Timothy syndrome
Encyclopedia
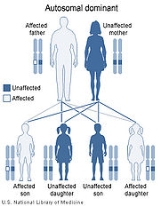
Timothy syndrome is a rare autosomal dominant disorder characterized by physical malformations, as well as neurological and developmental defects, including heart QT-prolongation, heart arrhythmias, structural heart defects, syndactyly
(webbing of fingers and toes) and autism
spectrum disorders.
Timothy syndrome often ends in early childhood death.
(~0.03% of births) and long QT syndrome
(1% per year) in a single patient. Other common symptoms of Timothy syndrome are cardiac arrhythmia (94%), heart malformations (59%), autism
or an autism spectrum disorder (80% who survive long enough for evaluation). Facial dysmorphologies such as flattened noses also occur in approximately half of patients. Children with this disorder have small teeth which, due to poor enamel
coating, are prone to dental cavities and often require removal. The average age of death due to complications of these symptoms is 2.5 years.
Atypical Timothy syndrome has largely the same symptoms as the classical form. Differences in the atypical form are the lack of syndactyly, the presence of musculoskeletal problems (particularly hyperflexible joints), and atrial fibrillation
. Patients with atypical Timothy syndrome also have more facial deformities, including protruding foreheads and tongues. Finally, one patient with atypical Timothy syndrome had a body development discrepancy wherein her upper body was normally developed (that of a 6-year-old) while her lower half resembled a 2- or 3-year-old.
Children with Timothy syndrome tend to be born via caesarean section
due to fetal distress.
 There are two recognized types of Timothy syndrome, classical (type-1) and atypical (type-2). They are both caused by mutations in CACNA1C, the gene encoding the calcium channel
There are two recognized types of Timothy syndrome, classical (type-1) and atypical (type-2). They are both caused by mutations in CACNA1C, the gene encoding the calcium channel
Cav1.2 α subunit. Timothy syndrome mutations in CACNA1C cause delayed channel closing and, thus, increased cellular excitability
.
Both classical and atypical Timothy syndromes are caused by mutation
s in CACNA1C. These mutations are in exon 8 (atypical form) and exon 8a (classical form), an alternatively spliced exon
. Exon 8a is highly expressed in the heart, brain, gastrointestinal system, lungs, immune system and smooth muscle. Exon 8 is also expressed in these regions and its level is approximately 5-fold higher than exon 8a expression.
There is one mutation found in patients with classical Cack syndrome, G406R, located just past the 6th membrane spanning segment of domain 1 (D1S6). The conserved glycine
at this position seems to be vital for proper voltage dependent inactivation as the mutant is lacking in this respect. Atypical Timothy syndrome mutations are similar, one being the identical G406R mutation in the other splice form and the second mutation being G402S, located a few amino acid
s upstream. The affect of these mutations on channel function is identical to the G406R mutation in classical Timothy syndrome. The lack of proper voltage-dependent inactivation in these mutants causes prolonged inward current and depolarization
during cardiac action potential
s. This leads to long QT syndrome
and resultant arrhythmia. Because exon 8 has greater expression in the heart versus exon 8a, patients with atypical Timothy syndrome have worsened cardiac defects compared to those with the classical form.
to maintain proper heart rhythm. With the characterization of Timothy syndrome mutations indicating that they cause defects in calcium
currents, it has been suggested that calcium channel
blockers may be effective as a therapeutic agent.
, one with an autism spectrum disorder, and the last had severe delays in language development. One patient with atypical Timothy syndrome was largely normal with the exception of heart arrhythmia. Likewise, the mother of two Timothy syndrome patients also carried the mutation but lacked any obvious phenotype. In both of these cases, however, the lack of severity of the disorder was due to mosaicism.
Syndactyly
Syndactyly is a condition wherein two or more digits are fused together. It occurs normally in some mammals, such as the siamang and kangaroo, but is an unusual condition in humans.-Classification:...
(webbing of fingers and toes) and autism
Autism
Autism is a disorder of neural development characterized by impaired social interaction and communication, and by restricted and repetitive behavior. These signs all begin before a child is three years old. Autism affects information processing in the brain by altering how nerve cells and their...
spectrum disorders.
Timothy syndrome often ends in early childhood death.
Signs and symptoms
The most striking sign of Timothy syndrome is the co-occurrence of both syndactylySyndactyly
Syndactyly is a condition wherein two or more digits are fused together. It occurs normally in some mammals, such as the siamang and kangaroo, but is an unusual condition in humans.-Classification:...
(~0.03% of births) and long QT syndrome
Long QT syndrome
The long QT syndrome is a rare inborn heart condition in which delayed repolarization of the heart following a heartbeat increases the risk of episodes of torsade de pointes . These episodes may lead to palpitations, fainting and sudden death due to ventricular fibrillation...
(1% per year) in a single patient. Other common symptoms of Timothy syndrome are cardiac arrhythmia (94%), heart malformations (59%), autism
Autism
Autism is a disorder of neural development characterized by impaired social interaction and communication, and by restricted and repetitive behavior. These signs all begin before a child is three years old. Autism affects information processing in the brain by altering how nerve cells and their...
or an autism spectrum disorder (80% who survive long enough for evaluation). Facial dysmorphologies such as flattened noses also occur in approximately half of patients. Children with this disorder have small teeth which, due to poor enamel
Tooth enamel
Tooth enamel, along with dentin, cementum, and dental pulp is one of the four major tissues that make up the tooth in vertebrates. It is the hardest and most highly mineralized substance in the human body. Tooth enamel is also found in the dermal denticles of sharks...
coating, are prone to dental cavities and often require removal. The average age of death due to complications of these symptoms is 2.5 years.
Atypical Timothy syndrome has largely the same symptoms as the classical form. Differences in the atypical form are the lack of syndactyly, the presence of musculoskeletal problems (particularly hyperflexible joints), and atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation is the most common cardiac arrhythmia . It is a common cause of irregular heart beat, identified clinically by taking a pulse. Chaotic electrical activity in the two upper chambers of the heart result in the muscle fibrillating , instead of achieving coordinated contraction...
. Patients with atypical Timothy syndrome also have more facial deformities, including protruding foreheads and tongues. Finally, one patient with atypical Timothy syndrome had a body development discrepancy wherein her upper body was normally developed (that of a 6-year-old) while her lower half resembled a 2- or 3-year-old.
Children with Timothy syndrome tend to be born via caesarean section
Caesarean section
A Caesarean section, is a surgical procedure in which one or more incisions are made through a mother's abdomen and uterus to deliver one or more babies, or, rarely, to remove a dead fetus...
due to fetal distress.
Diagnosis
Syndactyly and other deformities are typically observed and diagnosed at birth. Long QT syndrome sometimes presents itself as a complication due to surgery to correct syndactyly. Other times, children collapse spontaneously while playing. In all cases it is confirmed with ECG measurements. Sequencing of the CACNA1C gene further confirms the diagnosis.Pathophysiology

Calcium channel
A Calcium channel is an ion channel which displays selective permeability to calcium ions. It is sometimes synonymous as voltage-dependent calcium channel, although there are also ligand-gated calcium channels.-Comparison tables:...
Cav1.2 α subunit. Timothy syndrome mutations in CACNA1C cause delayed channel closing and, thus, increased cellular excitability
Membrane potential
Membrane potential is the difference in electrical potential between the interior and exterior of a biological cell. All animal cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane composed of a lipid bilayer with a variety of types of proteins embedded in it...
.
Both classical and atypical Timothy syndromes are caused by mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
s in CACNA1C. These mutations are in exon 8 (atypical form) and exon 8a (classical form), an alternatively spliced exon
Splicing (genetics)
In molecular biology and genetics, splicing is a modification of an RNA after transcription, in which introns are removed and exons are joined. This is needed for the typical eukaryotic messenger RNA before it can be used to produce a correct protein through translation...
. Exon 8a is highly expressed in the heart, brain, gastrointestinal system, lungs, immune system and smooth muscle. Exon 8 is also expressed in these regions and its level is approximately 5-fold higher than exon 8a expression.
There is one mutation found in patients with classical Cack syndrome, G406R, located just past the 6th membrane spanning segment of domain 1 (D1S6). The conserved glycine
Glycine
Glycine is an organic compound with the formula NH2CH2COOH. Having a hydrogen substituent as its 'side chain', glycine is the smallest of the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. Its codons are GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG cf. the genetic code.Glycine is a colourless, sweet-tasting crystalline solid...
at this position seems to be vital for proper voltage dependent inactivation as the mutant is lacking in this respect. Atypical Timothy syndrome mutations are similar, one being the identical G406R mutation in the other splice form and the second mutation being G402S, located a few amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
s upstream. The affect of these mutations on channel function is identical to the G406R mutation in classical Timothy syndrome. The lack of proper voltage-dependent inactivation in these mutants causes prolonged inward current and depolarization
Depolarization
In biology, depolarization is a change in a cell's membrane potential, making it more positive, or less negative. In neurons and some other cells, a large enough depolarization may result in an action potential...
during cardiac action potential
Cardiac action potential
In electrocardiography, the cardiac action potential is a specialized action potential in the heart, necessary for the electrical conduction system of the heart....
s. This leads to long QT syndrome
Long QT syndrome
The long QT syndrome is a rare inborn heart condition in which delayed repolarization of the heart following a heartbeat increases the risk of episodes of torsade de pointes . These episodes may lead to palpitations, fainting and sudden death due to ventricular fibrillation...
and resultant arrhythmia. Because exon 8 has greater expression in the heart versus exon 8a, patients with atypical Timothy syndrome have worsened cardiac defects compared to those with the classical form.
Treatment
Surgery is typically used to correct structural heart defects and syndactyly. Propanolol or beta-adrenergic blockers are often prescribed as well as insertion of a pacemakerArtificial pacemaker
A pacemaker is a medical device that uses electrical impulses, delivered by electrodes contacting the heart muscles, to regulate the beating of the heart...
to maintain proper heart rhythm. With the characterization of Timothy syndrome mutations indicating that they cause defects in calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
currents, it has been suggested that calcium channel
Calcium channel
A Calcium channel is an ion channel which displays selective permeability to calcium ions. It is sometimes synonymous as voltage-dependent calcium channel, although there are also ligand-gated calcium channels.-Comparison tables:...
blockers may be effective as a therapeutic agent.
Prognosis
The prognosis for patients diagnosed with Timothy syndrome is very poor. Of 17 children analyzed in one study, 10 died at an average age of 2.5 years. Of those that did survive, 3 were diagnosed with autismAutism
Autism is a disorder of neural development characterized by impaired social interaction and communication, and by restricted and repetitive behavior. These signs all begin before a child is three years old. Autism affects information processing in the brain by altering how nerve cells and their...
, one with an autism spectrum disorder, and the last had severe delays in language development. One patient with atypical Timothy syndrome was largely normal with the exception of heart arrhythmia. Likewise, the mother of two Timothy syndrome patients also carried the mutation but lacked any obvious phenotype. In both of these cases, however, the lack of severity of the disorder was due to mosaicism.

