Treaty of Saint-Germain
Encyclopedia
The Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye, was signed on 10 September 1919 by the victorious Allies of World War I
on the one hand and by the new Republic of Austria
on the other. Like the Treaty of Versailles
with Germany
, it contained the Covenant of the League of Nations
and as a result was not ratified by the United States
.
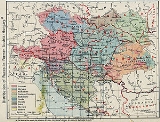
The treaty declared that the Austro-Hungarian
Empire was to be dissolved. The new Republic of Austria, consisting of most of the German-speaking Alpine part of the former Austrian Empire
, but not the German-speaking Sudetenland
, nor South Tyrol
, recognized the independence of Hungary
, Czechoslovakia
, Poland
, and the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs
. The treaty included 'war reparations' of large sums of money, directed towards the allies, to pay for the costs of the war.
Austria was reduced not only by the loss of crownlands incorporated into the newly created states of Czechoslovakia, Poland, and Yugoslavia (the “successor states”) but by the cession of the southern half of the County of Tyrol
(today the provinces of Trentino and South Tyrol
), Trieste
, Istria
and several Dalmatia
n islands to Italy
and the cession of Bukovina
to Romania
. In total, it lost land to Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia, Poland, Romania, and Italy. Burgenland
, previously a part of Hungary, was awarded to Austria.
An important article of the treaty required Austria to refrain from directly or indirectly compromising its independence, which meant that Austria
could not enter into political or economic union with Germany
without the agreement of the council of the League of Nations
. Accordingly, the new republic's initial self-chosen name of German Austria
(Deutschösterreich) had to be changed to Austria. Many Austrians would come to find this term harsh, due to Austria's later economic weakness, which was caused by loss of land. The economic weakness of Austria would later lead to support for the idea of Anschluss
(political union) with Nazi Germany.
The Austrian Army was limited to a force of 30,000 volunteers. There were numerous provisions dealing with Danubian navigation, the transfer of railways, and other details involved in the breakup of a great empire into several small independent states.
The Treaty of Trianon
in June 1920 between Hungary
and the Allies completed the disposition of the former Dual Monarchy.
The vast reduction of population, territory and resources of the new Austria relative to the old empire wreaked havoc on the economy of the old nation, most notably in Vienna
, an imperial capital without an empire to support it.
The treaty signing ceremony took place at the Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye
.
Allies of World War I
The Entente Powers were the countries at war with the Central Powers during World War I. The members of the Triple Entente were the United Kingdom, France, and the Russian Empire; Italy entered the war on their side in 1915...
on the one hand and by the new Republic of Austria
First Austrian Republic
The Republic of Austria encompasses the period of Austrian history following the signing of the Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye of September 1919, the settlement after the end of World War I which put an end to the Republic of German Austria, continuing up to World War II...
on the other. Like the Treaty of Versailles
Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was one of the peace treaties at the end of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1919, exactly five years after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The other Central Powers on the German side of...
with Germany
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
, it contained the Covenant of the League of Nations
League of Nations
The League of Nations was an intergovernmental organization founded as a result of the Paris Peace Conference that ended the First World War. It was the first permanent international organization whose principal mission was to maintain world peace...
and as a result was not ratified by the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
.
The treaty declared that the Austro-Hungarian
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary , more formally known as the Kingdoms and Lands Represented in the Imperial Council and the Lands of the Holy Hungarian Crown of Saint Stephen, was a constitutional monarchic union between the crowns of the Austrian Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary in...
Empire was to be dissolved. The new Republic of Austria, consisting of most of the German-speaking Alpine part of the former Austrian Empire
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire was a modern era successor empire, which was centered on what is today's Austria and which officially lasted from 1804 to 1867. It was followed by the Empire of Austria-Hungary, whose proclamation was a diplomatic move that elevated Hungary's status within the Austrian Empire...
, but not the German-speaking Sudetenland
Sudetenland
Sudetenland is the German name used in English in the first half of the 20th century for the northern, southwest and western regions of Czechoslovakia inhabited mostly by ethnic Germans, specifically the border areas of Bohemia, Moravia, and those parts of Silesia being within Czechoslovakia.The...
, nor South Tyrol
South Tyrol
South Tyrol , also known by its Italian name Alto Adige, is an autonomous province in northern Italy. It is one of the two autonomous provinces that make up the autonomous region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol. The province has an area of and a total population of more than 500,000 inhabitants...
, recognized the independence of Hungary
Kingdom of Hungary (1920–1946)
The Kingdom of Hungary also known as the Regency, existed from 1920 to 1946 and was a de facto country under Regent Miklós Horthy. Horthy officially represented the abdicated Hungarian monarchy of Charles IV, Apostolic King of Hungary...
, Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovak Republic (1918–1938)
The First Czechoslovak Republic , refers to the first Czechoslovak state that existed from 1918 to 1938. The state was commonly called Czechoslovakia . It was composed of Bohemia, Moravia, Czech Silesia, Slovakia and Subcarpathian Ruthenia...
, Poland
Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, Second Commonwealth of Poland or interwar Poland refers to Poland between the two world wars; a period in Polish history in which Poland was restored as an independent state. Officially known as the Republic of Poland or the Commonwealth of Poland , the Polish state was...
, and the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs
State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs
The State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs was a short-lived state formed from the southernmost parts of the Austro-Hungarian monarchy after its dissolution at the end of the World War I by the resident population of Slovenes, Croats, and Serbs...
. The treaty included 'war reparations' of large sums of money, directed towards the allies, to pay for the costs of the war.
Austria was reduced not only by the loss of crownlands incorporated into the newly created states of Czechoslovakia, Poland, and Yugoslavia (the “successor states”) but by the cession of the southern half of the County of Tyrol
County of Tyrol
The County of Tyrol, Princely County from 1504, was a State of the Holy Roman Empire, from 1814 a province of the Austrian Empire and from 1867 a Cisleithanian crown land of Austria-Hungary...
(today the provinces of Trentino and South Tyrol
South Tyrol
South Tyrol , also known by its Italian name Alto Adige, is an autonomous province in northern Italy. It is one of the two autonomous provinces that make up the autonomous region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol. The province has an area of and a total population of more than 500,000 inhabitants...
), Trieste
Trieste
Trieste is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is situated towards the end of a narrow strip of land lying between the Adriatic Sea and Italy's border with Slovenia, which lies almost immediately south and east of the city...
, Istria
Istria
Istria , formerly Histria , is the largest peninsula in the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula is located at the head of the Adriatic between the Gulf of Trieste and the Bay of Kvarner...
and several Dalmatia
Dalmatia
Dalmatia is a historical region on the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea. It stretches from the island of Rab in the northwest to the Bay of Kotor in the southeast. The hinterland, the Dalmatian Zagora, ranges from fifty kilometers in width in the north to just a few kilometers in the south....
n islands to Italy
Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946)
The Kingdom of Italy was a state forged in 1861 by the unification of Italy under the influence of the Kingdom of Sardinia, which was its legal predecessor state...
and the cession of Bukovina
Bukovina
Bukovina is a historical region on the northern slopes of the northeastern Carpathian Mountains and the adjoining plains.-Name:The name Bukovina came into official use in 1775 with the region's annexation from the Principality of Moldavia to the possessions of the Habsburg Monarchy, which became...
to Romania
Kingdom of Romania
The Kingdom of Romania was the Romanian state based on a form of parliamentary monarchy between 13 March 1881 and 30 December 1947, specified by the first three Constitutions of Romania...
. In total, it lost land to Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia, Poland, Romania, and Italy. Burgenland
Burgenland
Burgenland is the easternmost and least populous state or Land of Austria. It consists of two Statutarstädte and seven districts with in total 171 municipalities. It is 166 km long from north to south but much narrower from west to east...
, previously a part of Hungary, was awarded to Austria.
An important article of the treaty required Austria to refrain from directly or indirectly compromising its independence, which meant that Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
could not enter into political or economic union with Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
without the agreement of the council of the League of Nations
League of Nations
The League of Nations was an intergovernmental organization founded as a result of the Paris Peace Conference that ended the First World War. It was the first permanent international organization whose principal mission was to maintain world peace...
. Accordingly, the new republic's initial self-chosen name of German Austria
German Austria
Republic of German Austria was created following World War I as the initial rump state for areas with a predominantly German-speaking population within what had been the Austro-Hungarian Empire, without the Kingdom of Hungary, which in 1918 had become the Hungarian Democratic Republic.German...
(Deutschösterreich) had to be changed to Austria. Many Austrians would come to find this term harsh, due to Austria's later economic weakness, which was caused by loss of land. The economic weakness of Austria would later lead to support for the idea of Anschluss
Anschluss
The Anschluss , also known as the ', was the occupation and annexation of Austria into Nazi Germany in 1938....
(political union) with Nazi Germany.
The Austrian Army was limited to a force of 30,000 volunteers. There were numerous provisions dealing with Danubian navigation, the transfer of railways, and other details involved in the breakup of a great empire into several small independent states.
The Treaty of Trianon
Treaty of Trianon
The Treaty of Trianon was the peace agreement signed in 1920, at the end of World War I, between the Allies of World War I and Hungary . The treaty greatly redefined and reduced Hungary's borders. From its borders before World War I, it lost 72% of its territory, which was reduced from to...
in June 1920 between Hungary
Kingdom of Hungary (1920–1946)
The Kingdom of Hungary also known as the Regency, existed from 1920 to 1946 and was a de facto country under Regent Miklós Horthy. Horthy officially represented the abdicated Hungarian monarchy of Charles IV, Apostolic King of Hungary...
and the Allies completed the disposition of the former Dual Monarchy.
The vast reduction of population, territory and resources of the new Austria relative to the old empire wreaked havoc on the economy of the old nation, most notably in Vienna
Vienna
Vienna is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Austria and one of the nine states of Austria. Vienna is Austria's primary city, with a population of about 1.723 million , and is by far the largest city in Austria, as well as its cultural, economic, and political centre...
, an imperial capital without an empire to support it.
The treaty signing ceremony took place at the Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye
Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye
The Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye is a royal palace in the commune of Saint-Germain-en-Laye, in the département of Yvelines, about 19 km west of Paris, France. Today, it houses the Musée d'Archéologie Nationale ....
.
See also
- Aftermath of World War IAftermath of World War IThe fighting in World War I ended in western Europe when the Armistice took effect at 11:00 am GMT on November 11, 1918, and in eastern Europe by the early 1920s. During and in the aftermath of the war the political, cultural, and social order was drastically changed in Europe, Asia and Africa,...
- Minority TreatiesMinority TreatiesMinority Treaties refer to the treaties, League of Nations Mandates, and unilateral declarations made by countries applying for membership in the League of Nations and United Nations...
- Paris Peace Conference, 1919Paris Peace Conference, 1919The Paris Peace Conference was the meeting of the Allied victors following the end of World War I to set the peace terms for the defeated Central Powers following the armistices of 1918. It took place in Paris in 1919 and involved diplomats from more than 32 countries and nationalities...
- Treaty of TrianonTreaty of TrianonThe Treaty of Trianon was the peace agreement signed in 1920, at the end of World War I, between the Allies of World War I and Hungary . The treaty greatly redefined and reduced Hungary's borders. From its borders before World War I, it lost 72% of its territory, which was reduced from to...
- US-Austrian Peace Treaty (1921)
External links
- Animated map of Europe at the end of the First World War
- Text of the Treaty, from the website of the Australasian Legal Information InstituteAustralasian Legal Information InstituteThe Australasian Legal Information Institute is an institution operated jointly by the Faculties of Law of the University of Technology Sydney and the University of New South Wales. It is notable for establishing Australia's largest on-line database on Australian legislation and case law...
, hosted by UNSWUniversity of New South WalesThe University of New South Wales , is a research-focused university based in Kensington, a suburb in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia...
and UTSUniversity of Technology, SydneyThe University of Technology Sydney is a university in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. The university was founded in its current form in 1981, although its origins trace back to the 1870s. UTS is notable for its central location as the only university with its main campuses within the Sydney CBD...

