
Turbo-compound engine
Encyclopedia
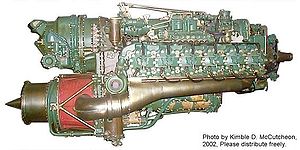
Reciprocating engine
A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common features of all types...
that employs a blowdown turbine
Turbine
A turbine is a rotary engine that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work.The simplest turbines have one moving part, a rotor assembly, which is a shaft or drum with blades attached. Moving fluid acts on the blades, or the blades react to the flow, so that they move and...
to recover energy from the exhaust gases. The turbine is usually mechanically connected to the crankshaft
Crankshaft
The crankshaft, sometimes casually abbreviated to crank, is the part of an engine which translates reciprocating linear piston motion into rotation...
but electric and hydraulic systems have been investigated as well. The turbine increases the output of the engine without increasing its fuel consumption, thus reducing the specific fuel consumption. The turbine is referred to as a blowdown turbine (or power-recovery turbine), as it recovers the energy developed in the exhaust manifold during blowdown, that is the first period of the exhaust process when the piston still is on its expansion stroke (this is possible since the exhaust valves open before bottom dead center).
When a blowdown turbine is attached to an engine it will not reduce power due to exhaust gas
Exhaust gas
Exhaust gas or flue gas is emitted as a result of the combustion of fuels such as natural gas, gasoline/petrol, diesel fuel, fuel oil or coal. According to the type of engine, it is discharged into the atmosphere through an exhaust pipe, flue gas stack or propelling nozzle.It often disperses...
flow restriction, since a blowdown turbine is a velocity turbine, not a pressure turbine as is a turbo supercharger. The exhaust restriction imparted by the three blowdown turbines used on the Wright R3350 is equal to a well-designed jet stack system used on a conventional radial engine. However, the blowdown turbines recover about 550 hp at METO (maximum continuous except for take-off) power.
Turbo-compounding was used on on several airplane engines after World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, including the Napier Nomad
Napier Nomad
The Napier Nomad was a complex British compression-ignition aircraft engine designed and built by Napier & Son in 1949. Two versions were flight tested:...
and the Wright R3350 being examples. In the case of the R-3350, maintenance crews sometimes nicknamed the turbine the "Parts Recovery Turbine" due to its negative effect on engine reliability. Turbo-compound versions of the Napier Deltic
Napier Deltic
The Napier Deltic engine is a British opposed-piston valveless, two-stroke diesel engine used in marine and locomotive applications, designed and produced by Napier & Son...
, Rolls-Royce Crecy
Rolls-Royce Crecy
The Rolls-Royce Crecy was an unusual British experimental two-stroke, 90-degree, V12, liquid-cooled aero-engine of 1,536 cu.in capacity, featuring sleeve valves and direct petrol injection...
, and Allison V-1710 were constructed but none was developed beyond the prototype stage. It was realized in many cases the power produced by the simple turbine was approaching that of the enormously complex and maintenance-intensive piston engine to which it was attached. As a result, turbo-compound aero engines were soon supplanted by turboprop
Turboprop
A turboprop engine is a type of turbine engine which drives an aircraft propeller using a reduction gear.The gas turbine is designed specifically for this application, with almost all of its output being used to drive the propeller...
and turbojet engines.
Some modern heavy truck diesel manufacturers have incorporated turbo-compounding into their modern designs. Examples include the Detroit Diesel
Detroit Diesel
As a corporation, Daimler Trucks North America has decided to rename the company "DETROIT".Detroit Diesel Corporation is an American-based diesel engine producer headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, USA...
DD15 and Scania
Scania AB
Scania Aktiebolag , commonly referred to as Scania AB or just Scania, is a major Swedish automotive industry manufacturer of commercial vehicles - specifically heavy trucks and buses...
in production from 2001
Turbo-compound engines
Detroit DieselDetroit Diesel
As a corporation, Daimler Trucks North America has decided to rename the company "DETROIT".Detroit Diesel Corporation is an American-based diesel engine producer headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, USA...
- DD15
Napier
Napier & Son
D. Napier & Son Limited was a British engine and pre-Great War automobile manufacturer and one of the most important aircraft engine manufacturers in the early to mid-20th century...
- Napier NomadNapier NomadThe Napier Nomad was a complex British compression-ignition aircraft engine designed and built by Napier & Son in 1949. Two versions were flight tested:...
Wright Aeronautical
Wright Aeronautical
Wright Aeronautical was an aircraft and aircraft engine manufacturer located in New Jersey.-History:This American company evolved from the 1909-1916 Wright Company, which merged with the Glenn L. Martin Company in 1916 to form the Wright-Martin Aircraft Corporation. Glenn Martin resigned from...
- Wright R-3350Wright R-3350The Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone was one of the most powerful radial aircraft engines produced in the United States. It was a twin row, supercharged, air-cooled, radial engine with 18 cylinders. Power ranged from 2,200 to over 3,700 hp , depending on the model...
- The turbo-compound version was the only turbo-compound aero-engineAircraft engineAn aircraft engine is the component of the propulsion system for an aircraft that generates mechanical power. Aircraft engines are almost always either lightweight piston engines or gas turbines...
to see mass production and widespread usage.
Dobrynin
Dobrynin VD-4K
Dobrynin VD-4K
-See also:-External links:* *...
See also
- Sequential twin-turbo
- MotorjetMotorjetA motorjet is a rudimentary type of jet engine which is sometimes referred to as thermojet, a term now commonly used to describe a particular and completely unrelated pulsejet design.- Design :...
- TurbosteamerTurbosteamerA turbosteamer is a term used by BMW to describe a combined cycle engine. It uses a steam engine to convert waste heat energy from an internal combustion engine into supplemental power for the vehicle. The turbosteamer device is affixed to the exhaust and cooling system...
- CogenerationCogenerationCogeneration is the use of a heat engine or a power station to simultaneously generate both electricity and useful heat....
- TurbochargerTurbochargerA turbocharger, or turbo , from the Greek "τύρβη" is a centrifugal compressor powered by a turbine that is driven by an engine's exhaust gases. Its benefit lies with the compressor increasing the mass of air entering the engine , thereby resulting in greater performance...
- Gas turbineGas turbineA gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of internal combustion engine. It has an upstream rotating compressor coupled to a downstream turbine, and a combustion chamber in-between....

