
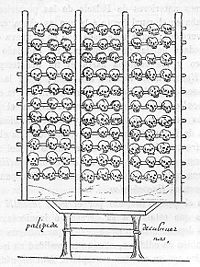
Tzompantli
Encyclopedia
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a region and culture area in the Americas, extending approximately from central Mexico to Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica, within which a number of pre-Columbian societies flourished before the Spanish colonization of the Americas in the 15th and...
n civilizations, which was used for the public display of human skull
Human skull
The human skull is a bony structure, skeleton, that is in the human head and which supports the structures of the face and forms a cavity for the brain.In humans, the adult skull is normally made up of 22 bones...
s, typically those of war captives
Human trophy taking in Mesoamerica
Most of the ancient civilizations of Mesoamerica such as the Olmec, Maya, Mixtec, Zapotec and Aztec cultures practised some kind of taking of human trophies during warfare. Captives taken during war would often be taken to their captors' city-states where they would be ritually tortured and...
or other sacrificial victims
Human sacrifice
Human sacrifice is the act of killing one or more human beings as part of a religious ritual . Its typology closely parallels the various practices of ritual slaughter of animals and of religious sacrifice in general. Human sacrifice has been practised in various cultures throughout history...
.
Etymology
The name comes from the Classical NahuatlClassical Nahuatl
Classical Nahuatl is a term used to describe the variants of the Nahuatl language that were spoken in the Valley of Mexico — and central Mexico as a lingua franca — at the time of the 16th-century Spanish conquest of Mexico...
language of the Aztec
Aztec
The Aztec people were certain ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica in the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries, a period referred to as the late post-classic period in Mesoamerican chronology.Aztec is the...
s, however it is also commonly applied to similar structures depicted in other civilizations. Its precise etymology
Etymology
Etymology is the study of the history of words, their origins, and how their form and meaning have changed over time.For languages with a long written history, etymologists make use of texts in these languages and texts about the languages to gather knowledge about how words were used during...
is uncertain, although its general interpretation is "skull rack" or "wall of skulls". It may be seen to be a compound of the Nahuatl words tzontecomatl ("skull"; from tzontli or tzom- "hair", "scalp" and tecomatl ("gourd
Gourd
A gourd is a plant of the family Cucurbitaceae. Gourd is occasionally used to describe crops like cucumbers, squash, luffas, and melons. The term 'gourd' however, can more specifically, refer to the plants of the two Cucurbitaceae genera Lagenaria and Cucurbita or also to their hollow dried out shell...
" or "container"), and pamitl ("banner"). This derivation has been ascribed to explain the depictions in several codices which associate these with banners; however, Nahuatl linguist Frances Karttunen
Frances Karttunen
Frances Esther Karttunen , also known as Frances Ruley Karttunen, is an American academic linguist, historian and author. In her linguistics career Karttunen has specialised in the study of Mesoamerican languages such as Mayan but in particular Nahuatl, on which topic she has authored seven books...
has proposed that pantli means merely "row" or "wall".
General information
It was most commonly erected as a linearly-arranged series of vertical posts connected by a series of horizontal crossbeams. The skulls were pierced or threaded laterally along these horizontal stakes. An alternate arrangement, more common in the Maya regions, was for the skulls to be impaled on top of one another along the vertical posts.Tzompantli are known chiefly from their depiction in Late Postclassic (13th to 16th centuries) and post-Conquest (mid-16th to 17th centuries) codices
Codex
A codex is a book in the format used for modern books, with multiple quires or gatherings typically bound together and given a cover.Developed by the Romans from wooden writing tablets, its gradual replacement...
, contemporary accounts of the conquistador
Conquistador
Conquistadors were Spanish soldiers, explorers, and adventurers who brought much of the Americas under the control of Spain in the 15th to 16th centuries, following Europe's discovery of the New World by Christopher Columbus in 1492...
es, and several other inscriptions. However, there is evidence that a tzompantli-like structure has been excavated from the Proto-Classic Zapotec civilization
Zapotec civilization
The Zapotec civilization was an indigenous pre-Columbian civilization that flourished in the Valley of Oaxaca of southern Mesoamerica. Archaeological evidence shows their culture goes back at least 2500 years...
at the La Coyotera, Oaxaca
Oaxaca
Oaxaca , , officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Oaxaca is one of the 31 states which, along with the Federal District, comprise the 32 federative entities of Mexico. It is divided into 571 municipalities; of which 418 are governed by the system of customs and traditions...
site, dated from c.2nd century BCE to 3rd century CE
Common Era
Common Era ,abbreviated as CE, is an alternative designation for the calendar era originally introduced by Dionysius Exiguus in the 6th century, traditionally identified with Anno Domini .Dates before the year 1 CE are indicated by the usage of BCE, short for Before the Common Era Common Era...
.
Tzompantli are also noted in other Mesoamerican pre-Columbian
Pre-Columbian
The pre-Columbian era incorporates all period subdivisions in the history and prehistory of the Americas before the appearance of significant European influences on the American continents, spanning the time of the original settlement in the Upper Paleolithic period to European colonization during...
cultures, such as the Toltec
Toltec
The Toltec culture is an archaeological Mesoamerican culture that dominated a state centered in Tula, Hidalgo in the early post-classic period of Mesoamerican chronology...
and Mixtec
Mixtec
The Mixtec are indigenous Mesoamerican peoples inhabiting the Mexican states of Oaxaca, Guerrero and Puebla in a region known as La Mixteca. The Mixtecan languages form an important branch of the Otomanguean language family....
.
Maya
Other examples are indicated from Maya civilizationMaya civilization
The Maya is a Mesoamerican civilization, noted for the only known fully developed written language of the pre-Columbian Americas, as well as for its art, architecture, and mathematical and astronomical systems. Initially established during the Pre-Classic period The Maya is a Mesoamerican...
sites such as Uxmal
Uxmal
Uxmal was dominant from 875 to 900 CE. The site appears to have been the capital of a regional state in the Puuc region from 850-950 CE. The Maya dynasty expanded their dominion over their neighbors. This prominence didn't last long...
and other Puuc
Puuc
Puuc is the name of either a region in the Mexican state of Yucatán or a Maya architectural style prevalent in that region. The word "puuc" is derived from the Maya term for "hill". Since the Yucatán is relatively flat, this term was extended to encompass the large karstic range of hills in the...
region sites of the Yucatán
Yucatán
Yucatán officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Yucatán is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 106 municipalities and its capital city is Mérida....
, dating from around the late 9th century decline of the Maya Classical Era. A particularly fine and intact inscription example survives at the extensive Chichen Itza
Chichen Itza
Chichen Itza is a large pre-Columbian archaeological site built by the Maya civilization located in the northern center of the Yucatán Peninsula, in the Municipality of Tinúm, Yucatán state, present-day Mexico....
site.

Aztec
There are numerous depictions of tzompantli in Aztec codicesAztec codices
Aztec codices are books written by pre-Columbian and colonial-era Aztecs. These codices provide some of the best primary sources for Aztec culture....
, dating from around the time or shortly after the Spanish conquest of Mexico
Spanish conquest of Mexico
The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire was one of the most important campaigns in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. The invasion began in February 1519 and was acclaimed victorious on August 13, 1521, by a coalition army of Spanish conquistadors and Tlaxcalan warriors led by Hernán Cortés...
, such as the Durán Codex, Ramírez Codex
Ramirez Codex
The Ramírez Codex is a post-conquest codex from the late 16th century entitled Relación del origen de los indios que hábitan esta Nueva España según sus Historias .Ascribed to Juan de Tovar, most scholars believe that he based this work on an...
and Codex Borgia
Codex Borgia
The Codex Borgia is a Mesoamerican ritual and divinatory manuscript. It is generally believed to have been written before the Spanish conquest of Mexico, somewhere within what is now today southern or western Puebla...
. During the stay of Cortes' expedition in the Aztec capital Tenochtitlan (initially as guest-captives of the Emperor Moctezuma II
Moctezuma II
Moctezuma , also known by a number of variant spellings including Montezuma, Moteuczoma, Motecuhzoma and referred to in full by early Nahuatl texts as Motecuhzoma Xocoyotzin, was the ninth tlatoani or ruler of Tenochtitlan, reigning from 1502 to 1520...
, before the battle which would lead to the conquest), they reported a wooden tzompantli altar adorned with the skulls from recent sacrifices. Within the complex of the Great Pyramid of Tenochtitlan
Great Pyramid of Tenochtitlan
The ' was one of the main temples of the Aztecs in their capital city of Tenochtitlan, which is now Mexico City. Its architectural style belongs to the late Postclassic period of Mesoamerica...
(Templo Mayor) itself, a relief in stucco
Stucco
Stucco or render is a material made of an aggregate, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as decorative coating for walls and ceilings and as a sculptural and artistic material in architecture...
depicted these sacrifices; the remains of this relief have survived and may now be seen in the ruins in the Zócalo
Zócalo
The Zócalo is the main plaza or square in the heart of the historic center of Mexico City. The plaza used to be known simply as the "Main Square" or "Arms Square," and today its formal name is Plaza de la Constitución...
of present-day Mexico City
Mexico City
Mexico City is the Federal District , capital of Mexico and seat of the federal powers of the Mexican Union. It is a federal entity within Mexico which is not part of any one of the 31 Mexican states but belongs to the federation as a whole...
.
According to Bernal Díaz del Castillo
Bernal Díaz del Castillo
Bernal Díaz del Castillo was a conquistador, who wrote an eyewitness account of the conquest of Mexico by the Spaniards for Hernán Cortés, himself serving as a rodelero under Cortés.-Early life:...
's eye-witness account (The Conquest of New Spain
The Conquest of New Spain
Historia verdadera de la conquista de la Nueva España is the first-person narrative of Bernal Díaz del Castillo , the 16th-century military adventurer, conquistador, and colonist settler, who served in three Mexican expeditions; that of Francisco Hernández de Córdoba to the Yucatán peninsula; the...
) written several decades after the event, after Cortes' expedition was forced to make their initial retreat from Tenochtitlan, the Aztecs erected a makeshift tzompantli to display the severed heads of men and horses they had captured from the invaders. This taunting is also depicted in an Aztec codex which relates the story, and the subsequent battles which led to the eventual capture of the city by the Spanish forces and their allies.
Based on numbers given by the Conquistador Andrés de Tapia and Fray Diego Durán
Diego Durán
Diego Durán was a Dominican friar best known for his authorship of one of the earliest Western books on the history and culture of the Aztecs, The History of the Indies of New Spain, a book that was much criticized in his lifetime for helping the "heathen" maintain their culture.Also known as the...
, Bernard Ortiz de Montellano has calculated that there were at most 60,000 skulls on the Hueyi Tzompantli (great Skullrack) of Tenochtitlan. There were at least five more skullracks in Tenochtitlan but by all accounts they were much smaller.
Association and meaning
Apart from their use to display the skulls of ritualistically-executed war captives, tzompantli often occur in the contexts of Mesoamerican ballcourtsMesoamerican ballgame
The Mesoamerican ballgame or Tlatchtli in Náhuatl was a sport with ritual associations played since 1,000 B.C. by the pre-Columbian peoples of Ancient Mexico and Central America...
, which were widespread throughout the region's civilizations and sites. In these contexts it appears that the tzompantli was used to display the losers' heads of this often highly-ritualised game. New research seems to indicate it is not the losers' heads that were taken, but the winners' heads. It was an honor to be the more worthy sacrifice. Not all games resulted in this outcome, however, and for those that did it is surmised that these participants were often notable captives. Tula
Tula, Hidalgo
Tula, formally, Tula de Allende, is a town and one of the 84 municipalities of Hidalgo, in central-eastern Mexico. The municipality covers an area of 305.8 km² , and as of 2005, the municipality had a total population of 93,296, with 28,432 in the town...
, the former Toltec
Toltec
The Toltec culture is an archaeological Mesoamerican culture that dominated a state centered in Tula, Hidalgo in the early post-classic period of Mesoamerican chronology...
capital, has a well-preserved tzompantli inscription on its ballcourt.
The association with ballcourts is also reflected in the Popol Vuh
Popol Vuh
Popol Vuh is a corpus of mytho-historical narratives of the Post Classic Quiché kingdom in Guatemala's western highlands. The title translates as "Book of the Community," "Book of Counsel," or more literally as "Book of the People."...
, the famous religious, mythological and cultural account of the K'iche' Maya. When Hun Hunahpu, father of the Maya Hero Twins
Maya Hero Twins
The Maya Hero Twins are the central figures of a narrative included within the colonial Quiché document called Popol Vuh, and constituting the oldest Maya myth to have been preserved in its entirety. Called Hunahpu and Xbalanque in Quiché, the Twins have also been identified in the art of the...
, was killed by the lords of the Underworld (Xibalba
Xibalba
Xibalba , roughly translated as "place of fear", is the name of the underworld in Maya mythology, ruled by the Maya death gods and their helpers. In 16th-century Verapaz, the entrance to Xibalba was traditionally held to be a cave in the vicinity of Cobán, Guatemala. According to some of the...
), his head was hung in a gourd
Gourd
A gourd is a plant of the family Cucurbitaceae. Gourd is occasionally used to describe crops like cucumbers, squash, luffas, and melons. The term 'gourd' however, can more specifically, refer to the plants of the two Cucurbitaceae genera Lagenaria and Cucurbita or also to their hollow dried out shell...
tree next to a ballcourt. The gourd tree is a clear representation of a tzompantli, and the image of skulls in trees as if they were fruits is also a common indicator of a tzompantli and the associations with some of the game's metaphorical interpretations.
See also
- Skull Chapel in CzermnaSkull Chapel in CzermnaSkull Chapel in Czermna is a chapel situated in Kudowa-Zdrój, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Poland. This unusual chapel was built in 1776 by the local parish priest Wacław Tomaszek. It is the mass grave of people who died during the Thirty Years’ War , three Silesian Wars , as well as of people who...
- Santa Maria della Concezione dei CappucciniSanta Maria della Concezione dei CappucciniSanta Maria della Concezione dei Cappuccini, or Our Lady of the Conception of the Capuchins, is a church in Rome, Italy, commissioned by Pope Urban VIII, whose brother, Antonio Barberini, was a Capuchin friar...
- Sedlec OssuarySedlec OssuaryThe Sedlec Ossuary is a small Roman Catholic chapel, located beneath the Cemetery Church of All Saints in Sedlec, a suburb of Kutná Hora in the Czech Republic...

