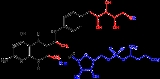
Tetrahydromethanopterin
Encyclopedia
Tetrahydromethanopterin (THMPT, ') is a coenzyme in methanogenesis
. It is the carrier of the C1 group as it is reduced to the methyl level, before transferring to the coenzyme M
.
Tetrahydrosarcinapterin (THSPT) is a modified form of THMPT, wherein a glutamyl
group linked to the 2-hydroxyglutaric acid
terminus.
donates the C1 group to the N5 site of the pterin to give the formyl- THMPT. The formyl group subsequently condenses intramolecularly to give methenyl- , which is then reduced to methylene- THMPT. Methylene- MPT is subsequently converted, using coenzyme F420
as the electron source, to methyl- THMPT, catalyzed by F420-dependent methylene- THMPT reductase. Methyl- THMPT is the methyl donor to coenzyme M
, a conversion mediated by methyl- THMPT:coenzyme M methyl-transferase.
(THFA). The most important difference between THMPT and THFA is that THFA has an electron-withdrawing carbonyl group on the phenyl ring. As a consequence, methenyl- THMPT is more difficult to reduce than methenyl- THFA. Reduction is effected by a so-called iron-sulfur cluster free hydrogenase. The cumbersome name distinguishes this hydrogenase from the so-called Fe-only hydrogenase
s that do contain Fe-S cluster.
Methanogenesis
Methanogenesis or biomethanation is the formation of methane by microbes known as methanogens. Organisms capable of producing methane have been identified only from the domain Archaea, a group phylogenetically distinct from both eukaryotes and bacteria, although many live in close association with...
. It is the carrier of the C1 group as it is reduced to the methyl level, before transferring to the coenzyme M
Coenzyme M
Coenzyme M is a coenzyme required for methyl-transfer reactions in the metabolism of methanogens. The coenzyme is an anion with the formula . It is named 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate and abbreviated HS–CoM. The cation is unimportant, but the sodium salt is most available...
.
Tetrahydrosarcinapterin (THSPT) is a modified form of THMPT, wherein a glutamyl
Glutamine
Glutamine is one of the 20 amino acids encoded by the standard genetic code. It is not recognized as an essential amino acid but may become conditionally essential in certain situations, including intensive athletic training or certain gastrointestinal disorders...
group linked to the 2-hydroxyglutaric acid
Glutaric acid
Glutaric acid is the organic compound with the formula HO2C3CO2H. Although the related "linear" dicarboxylic acids adipic and succinic acids are water-soluble only to a few percent at room temperature, the water-solubility of glutaric acid is over 50%....
terminus.
THMPT is the main platform for C1 transformations
N-FormylmethanofuranMethanofuran
Methanofuran describes a family of chemical compounds found in methanogenic archaea. These species feature a 2-aminomethylfuran linked to phenoxy group...
donates the C1 group to the N5 site of the pterin to give the formyl- THMPT. The formyl group subsequently condenses intramolecularly to give methenyl- , which is then reduced to methylene- THMPT. Methylene- MPT is subsequently converted, using coenzyme F420
Coenzyme F420
Coenzyme F420 or 8-hydroxy-5-deazaflavin is a coenzyme involved in redox reactions in methanogens , in many Actinobacteria, and sporadically in other bacterial lineages. It is a flavin derivative...
as the electron source, to methyl- THMPT, catalyzed by F420-dependent methylene- THMPT reductase. Methyl- THMPT is the methyl donor to coenzyme M
Coenzyme M
Coenzyme M is a coenzyme required for methyl-transfer reactions in the metabolism of methanogens. The coenzyme is an anion with the formula . It is named 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate and abbreviated HS–CoM. The cation is unimportant, but the sodium salt is most available...
, a conversion mediated by methyl- THMPT:coenzyme M methyl-transferase.
Comparison with tetrahydrofolic acid
THMPT is related to the better known tetrahydrofolic acidTetrahydrofolic acid
Tetrahydrofolic acid, or tetrahydrofolate, is a folic acid derivative.-Metabolism:-Human synthesis:It is produced from dihydrofolic acid by dihydrofolate reductase...
(THFA). The most important difference between THMPT and THFA is that THFA has an electron-withdrawing carbonyl group on the phenyl ring. As a consequence, methenyl- THMPT is more difficult to reduce than methenyl- THFA. Reduction is effected by a so-called iron-sulfur cluster free hydrogenase. The cumbersome name distinguishes this hydrogenase from the so-called Fe-only hydrogenase
Hydrogenase
A hydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyses the reversible oxidation of molecular hydrogen . Hydrogenases play a vital role in anaerobic metabolism....
s that do contain Fe-S cluster.

