
Total Ionic Strength Adjustment Buffer
Encyclopedia
A total ionic strength adjustment buffer (TISAB) is a buffer solution
which increases the ionic strength
of a solution to a relatively high level. This is important for potentiometric measurements, including ion selective electrode
s, because they measure the activity
of the analyte rather than its concentration. TISAB essentially masks most chemical interferences in the analyte solution and hence increases the accuracy of the reading.
There are four main constituents to TISAB, namely CDTA (cyclohexylenedinitrilotetraacetate), sodium hydroxide, sodium chloride and acetic acid (ethanoic acid), which are all dissolved in deionised water. Hence, TISAB having a density ~1.0 kg/L. Each constituent plays an important role to control the ionic strength and pH of the analyte solution, which may otherwise cause error and inaccuracy.
The activity of a substance in solution depends on the product of its concentration and the activity coefficient in that solution. The activity coefficient depends on the ionic strength of the solution in which the potentiometric measurements are made. This can be calculated for dilute solutions using the Debye-Hückel equation
; for more concentrated solutions other approximations must be used. In most cases, the analyst's goal is simply to make sure that the activity coefficient is constant across a set of solutions, with the assumption that no significant ion pairing exists in the solutions.
Example: An ion-selective electrode might be calibrated using dilute solutions of the analyte in distilled water. If this calibration is used to calculate the concentration of the analyte in sea water (high ionic strength), significant error is introduced by the difference between the activity of the analyte in the dilute solutions and the concentrated sample. This can be avoided by adding a small amount of ionic-strength buffer to the standards, so that the activity coefficients match more closely.
Adding a TISAB buffer to increase the ionic strength of the solution helps to "fix" the ionic strength at a stable level, making a linear correlation between the logarithm of the concentration of analyte and the measured voltage. By also adding the TISAB buffer to the samples from which the potentiometric equipment are calibrated, the linear correlation can be used to calculate the concentration of analyte in the solution.
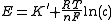
where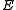 is measured voltage,
is measured voltage, 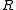 is the gas constant,
is the gas constant,  the temperature measured in kelvins,
the temperature measured in kelvins, 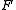 is the Faraday constant and
is the Faraday constant and  the charge of the analyte.
the charge of the analyte.  is the concentration of analyte.
is the concentration of analyte.
TISAB buffers often include chelators which bind ions that could otherwise interfere with the analyte.
Buffer solution
A buffer solution is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. It has the property that the pH of the solution changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. Buffer solutions are used as a...
which increases the ionic strength
Ionic strength
The ionic strength of a solution is a measure of the concentration of ions in that solution. Ionic compounds, when dissolved in water, dissociate into ions. The total electrolyte concentration in solution will affect important properties such as the dissociation or the solubility of different salts...
of a solution to a relatively high level. This is important for potentiometric measurements, including ion selective electrode
Ion selective electrode
An ion-selective electrode , also known as a specific ion electrode , is a transducer that converts the activity of a specific ion dissolved in a solution into an electrical potential, which can be measured by a voltmeter or pH meter. The voltage is theoretically dependent on the logarithm of the...
s, because they measure the activity
Activity (chemistry)
In chemical thermodynamics, activity is a measure of the “effective concentration” of a species in a mixture, meaning that the species' chemical potential depends on the activity of a real solution in the same way that it would depend on concentration for an ideal solution.By convention, activity...
of the analyte rather than its concentration. TISAB essentially masks most chemical interferences in the analyte solution and hence increases the accuracy of the reading.
Theory
TISAB is very commonly applied to fluoride ion analysis such as in fluoride ion selective electrodes.There are four main constituents to TISAB, namely CDTA (cyclohexylenedinitrilotetraacetate), sodium hydroxide, sodium chloride and acetic acid (ethanoic acid), which are all dissolved in deionised water. Hence, TISAB having a density ~1.0 kg/L. Each constituent plays an important role to control the ionic strength and pH of the analyte solution, which may otherwise cause error and inaccuracy.
The activity of a substance in solution depends on the product of its concentration and the activity coefficient in that solution. The activity coefficient depends on the ionic strength of the solution in which the potentiometric measurements are made. This can be calculated for dilute solutions using the Debye-Hückel equation
Debye-Hückel equation
The Debye–Hückel equation and Debye–Hückel limiting law, were derived by Peter Debye and Erich Hückel, who developed a theory with which to calculate activity coefficients of electrolyte solutions. Activities, rather than concentrations, are needed in many chemical calculations because solutions...
; for more concentrated solutions other approximations must be used. In most cases, the analyst's goal is simply to make sure that the activity coefficient is constant across a set of solutions, with the assumption that no significant ion pairing exists in the solutions.
Example: An ion-selective electrode might be calibrated using dilute solutions of the analyte in distilled water. If this calibration is used to calculate the concentration of the analyte in sea water (high ionic strength), significant error is introduced by the difference between the activity of the analyte in the dilute solutions and the concentrated sample. This can be avoided by adding a small amount of ionic-strength buffer to the standards, so that the activity coefficients match more closely.
Adding a TISAB buffer to increase the ionic strength of the solution helps to "fix" the ionic strength at a stable level, making a linear correlation between the logarithm of the concentration of analyte and the measured voltage. By also adding the TISAB buffer to the samples from which the potentiometric equipment are calibrated, the linear correlation can be used to calculate the concentration of analyte in the solution.
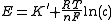
where
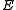 is measured voltage,
is measured voltage, 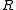 is the gas constant,
is the gas constant,  the temperature measured in kelvins,
the temperature measured in kelvins, 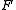 is the Faraday constant and
is the Faraday constant and  the charge of the analyte.
the charge of the analyte.  is the concentration of analyte.
is the concentration of analyte.TISAB buffers often include chelators which bind ions that could otherwise interfere with the analyte.

