaces. Such a technique consists of pumping a vacuum chamber
to pressures of less than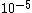 torr
torr
and heating a material to produce a flux
of vapor
in order to deposit the material onto a surface. The material to be vaporized is typically heated until its vapor pressure
is high enough to produce a flux of several Angstroms per second by using an electrically resistive heater or bombardment by a high voltage
beam.
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
in a liquid-filled container to be reduced below the vapor pressure
Vapor pressure
Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure of a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases in a closed system. All liquids have a tendency to evaporate, and some solids can sublimate into a gaseous form...
of the liquid, causing the liquid to evaporate at a lower temperature than normal. Although the process can be applied to any type of liquid at any vapor pressure, it is generally used to describe the boiling of water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
by lowering the container's internal pressure below standard atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure is the force per unit area exerted into a surface by the weight of air above that surface in the atmosphere of Earth . In most circumstances atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point...
and causing the water to boil at room temperature
Room temperature
-Comfort levels:The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers has listings for suggested temperatures and air flow rates in different types of buildings and different environmental circumstances. For example, a single office in a building has an occupancy ratio per...
.
When the process is applied to food
Food
Food is any substance consumed to provide nutritional support for the body. It is usually of plant or animal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals...
and the water is evaporated and removed, the food can be stored for long periods of time without spoiling. It is also used when boiling a substance at normal temperatures would chemically change the consistency of the product, such as egg whites coagulating when attempting to dehydrate the albumen into a powder.
This process was invented by Henri Nestlé
Henri Nestlé
Henri Nestlé, born Heinrich Nestle , was a German confectioner and founder of Nestlé, the world's largest food and beverage company, as well as one of the main creators of condensed milk.-Birth:...
in 1866, of Nestlé
Nestlé
Nestlé S.A. is the world's largest food and nutrition company. Founded and headquartered in Vevey, Switzerland, Nestlé originated in a 1905 merger of the Anglo-Swiss Milk Company, established in 1867 by brothers George Page and Charles Page, and Farine Lactée Henri Nestlé, founded in 1866 by Henri...
Chocolate fame, although the Shakers
Shakers
The United Society of Believers in Christ’s Second Appearing, known as the Shakers, is a religious sect originally thought to be a development of the Religious Society of Friends...
were already using a vacuum pan earlier than that (see condensed milk
Condensed milk
Condensed milk, also known as sweetened condensed milk, is cow's milk from which water has been removed and to which sugar has been added, yielding a very thick, sweet product which when canned can last for years without refrigeration if unopened. The two terms, condensed milk and sweetened...
).
This process is used industrially to make such food products as evaporated milk
Evaporated milk
Evaporated milk, also known as dehydrated milk, is a shelf-stable canned milk product with about 60% of the water removed from fresh milk. It differs from sweetened condensed milk, which contains added sugar. Sweetened condensed milk requires less processing since the added sugar inhibits ...
for milk chocolate, and tomato paste
Tomato paste
Tomato paste is a thick paste that is made by cooking tomatoes for several hours to reduce moisture, straining them to remove the seeds and skin, and cooking them again to reduce them to a thick, rich concentrate...
for ketchup
Ketchup
Ketchup is a sweet-and-tangy condiment typically made from tomatoes, vinegar, sugar or high-fructose corn syrup and an assortment of...
.
In the sugar industry the vacuum evaporation is used in the crystallization
Crystallization
Crystallization is the process of formation of solid crystals precipitating from a solution, melt or more rarely deposited directly from a gas. Crystallization is also a chemical solid–liquid separation technique, in which mass transfer of a solute from the liquid solution to a pure solid...
of sucrose
Sucrose
Sucrose is the organic compound commonly known as table sugar and sometimes called saccharose. A white, odorless, crystalline powder with a sweet taste, it is best known for its role in human nutrition. The molecule is a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose with the molecular formula...
solutions. Traditionally, this process was performed in batch mode, but nowadays also continuous vacuum pans are available
Vacuum evaporation is also a form of physical vapor deposition
Physical vapor deposition
Physical vapor deposition is a variety of vacuum deposition and is a general term used to describe any of a variety of methods to deposit thin films by the condensation of a vaporized form of the desired film material onto various workpiece surfaces...
used in the semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
, microelectronics
Microelectronics
Microelectronics is a subfield of electronics. As the name suggests, microelectronics relates to the study and manufacture of very small electronic components. Usually, but not always, this means micrometre-scale or smaller,. These devices are made from semiconductors...
, and optic
Optic
Optic may mean:* optic, a British term for a device for dispensing fixed amounts of alcoholic spirits* Optics, the study of the behavior and properties of light* An optical element or component, such as a lens, prism, or mirror...
al industries and in this context is a process of depositing thin films of material onto surfaces. Such a technique consists of pumping a vacuum chamber
Vacuum chamber
A vacuum chamber is a rigid enclosure from which air and other gases are removed by a vacuum pump. The resulting low pressure, commonly referred to as a vacuum, allows researchers to conduct physical experiments or to test mechanical devices which must operate in outer space...
to pressures of less than
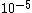 torr
torrTorr
The torr is a non-SI unit of pressure with the ratio of 760 to 1 standard atmosphere, chosen to be roughly equal to the fluid pressure exerted by a millimetre of mercury, i.e., a pressure of 1 torr is approximately equal to 1 mmHg...
and heating a material to produce a flux
Flux
In the various subfields of physics, there exist two common usages of the term flux, both with rigorous mathematical frameworks.* In the study of transport phenomena , flux is defined as flow per unit area, where flow is the movement of some quantity per time...
of vapor
Vapor
A vapor or vapour is a substance in the gas phase at a temperature lower than its critical point....
in order to deposit the material onto a surface. The material to be vaporized is typically heated until its vapor pressure
Vapor pressure
Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure of a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases in a closed system. All liquids have a tendency to evaporate, and some solids can sublimate into a gaseous form...
is high enough to produce a flux of several Angstroms per second by using an electrically resistive heater or bombardment by a high voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
beam.

