Ultrasonic sensor
Encyclopedia
Ultrasonic sensors work on a principle similar to radar
or sonar
which evaluate attributes of a target by interpreting the echoes from radio or sound waves respectively. Ultrasonic sensors generate high frequency sound waves and evaluate the echo which is received back by the sensor. Sensors calculate the time interval between sending the signal and receiving the echo to determine the distance to an object.
This technology can be used for measuring: wind speed and direction (anemometer), fullness of a tank and speed through air or water. For measuring speed or direction a device uses multiple detectors and calculates the speed from the relative distances to particulates in the air or water. To measure the amount of liquid in a tank, the sensor measures the distance to the surface of the fluid. Further applications include: humidifier
s, sonar
, medical ultrasonography
, burglar alarms and non-destructive testing.
Systems typically use a transducer which generates sound waves in the ultrasonic range, above 18,000 hertz, by turning electrical energy into sound, then upon receiving the echo turn the sound waves into electrical energy which can be measured and displayed.
The technology is limited by the shapes of surfaces and the density or consistency of the material. For example foam on the surface of a fluid in a tank could distort a reading.
An ultrasonic transducer is a device that converts energy into ultrasound
, or sound waves above the normal range of human hearing. While technically a dog whistle
is an ultrasonic transducer that converts mechanical energy in the form of air pressure into ultrasonic sound waves, the term is more apt to be used to refer to piezoelectric transducer
s that convert electrical energy into sound. Piezoelectric crystals have the property of changing size when a voltage
is applied, thus applying an alternating current
(AC) across them causes them to oscillate at very high frequencies, thus producing very high frequency sound waves.
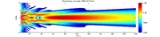
The location at which a transducer focuses the sound can be determined by the active transducer area and shape, the ultrasound frequency, and the sound velocity of the propagation medium.
The example shows the sound fields of an unfocused and a focusing ultrasonic transducer in water.
Alternative methods for creating and detecting ultrasound include magnetostriction
and capacitive
actuation
.
or vagina
. Clinicians who perform ultrasound-guided procedures often use a probe positioning system
to hold the ultrasonic transducer.
Air detection sensors are used in various roles. Non-invasive air detection capabilities in the most critical applications where the safety of a patient is mandatory. Many of the variables, which can affect performance of amplitude or continuous wave based sensing systems, are eliminated or greatly reduced, thus yielding accurate and repeatable detection. The principle behind the technology is that the transmit signal consists of short bursts of ultrasonic energy. After each burst, the electronics looks for a return signal within a small window of time corresponding to the time it takes for the energy to pass through the vessel. Only signal received during this window period will qualify for additional signal processing.
Ultrasonic sensors are gaining popularity in a number of uses including ultrasonic people detection an assisting in autonomous UAV navigation.
Because ultrasonic sensors use sound rather than light for detection, they work in applications where photoelectric sensor
s may not. Ultrasonics are a great solution for clear object detection and for liquid level measurement, applications that photoelectrics struggle with because of target translucence. Target color and/or reflectivity don't affect ultrasonic sensors which can operate reliably in high-glare environments.
Other types of transducers are used in commercially available ultrasonic cleaning devices. An ultrasonic transducer is affixed to a stainless steel pan which is filled with a solvent (frequently water or isopropanol) and a square wave is applied to it, imparting vibrational energy on the liquid.
Radar
Radar is an object-detection system which uses radio waves to determine the range, altitude, direction, or speed of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. The radar dish or antenna transmits pulses of radio...
or sonar
Sonar
Sonar is a technique that uses sound propagation to navigate, communicate with or detect other vessels...
which evaluate attributes of a target by interpreting the echoes from radio or sound waves respectively. Ultrasonic sensors generate high frequency sound waves and evaluate the echo which is received back by the sensor. Sensors calculate the time interval between sending the signal and receiving the echo to determine the distance to an object.
This technology can be used for measuring: wind speed and direction (anemometer), fullness of a tank and speed through air or water. For measuring speed or direction a device uses multiple detectors and calculates the speed from the relative distances to particulates in the air or water. To measure the amount of liquid in a tank, the sensor measures the distance to the surface of the fluid. Further applications include: humidifier
Humidifier
A humidifier is a household appliance that increases humidity in a single room or in the entire house. There are point-of-use humidifiers, which are commonly used to humidify a single room, and whole-house or furnace humidifiers, which connect to a home's HVAC system to provide humidity to the...
s, sonar
Sonar
Sonar is a technique that uses sound propagation to navigate, communicate with or detect other vessels...
, medical ultrasonography
Medical ultrasonography
Diagnostic sonography is an ultrasound-based diagnostic imaging technique used for visualizing subcutaneous body structures including tendons, muscles, joints, vessels and internal organs for possible pathology or lesions...
, burglar alarms and non-destructive testing.
Systems typically use a transducer which generates sound waves in the ultrasonic range, above 18,000 hertz, by turning electrical energy into sound, then upon receiving the echo turn the sound waves into electrical energy which can be measured and displayed.
The technology is limited by the shapes of surfaces and the density or consistency of the material. For example foam on the surface of a fluid in a tank could distort a reading.
Transducers

An ultrasonic transducer is a device that converts energy into ultrasound
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is cyclic sound pressure with a frequency greater than the upper limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is thus not separated from "normal" sound based on differences in physical properties, only the fact that humans cannot hear it. Although this limit varies from person to person, it is...
, or sound waves above the normal range of human hearing. While technically a dog whistle
Dog whistle
A dog whistle is a type of whistle used in the training of dogs and cats. It was invented by Francis Galton. This is discussed quite briefly in his book Inquiries into Human Faculty and its Development...
is an ultrasonic transducer that converts mechanical energy in the form of air pressure into ultrasonic sound waves, the term is more apt to be used to refer to piezoelectric transducer
Piezoelectricity
Piezoelectricity is the charge which accumulates in certain solid materials in response to applied mechanical stress. The word piezoelectricity means electricity resulting from pressure...
s that convert electrical energy into sound. Piezoelectric crystals have the property of changing size when a voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
is applied, thus applying an alternating current
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
(AC) across them causes them to oscillate at very high frequencies, thus producing very high frequency sound waves.
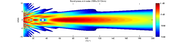
The location at which a transducer focuses the sound can be determined by the active transducer area and shape, the ultrasound frequency, and the sound velocity of the propagation medium.
The example shows the sound fields of an unfocused and a focusing ultrasonic transducer in water.
Detectors
Since piezoelectric crystals generate a voltage when force is applied to them, the same crystal can be used as an ultrasonic detector. Some systems use separate transmitter and receiver components while others combine both in a single piezoelectric transceiver.Alternative methods for creating and detecting ultrasound include magnetostriction
Magnetostriction
Magnetostriction is a property of ferromagnetic materials that causes them to change their shape or dimensions during the process of magnetization. The variation of material's magnetization due to the applied magnetic field changes the magnetostrictive strain until reaching its saturation value, λ...
and capacitive
Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
actuation
Actuator
An actuator is a type of motor for moving or controlling a mechanism or system. It is operated by a source of energy, usually in the form of an electric current, hydraulic fluid pressure or pneumatic pressure, and converts that energy into some kind of motion. An actuator is the mechanism by which...
.
Use in medicine
Medical ultrasonic transducers (probes) come in a variety of different shapes and sizes for use in making pictures of different parts of the body. The transducer may be passed over the surface of the body or inserted into a body opening such as the rectumRectum
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in some mammals, and the gut in others, terminating in the anus. The human rectum is about 12 cm long...
or vagina
Vagina
The vagina is a fibromuscular tubular tract leading from the uterus to the exterior of the body in female placental mammals and marsupials, or to the cloaca in female birds, monotremes, and some reptiles. Female insects and other invertebrates also have a vagina, which is the terminal part of the...
. Clinicians who perform ultrasound-guided procedures often use a probe positioning system
Probe positioning system
A probe positioning system is a tool for the positioning of a measuring device, such as an ultrasound transducer in a fixed, predetermined place to the object, such as a patient...
to hold the ultrasonic transducer.
Air detection sensors are used in various roles. Non-invasive air detection capabilities in the most critical applications where the safety of a patient is mandatory. Many of the variables, which can affect performance of amplitude or continuous wave based sensing systems, are eliminated or greatly reduced, thus yielding accurate and repeatable detection. The principle behind the technology is that the transmit signal consists of short bursts of ultrasonic energy. After each burst, the electronics looks for a return signal within a small window of time corresponding to the time it takes for the energy to pass through the vessel. Only signal received during this window period will qualify for additional signal processing.
Use in industry
Ultrasonic sensors are used to detect the presence of targets and to measure the distance to targets in many automated factories and process plants. Sensors with an on or off digital output are available for detecting the presence of objects, and sensors with an analog output which varies proportionally to the sensor to target separation distance are commercially available.Ultrasonic sensors are gaining popularity in a number of uses including ultrasonic people detection an assisting in autonomous UAV navigation.
Because ultrasonic sensors use sound rather than light for detection, they work in applications where photoelectric sensor
Photoelectric sensor
A photoelectric sensor, or photoeye, is a device used to detect the distance, absence, or presence of an object by using a light transmitter, often infrared, and a photoelectric receiver. They are used extensively in industrial manufacturing. There are three different functional types: opposed ,...
s may not. Ultrasonics are a great solution for clear object detection and for liquid level measurement, applications that photoelectrics struggle with because of target translucence. Target color and/or reflectivity don't affect ultrasonic sensors which can operate reliably in high-glare environments.
Other types of transducers are used in commercially available ultrasonic cleaning devices. An ultrasonic transducer is affixed to a stainless steel pan which is filled with a solvent (frequently water or isopropanol) and a square wave is applied to it, imparting vibrational energy on the liquid.
External links
- Ultrasonic Acoustic Sensing Brown University
- Laser Ultrasonic Sensor Streamlines Papermaking Process, Lawrence Berkeley Lab, Dan Krotz
- Ultrasonic Flaw Detection for Technicians, Chapter 2, 3rd ed., 2004 by J. C. Drury (~5 pages)
- Measure distance using the ultrasonic sensor
- Ultra Technology More uniform fibre distribution in paper with ultrasonicsUltrasonicsUltrasonics is a term meaning the application of ultrasound. It is often used in industry as a shorthand term for any equipment employing ultrasonic principles....
in the paper machine wet end. - Ultrasound transducer entry in the public domain NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms
- Ultrasonic Transmitter and Receiver circuit diagram
- Ultrasonic Sensors for Industry
- Siemens Ultrasonic Level Measurement
- Choosing an Ultrasonic Sensor for Proximity or Distance Measurement Sensors Magazine.
- Transducer Info Center.
- Outdoor Ultrasonic Sensors

