
Thermodynamic instruments
Encyclopedia
A thermodynamic instrument is any device which facilitates the quantitative measurement of thermodynamic systems. In order for a thermodynamic parameter to be truly defined, a technique for its measurement must be specified. For example, the ultimate definition of temperature is "what a thermometer reads". The question follows - what is a thermometer?
There are two types of thermodynamic instruments, the meter and the reservoir. A thermodynamic meter is any device which measures any parameter of a thermodynamic system. A thermodynamic reservoir is a system which is so large that it does not appreciably alter its state parameters when brought into contact with the test system.
In some cases, the thermodynamic parameter is actually defined in terms of an idealized measuring instrument. For example, the zeroth law of thermodynamics
states that if two bodies are in thermal equilibrium with a third body, they are also in thermal equilibrium with each other. This principle, as noted by James Maxwell in 1872, asserts that it is possible to measure temperature. An idealized thermometer is a sample of an ideal gas at constant pressure. From the ideal gas law
, the volume of such a sample can be used as an indicator of temperature; in this manner it defines temperature. Although pressure is defined mechanically, a pressure-measuring device called a barometer
may also be constructed from a sample of an ideal gas held at a constant temperature. A calorimeter
is a device which is used to measure and define the internal energy of a system.
Some common thermodynamic meters are:
" in the below description of a theoretical thermometer is essentially a "pressure reservoir" which imposes atmospheric pressure upon the thermometer.
Some common reservoirs are:
es. The behavior of an ideal gas is given by the ideal gas law:
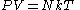
where P is pressure, V is volume, N is the number of particles (total mass divided by mass per particle), k is Boltzmann's constant, and T is temperature. In fact, this equation is more than a phenomenological equation, it gives an operational, or experimental, definition of temperature. A thermometer is a tool that measures temperature - a primitive thermometer would simply be a small container of an ideal gas, that was allowed to expand against atmospheric pressure. If we bring it into thermal contact with the system whose temperature we wish to measure, wait until it equilibrates, and then measure the volume of the thermometer, we will be able to calculate the temperature of the system in question via T=PV/Nk. Hopefully, the thermometer will be small enough that it does not appreciably alter the temperature of the system it is measuring, and also that the atmospheric pressure is not affected by the expansion of the thermometer.
The ideal gas thermometer
can be defined more precisely by saying it is a system containing an ideal gas, which is thermally connected to the system it is measuring, while being dynamically and materially insulated from it. It is simultaneously dynamically connected to an external pressure reservoir, from which it is materially and thermally insulated. Other thermometers (e.g. mercury thermometers, which display the volume of mercury to the observer) may now be constructed, and calibrated against the ideal gas thermometer.
There are two types of thermodynamic instruments, the meter and the reservoir. A thermodynamic meter is any device which measures any parameter of a thermodynamic system. A thermodynamic reservoir is a system which is so large that it does not appreciably alter its state parameters when brought into contact with the test system.
Overview
Two general complementary tools are the meter and the reservoir. It is important that these two types of instruments are distinct. A meter does not perform its task accurately if it behaves like a reservoir of the state variable it is trying to measure. If, for example, a thermometer, were to act as a temperature reservoir it would alter the temperature of the system being measured, and the reading would be incorrect. Ideal meters have no effect on the state variables of the system they are measuring.Thermodynamic meters
A meter is a thermodynamic system which displays some aspect of its thermodynamic state to the observer. The nature of its contact with the system it is measuring can be controlled, and it is sufficiently small that it does not appreciably affect the state of the system being measured. The theoretical thermometer described below is just such a meter.In some cases, the thermodynamic parameter is actually defined in terms of an idealized measuring instrument. For example, the zeroth law of thermodynamics
Zeroth law of thermodynamics
The zeroth law of thermodynamics is a generalization principle of thermal equilibrium among bodies, or thermodynamic systems, in contact.The zeroth law states that if two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, they are also in thermal equilibrium with each other.Systems are said to...
states that if two bodies are in thermal equilibrium with a third body, they are also in thermal equilibrium with each other. This principle, as noted by James Maxwell in 1872, asserts that it is possible to measure temperature. An idealized thermometer is a sample of an ideal gas at constant pressure. From the ideal gas law
Ideal gas law
The ideal gas law is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation to the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stated by Émile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of Boyle's law and Charles's law...
, the volume of such a sample can be used as an indicator of temperature; in this manner it defines temperature. Although pressure is defined mechanically, a pressure-measuring device called a barometer
Barometer
A barometer is a scientific instrument used in meteorology to measure atmospheric pressure. Pressure tendency can forecast short term changes in the weather...
may also be constructed from a sample of an ideal gas held at a constant temperature. A calorimeter
Calorimeter
A calorimeter is a device used for calorimetry, the science of measuring the heat of chemical reactions or physical changes as well as heat capacity. Differential scanning calorimeters, isothermal microcalorimeters, titration calorimeters and accelerated rate calorimeters are among the most common...
is a device which is used to measure and define the internal energy of a system.
Some common thermodynamic meters are:
- ThermometerThermometerDeveloped during the 16th and 17th centuries, a thermometer is a device that measures temperature or temperature gradient using a variety of different principles. A thermometer has two important elements: the temperature sensor Developed during the 16th and 17th centuries, a thermometer (from the...
- a device which measures temperature as described above - BarometerBarometerA barometer is a scientific instrument used in meteorology to measure atmospheric pressure. Pressure tendency can forecast short term changes in the weather...
- a device which measures pressure. An ideal gas barometer may be constructed by mechanically connecting an ideal gas to the system being measured, while thermally insulating it. The volume will then measure pressure, by the ideal gas equation P=NkT/V . - CalorimeterCalorimeterA calorimeter is a device used for calorimetry, the science of measuring the heat of chemical reactions or physical changes as well as heat capacity. Differential scanning calorimeters, isothermal microcalorimeters, titration calorimeters and accelerated rate calorimeters are among the most common...
- a device which measures the heat energy added to a system. A simple calorimeter is simply a thermometer connected to a thermally isolated system.
Thermodynamic reservoirs
A reservoir is a thermodynamic system which controls the state of a system, usually by "imposing" itself upon the system being controlled. This means that the nature of its contact with the system can be controlled. A reservoir is so large that its thermodynamic state is not appreciably affected by the state of the system being controlled. The term "atmospheric pressureAtmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure is the force per unit area exerted into a surface by the weight of air above that surface in the atmosphere of Earth . In most circumstances atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point...
" in the below description of a theoretical thermometer is essentially a "pressure reservoir" which imposes atmospheric pressure upon the thermometer.
Some common reservoirs are:
- Pressure reservoir - by far the most common pressure reservoir is the Earth's atmosphere.
- Temperature reservoir - A large quantity of water at its triple point forms an effective temperature reservoir.
Theory
Let's assume that we understand mechanics well enough to understand and measure volume, area, mass, and force. These may be combined to understand the concept of pressure, which is force per unit area and density, which is mass per unit volume. It has been experimentally determined that, at low enough pressures and densities, all gases behave as ideal gasIdeal gas
An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of a set of randomly-moving, non-interacting point particles. The ideal gas concept is useful because it obeys the ideal gas law, a simplified equation of state, and is amenable to analysis under statistical mechanics.At normal conditions such as...
es. The behavior of an ideal gas is given by the ideal gas law:
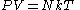
where P is pressure, V is volume, N is the number of particles (total mass divided by mass per particle), k is Boltzmann's constant, and T is temperature. In fact, this equation is more than a phenomenological equation, it gives an operational, or experimental, definition of temperature. A thermometer is a tool that measures temperature - a primitive thermometer would simply be a small container of an ideal gas, that was allowed to expand against atmospheric pressure. If we bring it into thermal contact with the system whose temperature we wish to measure, wait until it equilibrates, and then measure the volume of the thermometer, we will be able to calculate the temperature of the system in question via T=PV/Nk. Hopefully, the thermometer will be small enough that it does not appreciably alter the temperature of the system it is measuring, and also that the atmospheric pressure is not affected by the expansion of the thermometer.
The ideal gas thermometer
Gas thermometer
A gas thermometer measures temperature by the variation in volume or pressure of a gas. One common apparatus is a constant volume thermometer. It consists of a bulb connected by a capillary tube to a manometer. The bulb is filled with a gas such that the volume of the gas in the bulb remains...
can be defined more precisely by saying it is a system containing an ideal gas, which is thermally connected to the system it is measuring, while being dynamically and materially insulated from it. It is simultaneously dynamically connected to an external pressure reservoir, from which it is materially and thermally insulated. Other thermometers (e.g. mercury thermometers, which display the volume of mercury to the observer) may now be constructed, and calibrated against the ideal gas thermometer.

