
Universal Soil Loss Equation
Encyclopedia
The Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) is a mathematical model
used to describe soil
erosion
processes.
Erosion models play critical roles in soil and water
resource conservation
and nonpoint source pollution
assessments, including: sediment
load assessment and inventory, conservation planning and design for sediment control
, and for the advancement of scientific understanding. The USLE or one of its derivatives are main models used by United States
government agencies to measure water erosion.
The USLE was developed in the U.S. based on soil erosion data collected beginning in the 1930s by the USDA Soil Conservation Service (now the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service
). The model has been used for decades for purposes of conservation planning both in the United States where it originated and around the world, and has been used to help implement the United States' multi-billion dollar conservation program. The Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) continues to be used for similar purposes.
and through the solutions of the equations describing those processes provide estimates of soil loss and sediment yields from specified land surface areas. Erosion science is not sufficiently advanced for there to exist completely process-based models which do not include empirical aspects. The primary indicator, perhaps, for differentiating process-based from other types of erosion models is the use of the sediment continuity equation discussed below. Empirical models relate management and environmental factors directly to soil loss and/or sedimentary yields through statistical relationships. Lane et al. provided a detailed discussion regarding the nature of process-based and empirical erosion models, as well as a discussion of what they termed conceptual model
s, which lie somewhere between the process-based and purely empirical models. Current research effort involving erosion modeling is weighted toward the development of process-based erosion models. On the other hand, the standard model for most erosion assessment and conservation planning is the empirically based USLE, and there continues to be active research and development of USLE-based erosion prediction
technology.
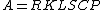
The USLE has another concept of experimental importance, the unit plot concept. The unit plot is defined as the standard plot condition to determine the soil's erodibility. These conditions are when the LS factor = 1 (slope = 9% and length = 72.6 feet) where the plot is fallow and tillage
is up and down slope and no conservation practices are applied (CP=1). In this state:

A simpler method to predict K was presented by Wischmeier et al. which includes the particle size of the soil, organic matter content, soil structure and profile permeability. The soil erodibility factor K can be approximated from a nomograph if this information is known. The LS factors can easily be determined from a slope effect chart by knowing the length and gradient of the slope. The cropping management factor (C) and conservation practices factor (P) are more difficult to obtain and must be determined empirically from plot data. They are described in soil loss ratios (C or P with / C or P without).
Mathematical model
A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used not only in the natural sciences and engineering disciplines A mathematical model is a...
used to describe soil
Soil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
erosion
Erosion
Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere...
processes.
Erosion models play critical roles in soil and water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
resource conservation
Conservation ethic
Conservation is an ethic of resource use, allocation, and protection. Its primary focus is upon maintaining the health of the natural world: its, fisheries, habitats, and biological diversity. Secondary focus is on materials conservation and energy conservation, which are seen as important to...
and nonpoint source pollution
Nonpoint source pollution
Nonpoint source pollution refers to both water and air pollution from diffuse sources. Nonpoint source water pollution affects a water body from sources such as polluted runoff from agricultural areas draining into a river, or wind-borne debris blowing out to sea. Nonpoint source air pollution...
assessments, including: sediment
Sediment
Sediment is naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of fluids such as wind, water, or ice, and/or by the force of gravity acting on the particle itself....
load assessment and inventory, conservation planning and design for sediment control
Sediment control
A sediment control is a practice or device designed to keep eroded soil on a construction site, so that it does not wash off and cause water pollution to a nearby stream, river, lake, or bay...
, and for the advancement of scientific understanding. The USLE or one of its derivatives are main models used by United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
government agencies to measure water erosion.
The USLE was developed in the U.S. based on soil erosion data collected beginning in the 1930s by the USDA Soil Conservation Service (now the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service
Natural Resources Conservation Service
The Natural Resources Conservation Service , formerly known as the Soil Conservation Service , is an agency of the United States Department of Agriculture that provides technical assistance to farmers and other private landowners and managers.Its name was changed in 1994 during the Presidency of...
). The model has been used for decades for purposes of conservation planning both in the United States where it originated and around the world, and has been used to help implement the United States' multi-billion dollar conservation program. The Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) continues to be used for similar purposes.
Overview of Erosion Models
The two primary types of erosion models are process-based models and empirically based models. Process-based (physically based) models mathematically describe the erosion processes of detachment, transport, and depositionDeposition (chemistry)
In chemistry, deposition is the settling of particles or sediment from a solution, suspension and mixture or vapor onto a pre-existing surface...
and through the solutions of the equations describing those processes provide estimates of soil loss and sediment yields from specified land surface areas. Erosion science is not sufficiently advanced for there to exist completely process-based models which do not include empirical aspects. The primary indicator, perhaps, for differentiating process-based from other types of erosion models is the use of the sediment continuity equation discussed below. Empirical models relate management and environmental factors directly to soil loss and/or sedimentary yields through statistical relationships. Lane et al. provided a detailed discussion regarding the nature of process-based and empirical erosion models, as well as a discussion of what they termed conceptual model
Conceptual model
In the most general sense, a model is anything used in any way to represent anything else. Some models are physical objects, for instance, a toy model which may be assembled, and may even be made to work like the object it represents. They are used to help us know and understand the subject matter...
s, which lie somewhere between the process-based and purely empirical models. Current research effort involving erosion modeling is weighted toward the development of process-based erosion models. On the other hand, the standard model for most erosion assessment and conservation planning is the empirically based USLE, and there continues to be active research and development of USLE-based erosion prediction
Erosion prediction
There are dozens of erosion prediction models. Most have been developed for agricultural areas and are design to compare predicted annual rates of soil loss from broad areas under various cropland and rangeland management techniques. Some are purely statistical models, others mechanistic...
technology.
Description of USLE
The USLE was developed from erosion plot and rainfall simulator experiments. The USLE is composed of six factors to predict the long-term average annual soil loss (A). The equation includes the rainfall erosivity factor (R), the soil erodibility factor (K), the topographic factors (L and S) and the cropping management factors (C and P). The equation takes the simple product form: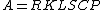
The USLE has another concept of experimental importance, the unit plot concept. The unit plot is defined as the standard plot condition to determine the soil's erodibility. These conditions are when the LS factor = 1 (slope = 9% and length = 72.6 feet) where the plot is fallow and tillage
Tillage
Tillage is the agricultural preparation of the soil by mechanical agitation of various types, such as digging, stirring, and overturning. Examples of human-powered tilling methods using hand tools include shovelling, picking, mattock work, hoeing, and raking...
is up and down slope and no conservation practices are applied (CP=1). In this state:

A simpler method to predict K was presented by Wischmeier et al. which includes the particle size of the soil, organic matter content, soil structure and profile permeability. The soil erodibility factor K can be approximated from a nomograph if this information is known. The LS factors can easily be determined from a slope effect chart by knowing the length and gradient of the slope. The cropping management factor (C) and conservation practices factor (P) are more difficult to obtain and must be determined empirically from plot data. They are described in soil loss ratios (C or P with / C or P without).
See also
- Certified Professional in Erosion and Sediment Control (CPESCCPESCCertified Professional in Erosion and Sediment Control is a qualification indicating the holder has educational training, expertise and experience in controlling erosion and sedimentation, and met certification standards....
) - Erosion controlErosion controlErosion control is the practice of preventing or controlling wind or water erosion in agriculture, land development and construction. Effective erosion controls are important techniques in preventing water pollution and soil loss.-Introduction:...

