
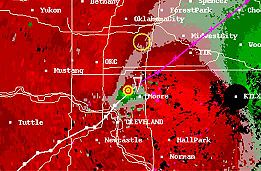
Tornado vortex signature
Encyclopedia
Pulse-doppler radar
Pulse-Doppler is a 4D radar system capable of detecting both target 3D location as well as measuring radial velocity . It uses the Doppler effect to avoid overloading computers and operators as well as to reduce power consumption...
weather radar
Weather radar
Weather radar, also called weather surveillance radar and Doppler weather radar, is a type of radar used to locate precipitation, calculate its motion, estimate its type . Modern weather radars are mostly pulse-Doppler radars, capable of detecting the motion of rain droplets in addition to the...
detected rotation algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
that indicates the likely presence of a strong mesocyclone
Mesocyclone
A mesocyclone is a vortex of air, approximately 2 to 10 miles in diameter , within a convective storm....
that is in some stage of tornadogenesis
Tornadogenesis
Tornadogenesis is the process by which a tornado forms. There are many types of tornadoes, and each type of tornado can have several different methods of formation. Scientific study is ongoing, as some aspects of tornado formation remain a mystery....
. It may give meteorologists the ability to pinpoint and track the location of tornadic rotation within a larger storm, but it is not an important feature in the National Weather Service's warning operations.
Display
It is often visible on the Doppler radar storm relative velocity product as side by side inbound and outbound velocitiesVelocity
In physics, velocity is speed in a given direction. Speed describes only how fast an object is moving, whereas velocity gives both the speed and direction of the object's motion. To have a constant velocity, an object must have a constant speed and motion in a constant direction. Constant ...
, a signature known as a velocity couplet or "gate-to-gate" shear. In many cases, the TVS is a strong mesocyclone aloft, not an actual tornado, although the presence of an actual tornado on the ground can occasionally be inferred based on a strong couplet in concert with a debris cloud signature, or through confirmation from storm spotters. When the algorithm is tripped, a TVS icon and pertinent information appear. Radar analysis of the velocity couplet as well as the automated TVS are very significant to issuing tornado warnings
Tornado warning
A tornado warning is an alert issued by government weather services to warn that severe thunderstorms with tornadoes may be imminent. It can be issued after a tornado or funnel cloud has been spotted by eye, or more commonly if there are radar indications of tornado formation...
and can suggest the strength and location of possible tornadoes. Although many tornadoes, especially the stronger ones, coincide with a TVS, many weak EF0-1 tornadoes can and do occur without a TVS, especially if they are not produced from an identified mesocyclone. Likewise, phenomena such as "fair-weather" waterspouts and gustnadoes
Gustnado
A gustnado is a specific type of short-lived, low-level rotating cloud that can form in a severe thunderstorm. The name is a portmanteau of "gust front tornado", as gustnadoes form due to non-tornadic cyclonic features in the downdraft from the gust front of a strong thunderstorm, especially one...
, though cyclonic and occasionally destructive, do not normally produce a signature identifiable by a TVS.
Intensity
A TVS can be measured by gate to gate wind shearWind shear
Wind shear, sometimes referred to as windshear or wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere...
, which is the change of wind speed
Wind speed
Wind speed, or wind velocity, is a fundamental atmospheric rate.Wind speed affects weather forecasting, aircraft and maritime operations, construction projects, growth and metabolism rate of many plant species, and countless other implications....
and direction
Wind direction
Wind direction is reported by the direction from which it originates. For example, a northerly wind blows from the north to the south. Wind direction is usually reported in cardinal directions or in azimuth degrees...
across the two gates of inbound and outbound velocities. Gates are the individual pixels on the radar display. For example, if the inbound velocity is -48 kn knots and the outbound is 39 knots (76.4 km/h), then there is 87 knots (170.5 km/h) of gate to gate shear. The impressiveness of a TVS not only has to do with the strength of the gate to gate shear, but it also incorporates the size and depth of the TVS, and the strength of any surrounding mesocyclone
Mesocyclone
A mesocyclone is a vortex of air, approximately 2 to 10 miles in diameter , within a convective storm....
, among other things.
See also
- Convective storm detectionConvective storm detectionConvective storm detection is the meteorological observation of deep, moist convection and consists of detection, monitoring, and short-term prediction. This term includes the minority of storms which do not produce lightning and thunder. Convective storms can produce tornadoes as well as large...
- Hook echoHook echoThe hook echo is one of the classical hallmarks of tornado-producing supercell thunderstorms as seen on a weather radar. The echo is produced by rain, hail, or even debris being wrapped around the supercell...
- Bounded weak echo region (BWER)

