
UDFy-38135539
Encyclopedia
UDFy-38135539 is the Hubble Ultra Deep Field
(UDF) identifier for a galaxy
which has been calculated to have a light travel time of 13.1 billion years with a present comoving distance
of around 30 billion light-year
s. The galaxy is suspected to be the second most distant object yet identified after UDFj-39546284
, though UDFy-38135539 is still the most distant object spectroscopically confirmed
.
It was discovered by three teams in September 2009 in sensitive infrared Hubble Space Telescope
images (source UDF-38135539 in Rychard Bouwens
et al., source HUDF.YD3 in Andrew Bunker et al. and source 1721 in Ross McLure et al.), and reported in the Astrophysical Journal, and the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. These teams independently identified this source as a likely extremely distant galaxy due to it having no measurable light at visible wavelengths
, by reason of absorption by hydrogen gas along the line of sight. Following the discovery of this candidate distant galaxy, another team targeted this object with ground-based spectroscopy
to confirm its distant nature, and the measurement of a redshift
is formally detailed in the 21 October 2010 article "Spectroscopic Confirmation of a Galaxy at Redshift z=8.6" in the journal Nature
, authored by an international team of colleagues comprising Matthew Lehnert, Nicole Nesvadba, Mark Swinbank, Jean-Gabriel Cuby, Simon Morris, Benjamin Clement, C. J. Evans, M.N. Bremer, and Stephane Basa.
, the most detailed deep space picture ever taken by the Hubble telescope, in August and September 2009. The image data was released to the scientific community, which led to the galaxy's detection by the teams of Bouwens, Bunker and McLure, and subsequent spectroscopic confirmation by the team of Lehnert and colleagues.
The faster that a galaxy is moving away from an observer, the more the light is skewed towards longer, redder wavelengths by the intervening expansion of the universe. This phenomenon is known as redshift
, and the greater the redshift observed on Earth
, the more distant the source of light is. As seen from the Hubble photo, the galaxy could have possibly been an object intrinsically red and relatively close to Earth, and therefore, confirmation using suitably sensitive spectroscopic
equipment was needed. This was possible using the European Southern Observatory
's SINFONI-equipped Very Large Telescope
unit Yepun, located atop Cerro Paranal
in Chile
's Atacama Desert
. Lehnert's team observed the galaxy for 16 hours, and then analysed their results over 2 months, and published their findings in Nature
, in October 2010.
, and is estimated to have contained roughly a billion star
s, although it was only at most one tenth of the diameter of our own galaxy, the Milky Way
, and had less than 1% of the mass of the Milky Way's stars. According to Lehnert (of the Observatoire de Paris), it was forming the same number of stars per year as our galaxy, but they were much smaller and less massive, making it "intensely star forming". The team's analysis determined that light from the galaxy has a redshift of 8.55. For comparison, light from the previous record-holder for most distant object, the gamma-ray burst GRB 090423
, has a redshift of 8.2. Light from the galaxy that we now observe on Earth was emitted 13.1 billion years ago, only 600 million years after the estimated age of the Big Bang
, when the universe was only 4% of its current age.
The light travel distance of the light that we observe from UDFy-38135539 is more than 4 billion parsec
s (13.1 billion light years), and it has a luminosity distance of 86.9 billion parsecs (about 283 billion light years). There are a number of different distance measures in cosmology
, and both "light travel distance" and "luminosity distance" are different from the comoving distance
or "proper distance" generally used in defining the size of the observable universe
(comoving distance and proper distance are defined to be equal at the present cosmological time, so they can be used interchangeably when talking about the distance to an object at present, but proper distance increases with time due to the expansion of the universe, and is the distance used in Hubble's law
; see Uses of the proper distance for more on the physical meaning of this notion of 'distance'). The luminosity distance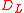 is related to a factor called the "comoving transverse distance"
is related to a factor called the "comoving transverse distance" 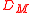 by the equation
by the equation 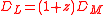 , where z is the redshift, and the comoving transverse distance is itself equal to the radial comoving distance (i.e., comoving distance between an object and ourselves) in a spatially flat universe. So with
, where z is the redshift, and the comoving transverse distance is itself equal to the radial comoving distance (i.e., comoving distance between an object and ourselves) in a spatially flat universe. So with 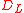 = 86.9 billion parsecs and z=8.55, the comoving distance would be about 9.1 billion parsecs (about 30 billion light years).
= 86.9 billion parsecs and z=8.55, the comoving distance would be about 9.1 billion parsecs (about 30 billion light years).
The infrared light that we now observe from the galaxy was emitted as ultraviolet radiation toward the end of an era when the universe was filled with atomic hydrogen, which absorbed at ultraviolet wavelengths. Because the galaxy's own light alone would not have been intense enough to ionize a large region and render it transparent, scientists suspect that a population of smaller, undetected galaxies, contributed to the reionization that makes UDFy-38135539 visible.
epoch: The universe's first stars were massive, and their intense ultraviolet radiation ionized hydrogen, eventually filling space with a UV-transparent plasma.
The UV-transparent "bubble" that surrounded UDFy-38135539 shows that, 600 million years after the Big Bang, stars in galaxies had almost completed the process of hydrogen reionization. Theoretical models and computer simulations suggest the first galaxies could have formed as early as 200 million years after the Big Bang.
The discovery makes UDFy-38135539 the first known galaxy observed during the reionization epoch, and those involved believe it will help scientists better understand the era. Caltech astronomer Brant Robertson, commenting on the study, stated that the "galaxy happens to reside at a very special time in cosmic history when the properties of gas in the universe were changing rapidly, and therefore this galaxy and others like it may teach us a lot about the early history of the universe". Michele Trenti, an astronomer who was not involved in the study but provided commentary published with the report, says that the discovery of the distant galaxy represents a "fundamental leap forward in observational cosmology".
becomes operational in 2018.
The James Webb telescope should be able to detect galaxies more than 13.4 billion light years away, less than 300 million years after the Big Bang. Bremer states that it, and eventually the European Extremely Large Telescope, which will have a mirror five times the diameter of Yepun's, and is tentatively scheduled for completion in 2018, will enable more detailed study of galaxies at such great distances. Lehnert states that this discovery is not "the limit, perhaps not even that close to it".
Trenti says redshift 8.6 is likely to be as high as we can reach with the current generation of telescopes, but that with Hubble, "it might be possible to find some galaxies up to redshift 10". Candidates with higher redshifts than UDFy-38135539's have been reported, but not yet confirmed with light spectrum instruments. Astronomers believe they have other candidates of similar distance which they hope to confirm soon.
Hubble Ultra Deep Field
The Hubble Ultra-Deep Field is an image of a small region of space in the constellation Fornax, composited from Hubble Space Telescope data accumulated over a period from September 24, 2003, through to January 16, 2004...
(UDF) identifier for a galaxy
Galaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
which has been calculated to have a light travel time of 13.1 billion years with a present comoving distance
Comoving distance
In standard cosmology, comoving distance and proper distance are two closely related distance measures used by cosmologists to define distances between objects...
of around 30 billion light-year
Light-year
A light-year, also light year or lightyear is a unit of length, equal to just under 10 trillion kilometres...
s. The galaxy is suspected to be the second most distant object yet identified after UDFj-39546284
UDFj-39546284
UDFj-39546284 is a compact galaxy of blue stars that existed as we see it 13.2 billion years ago, around 480 million years after the Big Bang. It is the oldest galaxy found and exceeds the previous distance record holder by roughly 150 million years. It could remain so until the anticipated launch...
, though UDFy-38135539 is still the most distant object spectroscopically confirmed
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and radiated energy. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, e.g., by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to comprise any interaction with radiative...
.
It was discovered by three teams in September 2009 in sensitive infrared Hubble Space Telescope
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope is a space telescope that was carried into orbit by a Space Shuttle in 1990 and remains in operation. A 2.4 meter aperture telescope in low Earth orbit, Hubble's four main instruments observe in the near ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared...
images (source UDF-38135539 in Rychard Bouwens
Rychard Bouwens
Rychard Bouwens is an assistant professor at the University of Leiden. He is also a former member of the Advanced Camera for Surveys Guaranteed Time Observation team and postdoctoral research astronomer at the University of California, Santa Cruz. His work helped lead to the discovery of...
et al., source HUDF.YD3 in Andrew Bunker et al. and source 1721 in Ross McLure et al.), and reported in the Astrophysical Journal, and the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. These teams independently identified this source as a likely extremely distant galaxy due to it having no measurable light at visible wavelengths
Visible spectrum
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called visible light or simply light. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 390 to 750 nm. In terms of...
, by reason of absorption by hydrogen gas along the line of sight. Following the discovery of this candidate distant galaxy, another team targeted this object with ground-based spectroscopy
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and radiated energy. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, e.g., by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to comprise any interaction with radiative...
to confirm its distant nature, and the measurement of a redshift
Redshift
In physics , redshift happens when light seen coming from an object is proportionally increased in wavelength, or shifted to the red end of the spectrum...
is formally detailed in the 21 October 2010 article "Spectroscopic Confirmation of a Galaxy at Redshift z=8.6" in the journal Nature
Nature (journal)
Nature, first published on 4 November 1869, is ranked the world's most cited interdisciplinary scientific journal by the Science Edition of the 2010 Journal Citation Reports...
, authored by an international team of colleagues comprising Matthew Lehnert, Nicole Nesvadba, Mark Swinbank, Jean-Gabriel Cuby, Simon Morris, Benjamin Clement, C. J. Evans, M.N. Bremer, and Stephane Basa.
Detection
The galaxy's image was first captured in the Hubble Ultra Deep FieldHubble Ultra Deep Field
The Hubble Ultra-Deep Field is an image of a small region of space in the constellation Fornax, composited from Hubble Space Telescope data accumulated over a period from September 24, 2003, through to January 16, 2004...
, the most detailed deep space picture ever taken by the Hubble telescope, in August and September 2009. The image data was released to the scientific community, which led to the galaxy's detection by the teams of Bouwens, Bunker and McLure, and subsequent spectroscopic confirmation by the team of Lehnert and colleagues.
The faster that a galaxy is moving away from an observer, the more the light is skewed towards longer, redder wavelengths by the intervening expansion of the universe. This phenomenon is known as redshift
Redshift
In physics , redshift happens when light seen coming from an object is proportionally increased in wavelength, or shifted to the red end of the spectrum...
, and the greater the redshift observed on Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
, the more distant the source of light is. As seen from the Hubble photo, the galaxy could have possibly been an object intrinsically red and relatively close to Earth, and therefore, confirmation using suitably sensitive spectroscopic
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and radiated energy. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, e.g., by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to comprise any interaction with radiative...
equipment was needed. This was possible using the European Southern Observatory
European Southern Observatory
The European Southern Observatory is an intergovernmental research organisation for astronomy, supported by fifteen countries...
's SINFONI-equipped Very Large Telescope
Very Large Telescope
The Very Large Telescope is a telescope operated by the European Southern Observatory on Cerro Paranal in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile. The VLT consists of four individual telescopes, each with a primary mirror 8.2m across, which are generally used separately but can be used together to...
unit Yepun, located atop Cerro Paranal
Cerro Paranal
Cerro Paranal , also known as Paranal Mountain is a mountain in the Atacama desert of northern Chile that is home to the Paranal Observatory. It is famous for hosting the Very Large Telescope and the VLT Survey Telescope. It is located 120 km west of Antofagasta and 80 km north of Taltal,...
in Chile
Chile
Chile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
's Atacama Desert
Atacama Desert
The Atacama Desert is a plateau in South America, covering a strip of land on the Pacific coast, west of the Andes mountains. It is, according to NASA, National Geographic and many other publications, the driest desert in the world...
. Lehnert's team observed the galaxy for 16 hours, and then analysed their results over 2 months, and published their findings in Nature
Nature (journal)
Nature, first published on 4 November 1869, is ranked the world's most cited interdisciplinary scientific journal by the Science Edition of the 2010 Journal Citation Reports...
, in October 2010.
Characteristics
The galaxy is located in the constellation FornaxFornax
Fornax is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for furnace. It was created in the 18th century and is now one of the 88 modern constellations.-History:Fornax was formed by Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in 1756...
, and is estimated to have contained roughly a billion star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
s, although it was only at most one tenth of the diameter of our own galaxy, the Milky Way
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
, and had less than 1% of the mass of the Milky Way's stars. According to Lehnert (of the Observatoire de Paris), it was forming the same number of stars per year as our galaxy, but they were much smaller and less massive, making it "intensely star forming". The team's analysis determined that light from the galaxy has a redshift of 8.55. For comparison, light from the previous record-holder for most distant object, the gamma-ray burst GRB 090423
GRB 090423
GRB 090423 is a gamma-ray burst detected by the Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission on April 23, 2009 at 07:55:19 UTC. The afterglow of GRB 090423 was detected in the infrared, and allowed astronomers to determine that the redshift of GRB 090423 is z = 8.2, which makes GRB 090423 the second...
, has a redshift of 8.2. Light from the galaxy that we now observe on Earth was emitted 13.1 billion years ago, only 600 million years after the estimated age of the Big Bang
Big Bang
The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model that explains the early development of the Universe. According to the Big Bang theory, the Universe was once in an extremely hot and dense state which expanded rapidly. This rapid expansion caused the young Universe to cool and resulted in...
, when the universe was only 4% of its current age.
The light travel distance of the light that we observe from UDFy-38135539 is more than 4 billion parsec
Parsec
The parsec is a unit of length used in astronomy. It is about 3.26 light-years, or just under 31 trillion kilometres ....
s (13.1 billion light years), and it has a luminosity distance of 86.9 billion parsecs (about 283 billion light years). There are a number of different distance measures in cosmology
Distance measures (cosmology)
Distance measures are used in physical cosmology to give a natural notion of the distance between two objects or events in the universe. They are often used to tie some observable quantity to another quantity that is not directly...
, and both "light travel distance" and "luminosity distance" are different from the comoving distance
Comoving distance
In standard cosmology, comoving distance and proper distance are two closely related distance measures used by cosmologists to define distances between objects...
or "proper distance" generally used in defining the size of the observable universe
Observable universe
In Big Bang cosmology, the observable universe consists of the galaxies and other matter that we can in principle observe from Earth in the present day, because light from those objects has had time to reach us since the beginning of the cosmological expansion...
(comoving distance and proper distance are defined to be equal at the present cosmological time, so they can be used interchangeably when talking about the distance to an object at present, but proper distance increases with time due to the expansion of the universe, and is the distance used in Hubble's law
Hubble's law
Hubble's law is the name for the astronomical observation in physical cosmology that: all objects observed in deep space are found to have a doppler shift observable relative velocity to Earth, and to each other; and that this doppler-shift-measured velocity, of various galaxies receding from...
; see Uses of the proper distance for more on the physical meaning of this notion of 'distance'). The luminosity distance
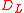 is related to a factor called the "comoving transverse distance"
is related to a factor called the "comoving transverse distance" 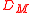 by the equation
by the equation 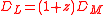 , where z is the redshift, and the comoving transverse distance is itself equal to the radial comoving distance (i.e., comoving distance between an object and ourselves) in a spatially flat universe. So with
, where z is the redshift, and the comoving transverse distance is itself equal to the radial comoving distance (i.e., comoving distance between an object and ourselves) in a spatially flat universe. So with 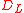 = 86.9 billion parsecs and z=8.55, the comoving distance would be about 9.1 billion parsecs (about 30 billion light years).
= 86.9 billion parsecs and z=8.55, the comoving distance would be about 9.1 billion parsecs (about 30 billion light years).The infrared light that we now observe from the galaxy was emitted as ultraviolet radiation toward the end of an era when the universe was filled with atomic hydrogen, which absorbed at ultraviolet wavelengths. Because the galaxy's own light alone would not have been intense enough to ionize a large region and render it transparent, scientists suspect that a population of smaller, undetected galaxies, contributed to the reionization that makes UDFy-38135539 visible.
Significance
The pre-stellar period that followed recombination is referred to as the Dark Ages. Although it was optically transparent, absorption by neutral atomic hydrogen made it opaque to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. The period of star birth that followed initiated the reionizationReionization
In Big Bang cosmology, reionization is the process that reionized the matter in the universe after the "dark ages," and is the second of two major phase changes of gas in the universe. As the majority of baryonic matter is in the form of hydrogen, reionization usually refers to the reionization of...
epoch: The universe's first stars were massive, and their intense ultraviolet radiation ionized hydrogen, eventually filling space with a UV-transparent plasma.
The UV-transparent "bubble" that surrounded UDFy-38135539 shows that, 600 million years after the Big Bang, stars in galaxies had almost completed the process of hydrogen reionization. Theoretical models and computer simulations suggest the first galaxies could have formed as early as 200 million years after the Big Bang.
The discovery makes UDFy-38135539 the first known galaxy observed during the reionization epoch, and those involved believe it will help scientists better understand the era. Caltech astronomer Brant Robertson, commenting on the study, stated that the "galaxy happens to reside at a very special time in cosmic history when the properties of gas in the universe were changing rapidly, and therefore this galaxy and others like it may teach us a lot about the early history of the universe". Michele Trenti, an astronomer who was not involved in the study but provided commentary published with the report, says that the discovery of the distant galaxy represents a "fundamental leap forward in observational cosmology".
Subsequent discoveries
Scientists hope to find older galaxies; however, closer to the Big Bang, fewer exist and they are dimmer on average. They will therefore be increasingly difficult to find, since they would be very faint with fewer observable stars. Trenti says that new "most distant" record holders will soon be announced, but only incremental distance gains will be realized until NASA's James Webb Space TelescopeJames Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope , previously known as Next Generation Space Telescope , is a planned next-generation space telescope, optimized for observations in the infrared. The main technical features are a large and very cold 6.5 meter diameter mirror, an observing position far from Earth,...
becomes operational in 2018.
The James Webb telescope should be able to detect galaxies more than 13.4 billion light years away, less than 300 million years after the Big Bang. Bremer states that it, and eventually the European Extremely Large Telescope, which will have a mirror five times the diameter of Yepun's, and is tentatively scheduled for completion in 2018, will enable more detailed study of galaxies at such great distances. Lehnert states that this discovery is not "the limit, perhaps not even that close to it".
Trenti says redshift 8.6 is likely to be as high as we can reach with the current generation of telescopes, but that with Hubble, "it might be possible to find some galaxies up to redshift 10". Candidates with higher redshifts than UDFy-38135539's have been reported, but not yet confirmed with light spectrum instruments. Astronomers believe they have other candidates of similar distance which they hope to confirm soon.
See also
Other known most distant objects- GRB 090423GRB 090423GRB 090423 is a gamma-ray burst detected by the Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission on April 23, 2009 at 07:55:19 UTC. The afterglow of GRB 090423 was detected in the infrared, and allowed astronomers to determine that the redshift of GRB 090423 is z = 8.2, which makes GRB 090423 the second...
is a gamma ray burst, which previously held the record for most distant object. - IOK-1IOK-1IOK-1 is a distant galaxy in Coma Berenices. When discovered in 2006, it was the oldest and most distant galaxy ever found, at redshift 6.96....
is the previous record holder for the commonly accepted most distant galaxy. - The methods used to determine the distances to very distant cosmic objects are described in the "Cosmic distance ladderCosmic distance ladderThe cosmic distance ladder is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A real direct distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible only for those objects that are "close enough" to Earth...
"

