.gif)
Treaty of Fort Stanwix (1784)
Encyclopedia
Treaty
A treaty is an express agreement under international law entered into by actors in international law, namely sovereign states and international organizations. A treaty may also be known as an agreement, protocol, covenant, convention or exchange of letters, among other terms...
signed in October 1784 at Fort Stanwix
Fort Stanwix
Fort Stanwix was a colonial fort whose construction was started on August 26, 1758, by British General John Stanwix, at the location of present-day Rome, New York, but was not completed until about 1762. The fort guarded a portage known as the Oneida Carrying Place during the French and Indian War...
, located in present-day Rome, New York
Rome, New York
Rome is a city in Oneida County, New York, United States. It is located in north-central or "upstate" New York. The population was 44,797 at the 2010 census. It is in New York's 24th congressional district. In 1758, British forces began construction of Fort Stanwix at this strategic location, but...
, between the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and Native Americans
Native Americans in the United States
Native Americans in the United States are the indigenous peoples in North America within the boundaries of the present-day continental United States, parts of Alaska, and the island state of Hawaii. They are composed of numerous, distinct tribes, states, and ethnic groups, many of which survive as...
. It was one of several treaties between Native Americans and the United States after the American victory in the Revolutionary War
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War , the American War of Independence, or simply the Revolutionary War, began as a war between the Kingdom of Great Britain and thirteen British colonies in North America, and ended in a global war between several European great powers.The war was the result of the...
.
The treaty served as a peace treaty between the Iroquois
Iroquois
The Iroquois , also known as the Haudenosaunee or the "People of the Longhouse", are an association of several tribes of indigenous people of North America...
and the Americans, since the Indians had been ignored in the Treaty of Paris
Treaty of Paris (1783)
The Treaty of Paris, signed on September 3, 1783, ended the American Revolutionary War between Great Britain on the one hand and the United States of America and its allies on the other. The other combatant nations, France, Spain and the Dutch Republic had separate agreements; for details of...
. Joseph Brant
Joseph Brant
Thayendanegea or Joseph Brant was a Mohawk military and political leader, based in present-day New York, who was closely associated with Great Britain during and after the American Revolution. He was perhaps the most well-known American Indian of his generation...
was the leading Indian at the start of negotiations. He said "But we must observe to you, that we are sent in order to make peace, and that we are not authorized, to stipulate any particular cession of lands." Brant had to leave early for a planned trip to England. The leading Indian representatives who signed the treaty were Cornplanter
Cornplanter
Gaiänt'wakê was a Seneca war-chief. He was the son of a Seneca mother, Aliquipiso, and a Dutch father, Johannes Abeel. He also carried the name John Abeel after his fur trader father...
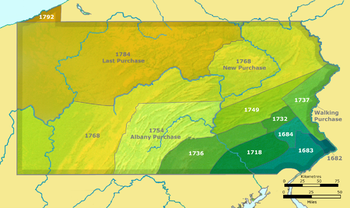
and Captain Aaron Hill. In this treaty the Iroquois Confederacy ceded all claims to the Ohio territory, a strip of land along the Niagara river, and all land west of mouth of Buffalo creek. In Pennsylvania the land acquired in this treaty is known as the "Last Purchase".
The Six Nations
Iroquois
The Iroquois , also known as the Haudenosaunee or the "People of the Longhouse", are an association of several tribes of indigenous people of North America...
council at Buffalo Creek refused to ratify the treaty, denying that their delegates had the power to give away such large tracts of land. They asked the Americans for return of the deeds and promised to indemnify them for any presents they had given. The general Indian confederacy
Western Confederacy
The Western Confederacy, also known as Western Indian Confederacy, was a loose confederacy of North American Natives in the Great Lakes region following the American Revolutionary War...
also disavowed the treaty because most of the Six Nations did not live in the Ohio territory. The Ohio Country natives, including the Shawnee
Shawnee
The Shawnee, Shaawanwaki, Shaawanooki and Shaawanowi lenaweeki, are an Algonquian-speaking people native to North America. Historically they inhabited the areas of Ohio, Virginia, West Virginia, Western Maryland, Kentucky, Indiana, and Pennsylvania...
Indians, the Mingo Indians, the Delaware
Delaware
Delaware is a U.S. state located on the Atlantic Coast in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It is bordered to the south and west by Maryland, and to the north by Pennsylvania...
Indians, and several other tribes rejected the treaty. A series of treaties and land sales with these tribes soon followed:
- 1785 Treaty of Fort McIntoshTreaty of Fort McIntoshThe Treaty of Fort McIntosh was a treaty between the United States government and representatives of the Wyandotte, Delaware, Chippewa and Ottawa nations of Native Americans...
with Wyandotte, DelawareLenapeThe Lenape are an Algonquian group of Native Americans of the Northeastern Woodlands. They are also called Delaware Indians. As a result of the American Revolutionary War and later Indian removals from the eastern United States, today the main groups live in Canada, where they are enrolled in the...
, Chippewa and Ottawa leaders for lands in OhioOhioOhio is a Midwestern state in the United States. The 34th largest state by area in the U.S.,it is the 7th‑most populous with over 11.5 million residents, containing several major American cities and seven metropolitan areas with populations of 500,000 or more.The state's capital is Columbus... - 1786 Treaty of Fort FinneyTreaty of Fort FinneyThe Treaty of Fort Finney, also known as the Treaty at the Mouth of the Great Miami, was signed in 1786 between the United States and Shawnee leaders after the American Revolutionary War, ceding parts of the Ohio country to the United States. The treaty was reluctantly signed by the Shawnees, and...
with ShawneeShawneeThe Shawnee, Shaawanwaki, Shaawanooki and Shaawanowi lenaweeki, are an Algonquian-speaking people native to North America. Historically they inhabited the areas of Ohio, Virginia, West Virginia, Western Maryland, Kentucky, Indiana, and Pennsylvania...
leaders for portions of Ohio - 1788 Phelps and Gorham PurchasePhelps and Gorham PurchaseThe Phelps and Gorham Purchase was the purchase in 1788 of the pre-emptive right to some 6,000,000 acres of land in western New York State for $1,000,000 . This was all land in western New York west of Seneca Lake between Lake Ontario and the Pennsylvania border...
with the Iroquois for lands in New York State east of the Genesee RiverGenesee RiverThe Genesee River is a North American river flowing northward through the Twin Tiers of Pennsylvania and New York. The river provided the original power for the Rochester area's 19th century mills and still provides hydroelectric power for downtown Rochester.... - 1789 Treaty of Fort HarmarTreaty of Fort HarmarThe Treaty of Fort Harmar was an agreement between the United States government and numerous Native American tribes with claims to the Ohio Country. it was signed at Fort Harmar, near present-day Marietta, Ohio, on January 9, 1789. Representatives of the Six Nations and other groups including the...
reiterating claims in Ohio - 1794 Treaty of CanandaiguaTreaty of CanandaiguaThe Treaty of Canandaigua is a treaty signed after the American Revolutionary War between the Grand Council of the Six Nations and President George Washington representing the United States of America....
establishing peace with the Iroquois and affirming lands rights in New York State east of the Genesee River - 1797 Treaty of Big TreeTreaty of Big TreeTreaty of Big Tree was a formal treaty, held from August 20, 1797 until September 16, 1797, between the Seneca nation and the United States of America. The delegates for both parties met at the residence of William Wadsworth, an early pioneer of the area and Captain of the local militia, in what is...
with the Iroquois for lands in New York State west of the Genesee River

