
Theophanes the Cretan
Encyclopedia

- For the ByzantineByzantineByzantine usually refers to the Roman Empire during the Middle Ages.Byzantine may also refer to:* A citizen of the Byzantine Empire, or native Greek during the Middle Ages...
icon painter who worked in Muscovy, see Theophanes the GreekTheophanes the GreekTheophanes the Greek was a Byzantine Greek artist and one of the greatest icon painters, or iconographers, of Muscovite Russia, and was noted as the teacher and mentor of the great Andrei Rublev.-Life and work:Theophanes was born in the capital of the Byzantine Empire, Constantinople...
.
Theophanis Strelitzas (Θεοφάνης Στρελίτζας), also known as Theophanes the Cretan (Θεοφάνης ο Κρης) or "of Crete
Crete
Crete is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, and one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. It forms a significant part of the economy and cultural heritage of Greece while retaining its own local cultural traits...
" or "Theophanes Bathas", was a leading icon
Icon
An icon is a religious work of art, most commonly a painting, from Eastern Christianity and in certain Eastern Catholic churches...
painter of the Cretan school
Cretan School
The term Cretan School describes an important school of icon painting, also known as Post-Byzantine art, which flourished while Crete was under Venetian rule during the late Middle Ages, reaching its climax after the Fall of Constantinople, becoming the central force in Greek painting during the...
in the first half of the sixteenth century, and in particular the most important figure in Greek wall-painting of the period.
He was born in Heraklion
Heraklion
Heraklion, or Heraclion is the largest city and the administrative capital of the island of Crete, Greece. It is the 4th largest city in Greece....
in Crete
Crete
Crete is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, and one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. It forms a significant part of the economy and cultural heritage of Greece while retaining its own local cultural traits...
(date unknown), and no doubt trained there, but all his known work was done in mainland Greece. Fresco
Fresco
Fresco is any of several related mural painting types, executed on plaster on walls or ceilings. The word fresco comes from the Greek word affresca which derives from the Latin word for "fresh". Frescoes first developed in the ancient world and continued to be popular through the Renaissance...
es bearing his signature survive in the Greek
Greek Orthodox Church
The Greek Orthodox Church is the body of several churches within the larger communion of Eastern Orthodox Christianity sharing a common cultural tradition whose liturgy is also traditionally conducted in Koine Greek, the original language of the New Testament...
monasteries of Mt. Athos, especially Stavronikita monastery
Stavronikita monastery
Stavronikita monastery is an Eastern Orthodox monastery at the monastic state of Mount Athos in Greece, dedicated to Saint Nicholas. It is built on top of a rock near the sea near the middle of the eastern shore of the Athonite peninsula, located between the monasteries of Iviron and Pantokratoros...
and Lavra, and Meteora
Meteora
The Metéora is one of the largest and most important complexes of Eastern Orthodox monasteries in Greece, second only to Mount Athos. The six monasteries are built on natural sandstone rock pillars, at the northwestern edge of the Plain of Thessaly near the Pineios river and Pindus Mountains, in...
which has his earliest dated work, from 1527. He also did many panel
Panel painting
A panel painting is a painting made on a flat panel made of wood, either a single piece, or a number of pieces joined together. Until canvas became the more popular support medium in the 16th century, it was the normal form of support for a painting not on a wall or vellum, which was used for...
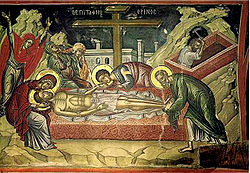
icons, either for iconostases or small portable works. Theophanes was active from about 1527-48, and trained his sons and several pupils, often themselves Cretan. By 1535 both he and his two sons had become monks in the Lavra monastery of Mount Athos, where many of his best works remain. Theophanes returned to Crete before his death in 1559.
Two detached wallpaintings attributed to Theophanes are in the Hermitage Museum
Hermitage Museum
The State Hermitage is a museum of art and culture in Saint Petersburg, Russia. One of the largest and oldest museums of the world, it was founded in 1764 by Catherine the Great and has been opened to the public since 1852. Its collections, of which only a small part is on permanent display,...
in Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg is a city and a federal subject of Russia located on the Neva River at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea...
. Like most Cretan painters of this date, his work shows some influence from Western painting, but less in his case than with many artists. Some faces are personalised or looking out to the viewer, and his figures are modelled to convey volume. His work is more conscious of visual perspective than older Byzantine artists, but he does not use the geometrical perspective schemes by then standard in the West. He uses traditional Byzantine compositions, in a rather austere and powerful manner.
He should not be confused with Theophanes the Greek
Theophanes the Greek
Theophanes the Greek was a Byzantine Greek artist and one of the greatest icon painters, or iconographers, of Muscovite Russia, and was noted as the teacher and mentor of the great Andrei Rublev.-Life and work:Theophanes was born in the capital of the Byzantine Empire, Constantinople...
(Feofan Grek), an icon painter who worked in Muscovite Russia in the late fourteenth century.

