
Unitary divisor
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, a natural number
a is a unitary divisor of a number b if a is a divisor
of b and if a and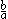 are coprime
are coprime
, having no common factor other than 1. Thus, 5 is a unitary divisor of 60, because 5 and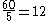 have only 1 as a common factor, while 6 is a divisor
have only 1 as a common factor, while 6 is a divisor
but not a unitary divisor of 60, as 6 and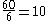 have a common factor other than 1, namely 2. 1 is a unitary divisor of every natural number.
have a common factor other than 1, namely 2. 1 is a unitary divisor of every natural number.
Equivalently, a given divisor a of b is a unitary divisor iff
every prime factor of a has the same multiplicity
in a as it has in b.
The sum of unitary divisors function is denoted by the lowercase Greek letter sigma thus: σ*(n). The sum of the k-th powers of the unitary
divisors is denoted by σ*k(n):
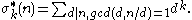
If the proper unitary divisors of a given number add up to that number, then that number is called a unitary perfect number
.
s of n. The sum of the unitary divisors of n is odd if n is a power of 2 (including 1), and even otherwise.
Both the count and the sum of the unitary divisors of n are multiplicative function
s of n that are not completely multiplicative. The Dirichlet generating function is
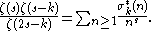
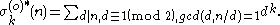
It is also multiplicative, with Dirichlet generating function
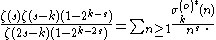
is σ(o)*0(n).
is σ(o)*1(n).
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, a natural number
Natural number
In mathematics, the natural numbers are the ordinary whole numbers used for counting and ordering . These purposes are related to the linguistic notions of cardinal and ordinal numbers, respectively...
a is a unitary divisor of a number b if a is a divisor
Divisor
In mathematics, a divisor of an integer n, also called a factor of n, is an integer which divides n without leaving a remainder.-Explanation:...
of b and if a and
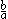 are coprime
are coprimeCoprime
In number theory, a branch of mathematics, two integers a and b are said to be coprime or relatively prime if the only positive integer that evenly divides both of them is 1. This is the same thing as their greatest common divisor being 1...
, having no common factor other than 1. Thus, 5 is a unitary divisor of 60, because 5 and
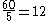 have only 1 as a common factor, while 6 is a divisor
have only 1 as a common factor, while 6 is a divisorDivisor
In mathematics, a divisor of an integer n, also called a factor of n, is an integer which divides n without leaving a remainder.-Explanation:...
but not a unitary divisor of 60, as 6 and
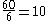 have a common factor other than 1, namely 2. 1 is a unitary divisor of every natural number.
have a common factor other than 1, namely 2. 1 is a unitary divisor of every natural number.Equivalently, a given divisor a of b is a unitary divisor iff
IFF
IFF, Iff or iff may refer to:Technology/Science:* Identification friend or foe, an electronic radio-based identification system using transponders...
every prime factor of a has the same multiplicity
Multiplicity (mathematics)
In mathematics, the multiplicity of a member of a multiset is the number of times it appears in the multiset. For example, the number of times a given polynomial equation has a root at a given point....
in a as it has in b.
The sum of unitary divisors function is denoted by the lowercase Greek letter sigma thus: σ*(n). The sum of the k-th powers of the unitary
divisors is denoted by σ*k(n):
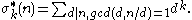
If the proper unitary divisors of a given number add up to that number, then that number is called a unitary perfect number
Unitary perfect number
A unitary perfect number is an integer which is the sum of its positive proper unitary divisors, not including the number itself. Some perfect numbers are not unitary perfect numbers, and some unitary perfect numbers are not regular perfect numbers.Thus, 60 is a unitary perfect...
.
Properties
The number of unitary divisors of a number n is 2k, where k is the number of distinct prime factorPrime factor
In number theory, the prime factors of a positive integer are the prime numbers that divide that integer exactly, without leaving a remainder. The process of finding these numbers is called integer factorization, or prime factorization. A prime factor can be visualized by understanding Euclid's...
s of n. The sum of the unitary divisors of n is odd if n is a power of 2 (including 1), and even otherwise.
Both the count and the sum of the unitary divisors of n are multiplicative function
Multiplicative function
In number theory, a multiplicative function is an arithmetic function f of the positive integer n with the property that f = 1 and whenevera and b are coprime, then...
s of n that are not completely multiplicative. The Dirichlet generating function is
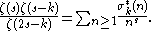
Odd unitary divisors
The sum of the k-th powers of the odd unitary divisors is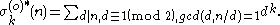
It is also multiplicative, with Dirichlet generating function
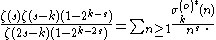
External links
- OEIS sequences: is σ0(n). is σ1(n). up to are σ2(n) to σ8(n).
is σ(o)*0(n).
is σ(o)*1(n).

