
Pacific hurricane
Encyclopedia
Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Tropical cyclones strengthen when water evaporated from the ocean is released as the saturated air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor...
that develops in the northeastern part of the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
. For organizational purposes, the northern Pacific Ocean is divided into three regions: the eastern, (North America to 140°W), central (140°W to 180°), and western (180° to 100°E). A Pacific hurricane, then, is a tropical cyclone in the northern Pacific Ocean east
Boxing the compass
Boxing the compass is the action of naming all thirty-two points of the compass in clockwise order. Such names are formed by the initials of the cardinal directions and their intermediate ordinal directions, and are very handy to refer to a heading in a general or colloquial fashion, without...
of 180°. Identical phenomena in the western north Pacific are called typhoons
Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Tropical cyclones strengthen when water evaporated from the ocean is released as the saturated air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor...
. This separation between the two basins is convenient, however, as tropical cyclones rarely form in the central north Pacific and few cross the dateline.
Eastern North Pacific
Hurricane season runs between May 15 and November 30 each year. These date encompass the vast majority of tropical cyclone activity in this region.The Regional Specialized Meteorological Center
Regional Specialized Meteorological Center
A Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre is responsible for the distribution of information, advisories, and warnings regarding the specific program they have a part of, agreed by consensus at the World Meteorological Organization as part of the World Weather Watch.-Tropical...
for this basin is the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
' National Hurricane Center
National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center , located at Florida International University in Miami, Florida, is the division of the National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting weather systems within the tropics between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 30th...
. Previous forecasters are the Eastern Pacific Hurricane Center
Eastern Pacific Hurricane Center
The Eastern Pacific Hurricane Center was formerly the Regional Specialized Meteorological Center responsible for forecasting Pacific hurricanes in the eastern north Pacific east of 140°W...
and the Joint Hurricane Warning Center. The RSMC monitors the eastern Pacific and issues reports, watches and warnings about tropical weather systems and cyclones as defined by the World Meteorological Organization
World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 189 Member States and Territories. It originated from the International Meteorological Organization , which was founded in 1873...
.
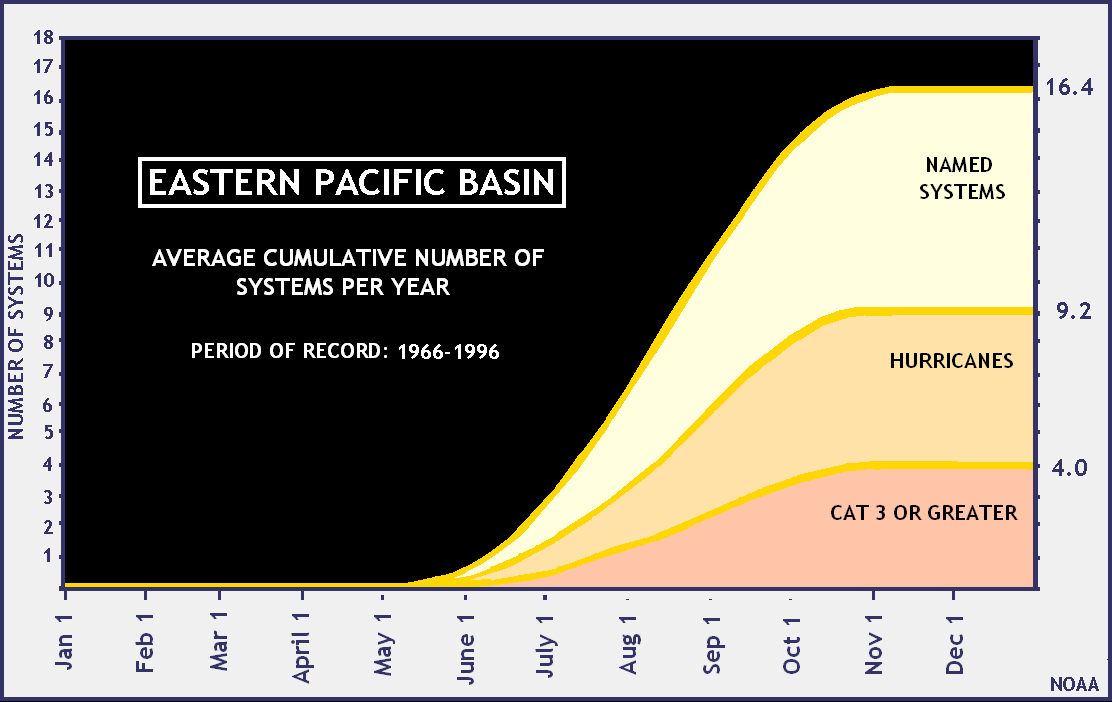
This area is, on average, the second-most active basin in the world. There are an average of 16 tropical storms annually, with 9 becoming hurricanes, and 4 becoming major hurricanes. Tropical cyclones in this region frequently affect mainland Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
and the Revillagigedo Islands
Revillagigedo Islands
The Revillagigedo Islands or Revillagigedo Archipelago are a group of four volcanic islands in the Pacific Ocean, known for their unique ecosystem...
. Less often, a system will affect the Continental United States or Central America
Central America
Central America is the central geographic region of the Americas. It is the southernmost, isthmian portion of the North American continent, which connects with South America on the southeast. When considered part of the unified continental model, it is considered a subcontinent...
. Northbound hurricanes typically reduce to tropical storms or dissipate before reaching the United States: there is only one recorded case of a Pacific system reaching California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
as a hurricane in almost 200 years of observations—the 1858 San Diego Hurricane
1858 San Diego Hurricane
The 1858 San Diego hurricane was a very rare California hurricane. It is the only known tropical cyclone to impact California as a hurricane, although other systems impacted California as tropical storms.-Meteorological history:...
.
Most east Pacific hurricanes originate from a tropical wave that drifts westward across the intertropical convergence zone, and across northern parts of South America. Once it reaches the Pacific, a surface low begins to develop, however, with only little or no convection. After reaching the Pacific, it starts to move north-westward and eventually west. By that time, it develops convection and thunderstorm activity from the warm ocean temperatures but remains disorganized. Winter in the east Pacific is usually covered with strong shear, which limits development. Once it becomes organized, it becomes a tropical depression. Formation usually occurs from south of the Gulf of Tehuantepec to south of Baja California with a more westerly location earlier in the season. In the eastern Pacific, development is more centered than anywhere. Most tropical cyclones in the eastern Pacific reach their peak strength as a strong tropical storm due to strong shear. If wind shear is low, storms can undergo major intensification as a result of very warm oceans, becoming a major hurricane. Major hurricanes weaken once they reach unfavorable areas for a tropical cyclone formation, and most of them do an eyewall replacement and weaken. Their remnants sometimes reach Hawaii and cause showers there.
There are a few types of Pacific hurricane tracks: one is a westerly track, another moves north-westward along Baja California and another moves north. Sometimes storms can move north-east either across Central America or mainland Mexico and possibly enter the Caribbean Sea becoming a North Atlantic basin tropical cyclone, but these are rare.
Central Pacific
Hurricane season runs from June 1 to November 30, with a strong peak in August and September. However, tropical cyclones have formed outside those dates. Should a tropical cyclone enter the central north Pacific from the western north Pacific, where they occur year-round, or from the eastern north Pacific, where the season starts in May, it is not known if such a system will be considered out of season or not.The Central Pacific Hurricane Center
Central Pacific Hurricane Center
The Central Pacific Hurricane Center of the United States National Weather Service is the official body responsible for tracking and issuing tropical cyclone warnings, watches, advisories, discussions, and statements for the Central North Pacific Basin...
is the RSMC for this basin and monitors the storms that develop or move into the defined area of responsibility. A previous forecaster was the Joint Hurricane Warning Center.
Central Pacific hurricanes are rare and on average 3 or 4 storms form or move in this area per year. Most often, storms that occur in the area are weak and often decline in strength upon entry. The only land masses impacted by tropical cyclones in this region are Hawaii
Hawaii
Hawaii is the newest of the 50 U.S. states , and is the only U.S. state made up entirely of islands. It is the northernmost island group in Polynesia, occupying most of an archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, southwest of the continental United States, southeast of Japan, and northeast of...
and Johnston Atoll
Johnston Atoll
Johnston Atoll is a atoll in the North Pacific Ocean about west of Hawaii. There are four islands located on the coral reef platform, two natural islands, Johnston Island and Sand Island, which have been expanded by coral dredging, as well as North Island and East Island , an additional two...
. Due to the small size of the islands in relation to the Pacific Ocean, direct hits and landfalls are rare.

