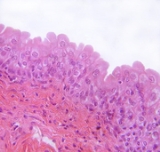
Urothelium
Encyclopedia
The urothelium is a form of transitional epithelial tissue
layer that lines much of the urinary tract, including the renal pelvis
, the ureter
s, the bladder
, and parts of the urethra
.
and trans-epithelial electrical resistance
.
Urothelium consists of approximately 3-5 cell layers, accompanied by a thick layer of protective glycoprotein
plaques at its luminal
(apical) surface, and is classified as transitional epithelium.
Biological tissue
Tissue is a cellular organizational level intermediate between cells and a complete organism. A tissue is an ensemble of cells, not necessarily identical, but from the same origin, that together carry out a specific function. These are called tissues because of their identical functioning...
layer that lines much of the urinary tract, including the renal pelvis
Renal pelvis
The renal pelvis or pyelum is the funnel-like dilated proximal part of the ureter in the kidney.In humans, the renal pelvis is the point of convergence of two or three major calyces...
, the ureter
Ureter
In human anatomy, the ureters are muscular tubes that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In the adult, the ureters are usually long and ~3-4 mm in diameter....
s, the bladder
Urinary bladder
The urinary bladder is the organ that collects urine excreted by the kidneys before disposal by urination. A hollow muscular, and distensible organ, the bladder sits on the pelvic floor...
, and parts of the urethra
Urethra
In anatomy, the urethra is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the genitals for the removal of fluids out of the body. In males, the urethra travels through the penis, and carries semen as well as urine...
.
Structure and function
Urothelial tissue is highly specific to the urinary tract, and has high elasticityElasticity (physics)
In physics, elasticity is the physical property of a material that returns to its original shape after the stress that made it deform or distort is removed. The relative amount of deformation is called the strain....
and trans-epithelial electrical resistance
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
.
Urothelium consists of approximately 3-5 cell layers, accompanied by a thick layer of protective glycoprotein
Glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins that contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to polypeptide side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycosylation. In proteins that have segments extending...
plaques at its luminal
Lumen (anatomy)
A lumen in biology is the inside space of a tubular structure, such as an artery or intestine...
(apical) surface, and is classified as transitional epithelium.
Pathology
Epithelia are sites of specific diseases.- CancerCancerCancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
s that originate in epithelial cells are termed carcinomas, and they are characterized as having lost the mature, differentiated morphology and molecular patterns of the normal tissue. Infectious diseases also afflict epithelia where diverse microbes (viruses, bacteria, fungi) have surface structures that bind specific features of particular epithelial cells (e.g., influenzaInfluenzaInfluenza, commonly referred to as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by RNA viruses of the family Orthomyxoviridae , that affects birds and mammals...
virus binds respiratory epithelium). Genetic defects can also inhibit normal epithelial integrity, such as defects in intercellular adhesion molecules that result in blistering diseases.
- The second most common infectious disease is urinary tract infectionUrinary tract infectionA urinary tract infection is a bacterial infection that affects any part of the urinary tract. Symptoms include frequent feeling and/or need to urinate, pain during urination, and cloudy urine. The main causal agent is Escherichia coli...
(UTI). UTIs afflict approximately half of all women during their lifetime, and about 25% of these women will suffer recurrent UTIs. The majority of these infections are due to uropathogenic Escherichia coliEscherichia coliEscherichia coli is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms . Most E. coli strains are harmless, but some serotypes can cause serious food poisoning in humans, and are occasionally responsible for product recalls...
bacteria (commonly known as E. coli). However, UTIs can also develop in healthcare settings and such infections are caused by a greater frequency of non-E. coli bacteria.
- One unusual condition which affects the urothelium is interstitial cystitisInterstitial cystitisInterstitial cystitis or bladder pain syndrome is a chronic, oftentimes severely debilitating disease of the urinary bladder...
(IC), a condition with symptoms similar to UTI (frequency, urgency, pressure and/or pain). Urine culture, however, is negative. During hydrodistention of the bladder, small petechial hemorrhages (aka glomerulationGlomerulationGlomerulation refers to bladder hemorrhages which are thought to be associated with some types of interstitial cystitis .The presence of glomerulations, also known as petechial hemorrhages, in the bladder suggests that the bladder wall has been damaged, irritated and/or inflamed...
s) are frequently found throughout the bladder. Larger "Hunner's Ulcers", known for their characteristic waterfall bleeding effect, represent larger areas of bladder wall thinning and/or trauma. The cause of IC is currently unknown though some suggest that it could be genetic, the result of traumatic injury (aka chemical exposure), infection, autoimmune disease, etc. Researcher Susan Keay (University of Maryland) has found an unusual protein in the urine of IC patients which appears to interfere with healing, known as an Antiproliferative Factor. Research efforts into IC are focused on the urothelium, including newly discovered signaling molecules which suggest that the urothelium is far more than a barrier, as well as how the urothelium interacts with proximal nerves and smooth muscle.
- Urothelium is susceptible to carcinoma. Because the bladder is in contact with urine for extended periods, chemicals that become concentrated in the urine can cause Bladder cancerBladder cancerBladder cancer is any of several types of malignant growths of the urinary bladder. It is a disease in which abnormal cells multiply without control in the bladder. The bladder is a hollow, muscular organ that stores urine; it is located in the pelvis...
. For example, cigarette smoking leads to the concentration of carcinogens in the urine and is a leading cause of bladder cancer. Occupational exposure to certain chemicals is also a risk factor for bladder cancer.

