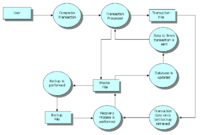
Transaction Processing System
Encyclopedia
A transaction processing system is a type of information system
. TPSs collect, store, modify, and retrieve the transactions
of an organization. A transaction is an event that generates or modifies data
that is eventually stored in an information system. To be considered a transaction processing system the computer must pass the ACID test
. The essence of a transaction program is that it manages data that must be left in a consistent state, e.g. if an electronic payment is made, the amount must be both withdrawn from one account and added to the other; it cannot complete only one of those steps. Either both must occur, or neither. In case of a failure preventing transaction completion, the partially executed transaction must be 'rolled back
' by the TPS. While this type of integrity must be provided also for batch transaction processing
, it is particularly important for online processing: if e.g. an airline seat reservation system is accessed by multiple operators, after an empty seat inquiry, the seat reservation data must be locked until the reservation is made, otherwise another user may get the impression a seat is still free while it is actually being booked at the time. Without proper transaction monitoring, double bookings may occur. Other transaction monitor functions include deadlock
detection and resolution (deadlocks may be inevitable in certain cases of cross-dependence on data), and transaction logging (in 'journals') for 'forward recovery' in case of massive failures.
Transaction Processing is not limited to application programs. The 'journaled file system' provided with IBMs AIX Unix operating system employs similar techniques to maintain file system integrity, including a journal.
is a form of transaction processing. Batch processing involves processing several transactions at the same time, and the results of each transaction are not immediately available when the transaction is being entered; there is a time delay.
Transactions are accumulated for a certain period (say for day) where updates are made especially after work.
Online transaction processing is the form of transaction processing that processes data as it becomes available.
Each transaction in real-time processing is unique. It is not part of a group of transactions, even though those transactions are processed in the same manner. Transactions in real-time processing are stand-alone both in the entry to the system and also in the handling of output.
Real-time processing requires the master file to be available more often for updating and reference than batch processing. The database is not accessible all of the time for batch processing.
Real-time processing has fewer errors than batch processing, as transaction data
is validated and entered immediately. With batch processing, the data is organised and stored before the master file is updated. Errors can occur during these steps.
Infrequent errors may occur in real-time processing; however, they are often tolerated. It is not practical to shut down the system for infrequent errors.
More computer operators are required in real-time processing, as the operations are not centralised. It is more difficult to maintain a real-time processing system than a batch processing system.
with a rapid response time is critical. Businesses cannot afford to have customers waiting for a TPS to respond, the turnaround time from the input of the transaction to the production for the output must be a few seconds or less.
and recovery procedures essential.
needs to consistently accept airline reservations from a range of travel agents, accepting different transactions data from different travel agents would be a problem.
is a collection of data neatly organized, which stores the accounting and operational records in the database
. Databases are always protective of their delicate data, so they usually have a restricted view of certain data. Databases are designed using hierarchical, network or relational structures; each structure is effective in its own sense.
The following features are included in real time transaction processing systems:
In a TPS, there are 5 different types of files. The TPS uses the files to store and organize its transaction data:
that collects information from different sources. When it's gathered in real-time transactions it can be used for analysis efficiently if it's stored in a data warehouse. It provides data that are consolidated, subject-oriented, historical and read-only:
 Since business organizations have become very dependent on TPSs, a breakdown in their TPS may stop the business' regular routines and thus stopping its operation for a certain amount of time. In order to prevent data loss and minimize disruptions when a TPS breaks down a well-designed backup
Since business organizations have become very dependent on TPSs, a breakdown in their TPS may stop the business' regular routines and thus stopping its operation for a certain amount of time. In order to prevent data loss and minimize disruptions when a TPS breaks down a well-designed backup
and recovery procedure is put into use. The recovery process can rebuild the system when it goes down.
failure, incorrect or invalid data, computer viruses, software application errors or natural or man-made disasters. As it's not possible to prevent all TPS failures, a TPS must be able to cope with failures. The TPS must be able to detect and correct errors when they occur. A TPS will go through a recovery of the database
to cope when the system fails, it involves the backup
, journal, checkpoint, and recovery manager:
If a checkpoint is interrupted and a recovery is required, then the database system must start recovery from a previous successful checkpoint. Checkpointing can be either transaction-consistent or non-transaction-consistent (called also fuzzy checkpointing). Transaction-consistent checkpointing produces a persistent database image that is sufficient to recover the database to the state that was externally perceived at the moment of starting the checkpointing. A non-transaction-consistent checkpointing results in a persistent database image that is insufficient to perform a recovery of the database state. To perform the database recovery, additional information is needed, typically contained in transaction logs. Transaction consistent checkpointing refers to a consistent database, which doesn't necessarily include all the latest committed transactions, but all modifications made by transactions, that were committed at the time checkpoint creation was started, are fully present. A non-consistent transaction refers to a checkpoint which is not necessarily a consistent database, and can't be recovered to one without all log records generated for open transactions included in the checkpoint. Depending on the type of database management system implemented a checkpoint may incorporate indexes or storage pages (user data), indexes and storage pages. If no indexes are incorporated into the checkpoint, indexes must be created when the database is restored from the checkpoint image.
Depending on how the system failed, there can be two different recovery procedures used. Generally, the procedures involves restoring data that has been collected from a backup device and then running the transaction processing again. Two types of recovery are backward recovery and forward recovery:
This procedure refers to at least three generations of backup
master files. thus, the most recent backup is the son, the oldest backup is the grandfather. It's commonly used for a batch transaction processing system with a magnetic tape
. If the system fails during a batch run, the master file is recreated by using the son backup and then restarting the batch. However if the son backup fails, is corrupted or destroyed, then the next generation up backup (father) is required. Likewise, if that fails, then the next generation up backup (grandfather) is required. Of course the older the generation, the more the data may be out of date. Organizations can have up to twenty generations of backup.
This only occurs when parts of the master file are backed up. The master file is usually backed up to magnetic tape
at regular times, this could be daily, weekly or monthly. Completed transactions since the last backup are stored separately and are called journals, or journal files. The master file can be recreated from the journal files on the backup tape if the system is to fail.
. Transactions will be collected and updated as a batch at when it's convenient or economical to process them. Historically, this was the most common method as the information technology
did not exist to allow real-time processing.
The two stages in batch processing are:
Updating in batch requires sequential access
- since it uses a magnetic tape
this is the only way to access data. A batch will start at the beginning of the tape, then reading it from the order it was stored; it's very time-consuming to locate specific transactions.
The information technology
used includes a secondary storage medium which can store large quantities of data inexpensively (thus the common choice of a magnetic tape
). The software used to collect data does not have to be online - it doesn't even need a user interface
.
and larger bandwidth
), real-time updating is possible.
Steps in a real-time update involve the sending of a transaction data to an online database in a master file. The person providing information is usually able to help with error correction and receives confirmation of the transaction completion.
Updating in real-time uses direct access
of data. This occurs when data are accessed without accessing previous data items. The storage device stores data in a particular location based on a mathematical procedure. This will then be calculated to find an approximate location of the data. If data are not found at this location, it will search through successive locations until it's found.
The information technology
used could be a secondary storage medium that can store large amounts of data and provide quick access (thus the common choice of a magnetic disk).
Management information system
A management information system provides information needed to manage organizations efficiently and effectively. Management information systems involve three primary resources: people, technology, and information. Management information systems are distinct from other information systems in that...
. TPSs collect, store, modify, and retrieve the transactions
Transaction processing
In computer science, transaction processing is information processing that is divided into individual, indivisible operations, called transactions. Each transaction must succeed or fail as a complete unit; it cannot remain in an intermediate state...
of an organization. A transaction is an event that generates or modifies data
Data
The term data refers to qualitative or quantitative attributes of a variable or set of variables. Data are typically the results of measurements and can be the basis of graphs, images, or observations of a set of variables. Data are often viewed as the lowest level of abstraction from which...
that is eventually stored in an information system. To be considered a transaction processing system the computer must pass the ACID test
ACID
In computer science, ACID is a set of properties that guarantee database transactions are processed reliably. In the context of databases, a single logical operation on the data is called a transaction...
. The essence of a transaction program is that it manages data that must be left in a consistent state, e.g. if an electronic payment is made, the amount must be both withdrawn from one account and added to the other; it cannot complete only one of those steps. Either both must occur, or neither. In case of a failure preventing transaction completion, the partially executed transaction must be 'rolled back
Rollback (data management)
In database technologies, a rollback is an operation which returns the database to some previous state. Rollbacks are important for database integrity, because they mean that the database can be restored to a clean copy even after erroneous operations are performed...
' by the TPS. While this type of integrity must be provided also for batch transaction processing
Batch processing
Batch processing is execution of a series of programs on a computer without manual intervention.Batch jobs are set up so they can be run to completion without manual intervention, so all input data is preselected through scripts or command-line parameters...
, it is particularly important for online processing: if e.g. an airline seat reservation system is accessed by multiple operators, after an empty seat inquiry, the seat reservation data must be locked until the reservation is made, otherwise another user may get the impression a seat is still free while it is actually being booked at the time. Without proper transaction monitoring, double bookings may occur. Other transaction monitor functions include deadlock
Deadlock
A deadlock is a situation where in two or more competing actions are each waiting for the other to finish, and thus neither ever does. It is often seen in a paradox like the "chicken or the egg"...
detection and resolution (deadlocks may be inevitable in certain cases of cross-dependence on data), and transaction logging (in 'journals') for 'forward recovery' in case of massive failures.
Transaction Processing is not limited to application programs. The 'journaled file system' provided with IBMs AIX Unix operating system employs similar techniques to maintain file system integrity, including a journal.
Contrasted with batch processing
Batch processingBatch processing
Batch processing is execution of a series of programs on a computer without manual intervention.Batch jobs are set up so they can be run to completion without manual intervention, so all input data is preselected through scripts or command-line parameters...
is a form of transaction processing. Batch processing involves processing several transactions at the same time, and the results of each transaction are not immediately available when the transaction is being entered; there is a time delay.
Transactions are accumulated for a certain period (say for day) where updates are made especially after work.
Online transaction processing is the form of transaction processing that processes data as it becomes available.
Real-time and batch processing
There are a number of differences between real-time and batch processing. These are outlined below:Each transaction in real-time processing is unique. It is not part of a group of transactions, even though those transactions are processed in the same manner. Transactions in real-time processing are stand-alone both in the entry to the system and also in the handling of output.
Real-time processing requires the master file to be available more often for updating and reference than batch processing. The database is not accessible all of the time for batch processing.
Real-time processing has fewer errors than batch processing, as transaction data
Transaction data
Transaction data are data describing an event and is usually described with verbs. Transaction data always has a time dimension, a numerical value and refers to one or more objects Transaction data are data describing an event (the change as a result of a transaction) and is usually described with...
is validated and entered immediately. With batch processing, the data is organised and stored before the master file is updated. Errors can occur during these steps.
Infrequent errors may occur in real-time processing; however, they are often tolerated. It is not practical to shut down the system for infrequent errors.
More computer operators are required in real-time processing, as the operations are not centralised. It is more difficult to maintain a real-time processing system than a batch processing system.
Rapid response
Fast performancePerformance testing
In software engineering, performance testing is in general testing performed to determine how a system performs in terms of responsiveness and stability under a particular workload...
with a rapid response time is critical. Businesses cannot afford to have customers waiting for a TPS to respond, the turnaround time from the input of the transaction to the production for the output must be a few seconds or less.
Reliability
Many organizations rely heavily on their TPS; a breakdown will disrupt operations or even stop the business. For a TPS to be effective its failure rate must be very low. If a TPS does fail, then quick and accurate recovery must be possible. This makes well–designed backupBackup
In information technology, a backup or the process of backing up is making copies of data which may be used to restore the original after a data loss event. The verb form is back up in two words, whereas the noun is backup....
and recovery procedures essential.
Inflexibility
A TPS wants every transaction to be processed in the same way regardless of the user, the customer or the time for day. If a TPS were flexible, there would be too many opportunities for non-standard operations, for example, a commercial airlineAirline
An airline provides air transport services for traveling passengers and freight. Airlines lease or own their aircraft with which to supply these services and may form partnerships or alliances with other airlines for mutual benefit...
needs to consistently accept airline reservations from a range of travel agents, accepting different transactions data from different travel agents would be a problem.
Controlled processing
The processing in a TPS must support an organization's operations. For example if an organization allocates roles and responsibilities to particular employees, then the TPS should enforce and maintain this requirement. An example of this is an ATM transaction.Atomicity
A transaction’s changes to the state are atomic: either all happen or none happen. These changes include database changes, messages, and actions on transducers.Consistency
Consistency: A transaction is a correct transformation of the state. The actions taken as a group do not violate any of the integrity constraints associated with the state. This requires that the transaction be a correct program!Isolation
Even though transactions execute concurrently, it appears to each transaction T, that others executed either before T or after T, but not both.Durability
Once a transaction completes successfully (commits), its changes to the state survive failures.Concurrency
Ensures that two users cannot change the same data at the same time. That is, one user cannot change a piece of data before another user has finished with it. For example, if an airline ticket agent starts to reserve the last seat on a flight, then another agent cannot tell another passenger that a seat is availableStoring and retrieving
Storing and retrieving information from a TPS must be efficient and effective. The data are stored in warehouses or other databases, the system must be well designed for its backup and recovery procedures.Databases and files
The storage and retrieval of data must be accurate as it is used many times throughout the day. A databaseDatabase
A database is an organized collection of data for one or more purposes, usually in digital form. The data are typically organized to model relevant aspects of reality , in a way that supports processes requiring this information...
is a collection of data neatly organized, which stores the accounting and operational records in the database
Database
A database is an organized collection of data for one or more purposes, usually in digital form. The data are typically organized to model relevant aspects of reality , in a way that supports processes requiring this information...
. Databases are always protective of their delicate data, so they usually have a restricted view of certain data. Databases are designed using hierarchical, network or relational structures; each structure is effective in its own sense.
- Hierarchical structure: organizes data in a series of levels, hence why it is called hierarchal. Its top to bottom like structure consists of nodesNode (computer science)A node is a record consisting of one or more fields that are links to other nodes, and a data field. The link and data fields are often implemented by pointers or references although it is also quite common for the data to be embedded directly in the node. Nodes are used to build linked, often...
and branches; each child node has branches and is only linked to one higher level parent node. - Network structure: Similar to hierarchical, network structures also organizes data using nodes and branches. But, unlike hierarchical, each child node can be linked to multiple, higher parent nodes.
- Relational structure: Unlike network and hierarchical, a relational database organizes its data in a series of related tables. This gives flexibility as relationships between the tables are built.
 |
 |
 |
The following features are included in real time transaction processing systems:
- Good data placement: The database should be designed to access patterns of data from many simultaneous users.
- Short transactions: Short transactions enables quick processing. This avoids concurrency and paces the systems.
- Real-time backup: BackupBackupIn information technology, a backup or the process of backing up is making copies of data which may be used to restore the original after a data loss event. The verb form is back up in two words, whereas the noun is backup....
should be scheduled between low times of activity to prevent lag of the server. - High normalizationDatabase normalizationIn the design of a relational database management system , the process of organizing data to minimize redundancy is called normalization. The goal of database normalization is to decompose relations with anomalies in order to produce smaller, well-structured relations...
: This lowers redundant information to increase the speed and improve concurrency, this also improves backups. - Archiving of historical data: Uncommonly used data are moved into other databases or backed up tables. This keeps tables small and also improves backup times.
- Good hardware configuration: HardwareHardwareHardware is a general term for equipment such as keys, locks, hinges, latches, handles, wire, chains, plumbing supplies, tools, utensils, cutlery and machine parts. Household hardware is typically sold in hardware stores....
must be able to handle many users and provide quick response times.
In a TPS, there are 5 different types of files. The TPS uses the files to store and organize its transaction data:
- Master file: Contains information about an organization’s business situation. Most transactions and databases are stored in the master file.
- Transaction file: It is the collection of transaction records. It helps to update the master file and also serves as audit trails and transaction history.
- Report file: Contains data that has been formatted for presentation to a user.
- Work file: Temporary files in the system used during the processing.
- Program file: Contains the instructions for the processing of data.
Data warehouse
A data warehouse is a databaseDatabase
A database is an organized collection of data for one or more purposes, usually in digital form. The data are typically organized to model relevant aspects of reality , in a way that supports processes requiring this information...
that collects information from different sources. When it's gathered in real-time transactions it can be used for analysis efficiently if it's stored in a data warehouse. It provides data that are consolidated, subject-oriented, historical and read-only:
- Consolidated: Data are organised with consistent naming conventions, measurements, attributes and semantics. It allows data from a data warehouse from across the organization to be effectively used in a consistent manner.
- Subject-oriented: Large amounts of data are stored across an organization, some data could be irrelevant for reports and makes queryingInformation retrievalInformation retrieval is the area of study concerned with searching for documents, for information within documents, and for metadata about documents, as well as that of searching structured storage, relational databases, and the World Wide Web...
the data difficult. It organizes only key business information from operational sources so that it's available for analysis. - Historical: Real-time TPS represent the current value at any time, an example could be stock levels. If past data are kept, querying the database could return a different response. It stores series of snapshots for an organisation's operational data generated over a period of time.
- Read-only: Once data are moved into a data warehouse, it becomes read-only, unless it was incorrect. Since it represents a snapshot of a certain time, it must never be updated. Only operations which occur in a data warehouse are loading and querying data.
Backup procedures

Backup
In information technology, a backup or the process of backing up is making copies of data which may be used to restore the original after a data loss event. The verb form is back up in two words, whereas the noun is backup....
and recovery procedure is put into use. The recovery process can rebuild the system when it goes down.
Recovery process
A TPS may fail for many reasons. These reasons could include a system failure, human errors, hardwareHardware
Hardware is a general term for equipment such as keys, locks, hinges, latches, handles, wire, chains, plumbing supplies, tools, utensils, cutlery and machine parts. Household hardware is typically sold in hardware stores....
failure, incorrect or invalid data, computer viruses, software application errors or natural or man-made disasters. As it's not possible to prevent all TPS failures, a TPS must be able to cope with failures. The TPS must be able to detect and correct errors when they occur. A TPS will go through a recovery of the database
Database
A database is an organized collection of data for one or more purposes, usually in digital form. The data are typically organized to model relevant aspects of reality , in a way that supports processes requiring this information...
to cope when the system fails, it involves the backup
Backup
In information technology, a backup or the process of backing up is making copies of data which may be used to restore the original after a data loss event. The verb form is back up in two words, whereas the noun is backup....
, journal, checkpoint, and recovery manager:
- Journal: A journal maintains an audit trail of transactions and database changes. Transaction logs and Database change logs are used, a transaction log records all the essential data for each transactions, including data values, time of transaction and terminal number. A database change log contains before and after copies of records that have been modified by transactions.
- Checkpoint: The purpose of checkpointing is to provide a snapshot of the data within the database. A checkpoint, in general, is any identifier or other reference that identifies at a point in time the state of the database. Modifications to database pages are performed in memory and are not necessarily written to disk after every update. Therefore, periodically, the database system must perform a checkpoint to write these updates which are held in-memory to the storage disk. Writing these updates to storage disk creates a point in time in which the database system can apply changes contained in a transaction log during recovery after an unexpected shut down or crash of the database system.
If a checkpoint is interrupted and a recovery is required, then the database system must start recovery from a previous successful checkpoint. Checkpointing can be either transaction-consistent or non-transaction-consistent (called also fuzzy checkpointing). Transaction-consistent checkpointing produces a persistent database image that is sufficient to recover the database to the state that was externally perceived at the moment of starting the checkpointing. A non-transaction-consistent checkpointing results in a persistent database image that is insufficient to perform a recovery of the database state. To perform the database recovery, additional information is needed, typically contained in transaction logs. Transaction consistent checkpointing refers to a consistent database, which doesn't necessarily include all the latest committed transactions, but all modifications made by transactions, that were committed at the time checkpoint creation was started, are fully present. A non-consistent transaction refers to a checkpoint which is not necessarily a consistent database, and can't be recovered to one without all log records generated for open transactions included in the checkpoint. Depending on the type of database management system implemented a checkpoint may incorporate indexes or storage pages (user data), indexes and storage pages. If no indexes are incorporated into the checkpoint, indexes must be created when the database is restored from the checkpoint image.
- Recovery Manager: A recovery manager is a program which restores the database to a correct condition which can restart the transaction processing.
Depending on how the system failed, there can be two different recovery procedures used. Generally, the procedures involves restoring data that has been collected from a backup device and then running the transaction processing again. Two types of recovery are backward recovery and forward recovery:
- Backward recovery: used to undoUndoUndo is a command in many computer programs. It erases the last change done to the document reverting it to an older state. In some more advanced programs such as graphic processing, undo will negate the last command done to the file being edited....
unwanted changes to the database. It reverses the changes made by transactions which have been aborted. It involves the logic of reprocessing each transaction, which is very time-consuming.
- Forward recovery: it starts with a backupBackupIn information technology, a backup or the process of backing up is making copies of data which may be used to restore the original after a data loss event. The verb form is back up in two words, whereas the noun is backup....
copy of the database. The transaction will then reprocess according to the transaction journal that occurred between the time the backup was made and the present time. It's much faster and more accurate.
Types of back-up procedures
There are two main types of Back-up Procedures: Grandfather-father-son and Partial backups:Grandfather-father-son
This procedure refers to at least three generations of backup
Backup
In information technology, a backup or the process of backing up is making copies of data which may be used to restore the original after a data loss event. The verb form is back up in two words, whereas the noun is backup....
master files. thus, the most recent backup is the son, the oldest backup is the grandfather. It's commonly used for a batch transaction processing system with a magnetic tape
Magnetic tape
Magnetic tape is a medium for magnetic recording, made of a thin magnetizable coating on a long, narrow strip of plastic. It was developed in Germany, based on magnetic wire recording. Devices that record and play back audio and video using magnetic tape are tape recorders and video tape recorders...
. If the system fails during a batch run, the master file is recreated by using the son backup and then restarting the batch. However if the son backup fails, is corrupted or destroyed, then the next generation up backup (father) is required. Likewise, if that fails, then the next generation up backup (grandfather) is required. Of course the older the generation, the more the data may be out of date. Organizations can have up to twenty generations of backup.
Partial backups
This only occurs when parts of the master file are backed up. The master file is usually backed up to magnetic tape
Magnetic tape
Magnetic tape is a medium for magnetic recording, made of a thin magnetizable coating on a long, narrow strip of plastic. It was developed in Germany, based on magnetic wire recording. Devices that record and play back audio and video using magnetic tape are tape recorders and video tape recorders...
at regular times, this could be daily, weekly or monthly. Completed transactions since the last backup are stored separately and are called journals, or journal files. The master file can be recreated from the journal files on the backup tape if the system is to fail.
Updating in a batch
This is used when transactions are recorded on paper (such as bills and invoices) or when it's being stored on a magnetic tapeMagnetic tape
Magnetic tape is a medium for magnetic recording, made of a thin magnetizable coating on a long, narrow strip of plastic. It was developed in Germany, based on magnetic wire recording. Devices that record and play back audio and video using magnetic tape are tape recorders and video tape recorders...
. Transactions will be collected and updated as a batch at when it's convenient or economical to process them. Historically, this was the most common method as the information technology
Information technology
Information technology is the acquisition, processing, storage and dissemination of vocal, pictorial, textual and numerical information by a microelectronics-based combination of computing and telecommunications...
did not exist to allow real-time processing.
The two stages in batch processing are:
- Collecting and storage of the transaction data into a transaction file - this involves sorting the data into sequential order.
- Processing the data by updating the master file - which can be difficult, this may involve data additions, updates and deletions that may require to happen in a certain order. If an error occurs, then the entire batch fails.
Updating in batch requires sequential access
Sequential access
In computer science, sequential access means that a group of elements is accessed in a predetermined, ordered sequence. Sequential access is sometimes the only way of accessing the data, for example if it is on a tape...
- since it uses a magnetic tape
Magnetic tape
Magnetic tape is a medium for magnetic recording, made of a thin magnetizable coating on a long, narrow strip of plastic. It was developed in Germany, based on magnetic wire recording. Devices that record and play back audio and video using magnetic tape are tape recorders and video tape recorders...
this is the only way to access data. A batch will start at the beginning of the tape, then reading it from the order it was stored; it's very time-consuming to locate specific transactions.
The information technology
Information technology
Information technology is the acquisition, processing, storage and dissemination of vocal, pictorial, textual and numerical information by a microelectronics-based combination of computing and telecommunications...
used includes a secondary storage medium which can store large quantities of data inexpensively (thus the common choice of a magnetic tape
Magnetic tape
Magnetic tape is a medium for magnetic recording, made of a thin magnetizable coating on a long, narrow strip of plastic. It was developed in Germany, based on magnetic wire recording. Devices that record and play back audio and video using magnetic tape are tape recorders and video tape recorders...
). The software used to collect data does not have to be online - it doesn't even need a user interface
User interface
The user interface, in the industrial design field of human–machine interaction, is the space where interaction between humans and machines occurs. The goal of interaction between a human and a machine at the user interface is effective operation and control of the machine, and feedback from the...
.
Updating in real-time
This is the immediate processing of data. It provides instant confirmation of a transaction. This involves a large amount of users who are simultaneously performing transactions to change data. Because of advances in technology (such as the increase in the speed of data transmissionData transmission
Data transmission, digital transmission, or digital communications is the physical transfer of data over a point-to-point or point-to-multipoint communication channel. Examples of such channels are copper wires, optical fibres, wireless communication channels, and storage media...
and larger bandwidth
Bandwidth (computing)
In computer networking and computer science, bandwidth, network bandwidth, data bandwidth, or digital bandwidth is a measure of available or consumed data communication resources expressed in bits/second or multiples of it .Note that in textbooks on wireless communications, modem data transmission,...
), real-time updating is possible.
Steps in a real-time update involve the sending of a transaction data to an online database in a master file. The person providing information is usually able to help with error correction and receives confirmation of the transaction completion.
Updating in real-time uses direct access
Direct access
Direct Access may refer to:*DirectAccess, a network technology in Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2*Direct access, a concept in computer science*Direct Access Archive, a proprietary file format...
of data. This occurs when data are accessed without accessing previous data items. The storage device stores data in a particular location based on a mathematical procedure. This will then be calculated to find an approximate location of the data. If data are not found at this location, it will search through successive locations until it's found.
The information technology
Information technology
Information technology is the acquisition, processing, storage and dissemination of vocal, pictorial, textual and numerical information by a microelectronics-based combination of computing and telecommunications...
used could be a secondary storage medium that can store large amounts of data and provide quick access (thus the common choice of a magnetic disk).
See also
- Transaction processingTransaction processingIn computer science, transaction processing is information processing that is divided into individual, indivisible operations, called transactions. Each transaction must succeed or fail as a complete unit; it cannot remain in an intermediate state...
- Online transaction processingOnline transaction processingOnline transaction processing, or OLTP, refers to a class of systems that facilitate and manage transaction-oriented applications, typically for data entry and retrieval transaction processing...
- Customer Integrated System
Further reading
- Gerhard Weikum, Gottfried Vossen, Transactional information systems: theory, algorithms, and the practice of concurrency control and recovery, Morgan Kaufmann, 2002, ISBN 1558605088

