
Timeline of the 1997 Pacific hurricane season
Encyclopedia
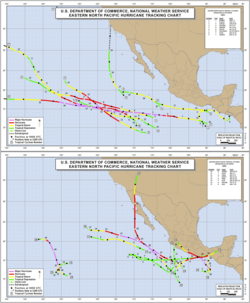
1997 Pacific hurricane season
The 1997 Pacific hurricane season was a very active hurricane season. With hundreds of deaths and billions of dollars in damage, this season was the costliest and one of the deadliest Pacific hurricane seasons. This was due to a strong El Niño...
was the most active season since the 1994 season
1994 Pacific hurricane season
The 1994 Pacific hurricane season officially started on May 15, 1994 in the eastern Pacific, and on June 1, 1994 in the central Pacific, and lasted until November 30, 1994. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean...
, producing 24 tropical depressions, 19 of which became tropical storms
Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Tropical cyclones strengthen when water evaporated from the ocean is released as the saturated air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor...
or hurricanes. The season officially started on May 15, 1997 in the Eastern Pacific—designated as the area east of 140°W
Longitude
Longitude is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees, minutes and seconds, and denoted by the Greek letter lambda ....
—and on June 1, 1997 in the Central Pacific, which is between the International Date Line
International Date Line
The International Date Line is a generally north-south imaginary line on the surface of the Earth, passing through the middle of the Pacific Ocean, that designates the place where each calendar day begins...
and 140°W. The season officially ended in both basins on November 30, 1997. These dates typically limit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the eastern Pacific basin
Pacific hurricane
A Pacific hurricane or tropical storm is a tropical cyclone that develops in the northeastern part of the Pacific Ocean. For organizational purposes, the northern Pacific Ocean is divided into three regions: the eastern, , central , and western...
. This timeline documents all the storm formations, strengthening, weakening, landfalls
Landfall (meteorology)
Landfall is the event of a tropical cyclone or a waterspout coming onto land after being over water. When a waterspout makes landfall it is reclassified as a tornado, which can then cause damage inland...
, extratropical transitions, as well as dissipation. The timeline also includes information which was not operationally released, meaning that information from post-storm reviews by the National Hurricane Center
National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center , located at Florida International University in Miami, Florida, is the division of the National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting weather systems within the tropics between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 30th...
, such as information on a storm that was not operationally warned on, has been included.
The first storm formed on June 1 and the final storm crossed into the western Pacific on December 6, thus ending the season. There were 24 cyclones in both the eastern and central Pacific, including 5 unnamed tropical depressions. Of these, 19 were in the east Pacific; 8 peaked at tropical storm intensity, while 10 reached hurricane status. Seven of these reached Category 3 intensity or higher on the Saffir-Simpson hurricane scale
Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale
The Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Scale , or the Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale , classifies hurricanes — Western Hemisphere tropical cyclones that exceed the intensities of tropical depressions and tropical storms — into five categories distinguished by the intensities of their sustained winds...
, including central Pacific cyclones Super Typhoons Oliwa
Typhoon Oliwa (1997)
Typhoon Oliwa was one of a record eleven super typhoons in the 1997 Pacific typhoon season. It formed in the central Pacific Ocean on September 2 to the southwest of Hawaii, but it became a typhoon in the western Pacific. Oliwa explosively deepened on September 8, increasing its winds...
and Paka
Typhoon Paka
Typhoon Paka was the last tropical cyclone in the 1997 Pacific Ocean hurricane and typhoon season, and was among the strongest Pacific typhoons in the month of December. Paka, which is the Hawaiian name for Pat, developed on November 28 from a trough well to the southwest of Hawaii...
, which became typhoons after crossing into the Western Pacific.
Activity in the Central Pacific was above average; two tropical storms formed in addition to several tropical depressions. Some of the storms entered the region from the east. The 1997 season was the fourth-most active in the Central Pacific since satellite observations began. Nine tropical cyclones entered or formed in the region during that period.
June
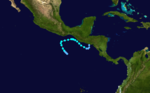
- The Central Pacific hurricane season officially begins.
- 0000 UTC – Tropical Depression One-E forms 300 miles (555 km) south of the Gulf of TehuantepecGulf of TehuantepecGulf of Tehuantepec is a large body of water on the Pacific coast of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, southeastern Mexico, at . Most of the hurricanes that form in the Eastern Pacific organize in or near this body of water...
.
June 2
- 1200 UTC – Tropical Depression One-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Andres.
June 6
- 0600 UTC – Tropical Storm Andres weakens into a tropical depression.
June 7
- 0100 UTC – Tropical Depression Andres makes landfall near San Salvador, El Salvador with wind of 30 mph (50 km/h).
- 0600 UTC – The surface circulation of Tropical Depression Andres rapidly dissipates over the mountains of Central America.

- 1800 UTC – Tropical Depression Two-E forms in the Gulf of TehuantepecGulf of TehuantepecGulf of Tehuantepec is a large body of water on the Pacific coast of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, southeastern Mexico, at . Most of the hurricanes that form in the Eastern Pacific organize in or near this body of water...
.
- June 10
- 0000 UTC – Tropical Depression Two-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Blanca.
June 12
- 0000 UTC – Tropical Storm Blanca weakens into a tropical depression.
- 1200 UTC – Tropical Depression Blanca loses its surface circulation.
June 21
- 1800 UTC – Tropical Depression Three-E forms.
June 24
- 0000 UTC – Tropical Depression Three-E dissipates.
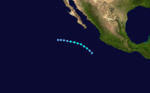
- 0600 UTC – Tropical Depression Four-E forms 450 miles (830 km) southeast of the southern tip of the Baja Peninsula.
- 1800 UTC – Tropical Depression Four-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Carlos.
June 27
- 0600 UTC – Tropical Storm Carlos weakens into Tropical Depression Carlos.
June 28
- 0600 UTC – Tropical Depression Carlos dissipates.
June 29
- 1200 UTC – Tropical Depression Five-E forms.
July
.jpg)
- 0600 UTC – Tropical Depression Five-E dissipates.
July 5
- 1200 UTC – It is estimated that Tropical Depression Six-E forms 600 miles (1110 km) southeast of the southern tip of the Baja Peninsula it is operationally upgraded to Tropical Storm Dolores.
July 6
- 0000 UTC – Tropical Depression Six-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Dolores.
July 7
- 1200 UTC – Tropical Storm Dolores strengthens into the first hurricane of the season.
July 10
- 0600 UTC – Hurricane Dolores weakens into Tropical Storm Dolores.
- July 11
- 0600 UTC – Tropical Storm Dolores weakens into a tropical depression.
July 12
- 0600 UTC – Tropical Depression Seven-E forms 850 miles (1575 km) south-southwest of the southern tip of the Baja Peninsula.
- 1800 UTC – Tropical Depression Seven-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Enrique.
- 1800 UTC – Tropical Depression Dolores dissipates.
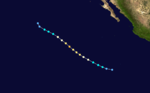
- 1200 UTC – Tropical Storm Enrique strengthens into the second hurricane of the season.
July 14
- 0000 UTC – Hurricane Enrique strengthens into a Category 2 hurricane.
- 1200 UTC – Tropical Depression Eight-E forms several hundred miles south of Manzanillo, Mexico.
- 1800 UTC – Hurricane Enrique strengthens into the first major hurricane (a hurricane with winds more than 111 mph (180 km/h) of the season.
July 15
- 0000 UTC – Hurricane Enrique weakens into a Category 2 hurricane.
- 0600 UTC – Hurricane Enrique weakens into a Category 1 hurricane.
- 1800 UTC – Tropical Depression Eight-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Felicia.
- 1800 UTC – Hurricane Enrique weakens into a tropical storm.
July 16
- 1200 UTC – Tropical Storm Enrique weakens into a tropical depression.
- 1800 UTC – Tropical Depression Enrique begins to dissipate and the last advisory is issued.
- 1800 UTC – Hurricane Enrique weakens into a tropical storm.
.jpg)
- 0600 UTC – Tropical Storm Felicia strengthens into the third hurricane of the season.
July 18
- 1200 UTC – Hurricane Felicia strengthens into a Category 2 hurricane.
- 1800 UTC – Hurricane Felicia strengthens into the second major hurricane of the season.
July 19
- 0600 UTC – Hurricane Felicia strengthens into a Category 4 hurricane.
July 20
- 0000 UTC – Hurricane Felicia weakens into a Category 3 hurricane.
- 1800 UTC – Hurricane Felicia weakens into a Category 2 hurricane.
July 21
- 0600 UTC – Hurricane Felicia weakens into a Category 1 hurricane.
- 1200 UTC – Hurricane Felicia weakens into a tropical storm.
July 22
- 0600 UTC – Tropical Storm Felicia weakens into a tropical depression.
- 1200 UTC – Tropical Depression Felicia dissipates.
July 27
- 0000 UTC – Tropical Depression One-C forms southwest of the Hawaiian IslandsHawaiian IslandsThe Hawaiian Islands are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, numerous smaller islets, and undersea seamounts in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some 1,500 miles from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost Kure Atoll...
. - 1800 UTC – Tropical Depression One-C dissipates.
July 30
- 1200 UTC – Tropical Depression Nine-E forms 300 miles (555 km) south of Salina Cruz, Mexico.
July 31
- 0600 UTC – Tropical Depression Nine-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Guillermo.
August
August 1- 1800 UTC – Tropical Storm Guillermo strengthens into the fourth hurricane of the season.
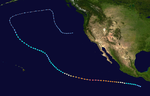
- 1200 UTC – Hurricane Guillermo strengthens into a Category 2 hurricane.
- 1800 UTC – Hurricane Guillermo strengthens into the third major hurricane of the season.
August 3
- 0000 UTC – Hurricane Guillermo strengthens into a Category 4 hurricane.
August 4
- 1800 UTC – Hurricane Guillermo strengthens into the first Category 5 hurricane of the season.
- August 5
- 1800 UTC – Hurricane Guillermo weakens into a Category 4 hurricane.
August 6
- 1800 UTC – Hurricane Guillermo weakens into a Category 3 hurricane
August 7
- 0600 UTC – Hurricane Guillermo weakens into a Category 2 hurricane.
- 1200 UTC – Hurricane Guillermo weakens into a Category 1 hurricane.
August 8
- 0600 UTC – Hurricane Guillermo weakens into a tropical storm.
August 10
- 0000 UTC – Tropical Depression Ten-E forms 920 miles (1700 km) south-southwest of the southern tip of the Baja Peninsula.
- 1800 UTC – Tropical Storm Guillermo weakens into a tropical depression.
.jpg)
- 1800 UTC – Tropical Depression Guillermo re-strengthens into a tropicial storm.
- 1800 UTC – Tropical Depression Ten-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Hilda.
August 14
- 0600 UTC – Tropical Storm Hilda weakens into a tropical depression.
August 15
- 0600 UTC – Tropical Depression Hilda dissipates.
- 1200 UTC – Tropical Storm Guillermo again weakens into a tropical depression.
August 16
- 0000 UTC – Tropical Depression Guillermo becomes extratropical.
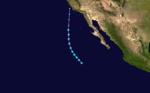
- 0000 UTC – Tropical Depression Eleven-E forms 450 miles (830 km) southwest of Cabo San Lucas, Mexico.
- 1200 UTC – Tropical Depression Eleven-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Ignacio.
August 18
- 0600 UTC – Tropical Storm Ignacio weakens into Tropical Depression Ignacio.
August 19
- 1200 UTC – Tropical Depression Ignacio becomes extratropical.
August 25
- 1200 UTC – Tropical Depression Twelve-E forms.
.jpg)
- 0000 UTC – Tropical Depression Twelve-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Jimena.
August 27
- 0000 UTC – Tropical Storm Jimena strengthens into the fifth hurricane of the season.
- 0600 UTC – Hurricane Jimena explosively strengthens into the fourth major hurricane of the season.
- 1200 UTC – Hurricane Jimena strengthens into a Category 4 hurricane.
August 29
- 0000 UTC – Hurricane Jimena weakens into a Category 3 hurricane.
- 0600 UTC – Hurricane Jimena rapidly falls apart as it weakens from a Category 3 hurricane to a tropical storm.
- 1800 UTC – Tropical Storm Jimena weakens into a tropical depression.
August 30
- 0000 UTC – Tropical Depression Jimena dissipates.
September
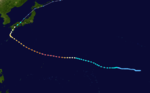
- 1800 UTC – Tropical Depression Two-C forms near the International Dateline.
September 3
- 0000 UTC – Tropical Depression Two-C strengthens into Tropical Storm Oliwa—the Hawaiian name for Oliver.
- 1800 UTC – Tropical Depression Thirteen-E forms 325 miles (600 km) south-southwest of the southern tip of the Baja Peninsula.
.jpg)
- 0000 UTC – Tropical Storm Oliwa moves past 140°W into the West Pacific and the last advisory is issued by the Central Pacific Hurricane CenterCentral Pacific Hurricane CenterThe Central Pacific Hurricane Center of the United States National Weather Service is the official body responsible for tracking and issuing tropical cyclone warnings, watches, advisories, discussions, and statements for the Central North Pacific Basin...
. - 0600 UTC – Tropical Depression Thirteen-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Kevin.
September 6
- 0600 UTC – Tropical Storm Kevin weakens into a tropical depression.
September 7
- 0600 UTC – Tropical Depression Kevin dissipates.
September 9
- 1200 UTC – Tropical Depression Fourteen-E forms 400 miles (740 km) south of Manzanillo, Mexico.
September 10
- 0000 UTC – Tropical Depression Fourteen-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Linda.

- 0000 UTC – Tropical Storm Linda strengthens into the fifth hurricane of the season.
- 1200 UTC – Hurricane Linda strengthens into the fourth major hurricane of the season, skipping Category 2 hurricane status.
- 1800 UTC – Hurricane Linda strengthens into a Category 4 hurricane.
September 12
- 0000 UTC – Hurricane Linda strengthens into the second, and final Category 5 hurricane of the season.
- 0600 UTC – Hurricane Linda's pressure drops to 902 mbar (hPaHPA-Organizations:*Halifax Port Authority, a port authority in Canada*Hamburg Port Authority, the port authority for the Port of Hamburg, Germany*Health Protection Agency, a health organization in the United Kingdom...
) or 26.64 in and 185 mph (300 km/h) making it the strongest storm in the Northeast Pacific ocean on record. - 1800 UTC – Tropical Depression Fifteen-E forms 1300 miles (2400 km) east-southeast of the Hawaiian IslandsHawaiian IslandsThe Hawaiian Islands are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, numerous smaller islets, and undersea seamounts in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some 1,500 miles from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost Kure Atoll...
.
September 13
- 1800 UTC – Hurricane Linda weakens into a Category 4 hurricane.

- 0000 UTC – Tropical Depression Fifteen-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Marty.
- 0600 UTC – Hurricane Linda weakens into a Category 3 hurricane.
- 1200 UTC – Hurricane Linda weakens into a Category 2 hurricane.
- 1800 UTC – Hurricane Linda weakens into a Category 1 hurricane.
September 15
- 1200 UTC – Hurricane Linda weakens into a tropical storm.
- 1200 UTC – Tropical Storm Marty weakens into a tropical depression.
September 16
- 0600 UTC – Tropical Depression Sixteen-E forms.
- 1800 UTC – Tropical Depression Sixteen-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Nora.
- 1800 UTC – Tropical Depression Marty dissipates.
September 17
- 0600 UTC – Tropical Storm Linda weakens into a tropical depression.
September 18
- 0000 UTC – Tropical Depression Linda dissipates.
- 1200 UTC – Tropical Storm Nora strengthens into the seventh hurricane of the season.
- 1800 UTC – Hurricane Nora strengthens into a Category 2 hurricane.
_goes.jpg)
- 1200 UTC – Hurricane Nora weakens into a Category 1 hurricane.
September 21
- 0600 UTC – Hurricane Nora re-strengthens into a Category 2 hurricane.
- 1200 UTC – Hurricane Nora rapidly strengthens into a Category 4 hurricane and the sixth major hurricane of the season.
- 1800 UTC – Hurricane Nora weakens into a Category 3 hurricane.
September 23
- 0000 UTC – Hurricane Nora weakens into a Category 2 hurricane.
- 1200 UTC – Hurricane Nora weakens into a Category 1 hurricane.
September 25
- 0630 UTC – Hurricane Nora makes landfall near Punta Eugenia, Mexico on the Baja Peninsula with winds of 85 mph (135 km/h).
- 1100 UTC – Hurricane Nora makes its final landfall near San Fernando, Mexico with winds of 80 mph (130 km/h).
- 1800 UTC – Hurricane Nora weakens into a tropical storm.
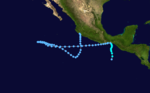
- 0000 UTC – Tropical Storm Nora rapidly dissipates into a tropical depression.
- 0600 UTC – The final advisory for dissipating Tropical Depression Nora is issued.
- 1200 UTC – Tropical Depression Seventeen-E forms 300 miles (555 km) south of the Gulf of TehuantepecGulf of TehuantepecGulf of Tehuantepec is a large body of water on the Pacific coast of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, southeastern Mexico, at . Most of the hurricanes that form in the Eastern Pacific organize in or near this body of water...
. - 1800 UTC – Tropical Depression Seventeen-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Olaf.
September 29
- 0000 UTC – Tropical Storm Olaf weakens into a tropical depression and makes landfall near Salina Cruz, Mexico with winds of 35 mph (55 km/h).
October
October 5- 1200 UTC – Tropical Depression Eighteen-E forms 200 miles (370 km) south of Puerto Angel, Mexico.

- 0600 UTC – Tropical Depression Eighteen-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Pauline.
- 1200 UTC – Tropical Depression Three-C forms southeast of the Hawaiian IslandsHawaiian IslandsThe Hawaiian Islands are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, numerous smaller islets, and undersea seamounts in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some 1,500 miles from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost Kure Atoll...
.
October 7
- 0000 UTC – Tropical Storm Pauline strengthens into the eighth hurricane of the season.
- 0600 UTC – Hurricane Pauline strengthens into the seventh and final major hurricane of the season.
- 1200 UTC – Hurricane Pauline strengthens into a Category 4 hurricane.
- 1200 UTC – Tropical Depression Three-C dissipates.
- 1800 UTC – Hurricane Pauline weakens into a Category 3 hurricane.
October 8
- 1800 UTC – Hurricane Pauline regains Category 4 hurricane status.
October 9
- 0000 UTC- Hurricane Pauline abruptly weakens and makes landfall in Mexico with winds of 110 mph (175 km/h).
- 0600 UTC – Hurricane Pauline weakens into a Category 1 hurricane.
- 1200 UTC – Hurricane Pauline weakens into a tropical storm.
October 10
- 0600 UTC – Tropical Storm Pauline weakens into a tropical depression.
- 1200 UTC – Tropical Depression Pauline dissipates.
October 12
- 1800 UTC – Tropical Depression Olaf makes landfall near Manzanillo, Mexico with winds of 30 mph (50 km/h) and dissipates.
October 31
- 0600 UTC – Tropical Depression Four-C forms southeast of the Hawaiian IslandsHawaiian IslandsThe Hawaiian Islands are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, numerous smaller islets, and undersea seamounts in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some 1,500 miles from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost Kure Atoll...
.
November
November 1- 0600 UTC – Tropical Depression Four-C dissipates.
November 7
- 0000 UTC – Tropical Depression Nineteen-E forms 500 miles (925 km) south-southwest of Acapulco, Mexico.
November 8
- 1200 UTC – Tropical Depression Nineteen-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Rick.

- 0600 UTC – Tropical Storm Rick strengthens into the ninth and final hurricane of the season.
- 1200 UTC – Hurricane Rick strengthens into a Category 2 hurricane.
- 1800 UTC – Hurricane Rick weakens into a Category 1 hurricane.
November 10
- 0100 UTC – Hurricane Rick makes landfall near Puerto Escondido, Mexico with winds of 85 mph (135 km/h).
- 1200 UTC – Hurricane Rick weakens into a tropical storm.
- 1800 UTC – Tropical Storm Rick weakens into a tropical depression.
November 11
- 0000 UTC – Tropical Depression Rick dissipates.
November 30
- The 1997 central and eastern Pacific hurricane seasons officially end.
December
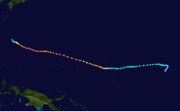
- 1200 UTC – Tropical Depression Five-C forms out of season near the Line IslandsLine IslandsThe Line Islands, Teraina Islands or Equatorial Islands, is a chain of eleven atolls and low coral islands in the central Pacific Ocean, south of the Hawaiian Islands, that stretches for 2,350 km in a northwest-southeast direction, making it one of the longest islands chains of the world...
. - 1800 UTC – Tropical Depression Five-C strengthens into Tropical Storm Paka, the Hawaiian name for Pat.
December 7
- 0000 UTC – Tropical Storm Paka crosses the International Date Line into the Western Pacific and the final advisory is issued, therefore ending the 1997 Pacific hurricane season.
See also
- 1997 Pacific hurricane season1997 Pacific hurricane seasonThe 1997 Pacific hurricane season was a very active hurricane season. With hundreds of deaths and billions of dollars in damage, this season was the costliest and one of the deadliest Pacific hurricane seasons. This was due to a strong El Niño...
- 1997 Pacific typhoon season1997 Pacific typhoon seasonThe 1997 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1997, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between May and November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern...

