Telecommunications in the United Kingdom
Encyclopedia
Until 1982, the main civil telecommunications system in the UK was a state monopoly
known (since reorganisation in 1969) as Post Office Telecommunications
. Broadcasting of radio and television was a duopoly of the BBC
and Independent Broadcasting Authority
(IBA): these two organisations controlled all broadcast services, and directly owned and operated the broadcast transmitter sites. Mobile phone and Internet services did not then exist.
The civil telecomms monopoly ended when Mercury Communications
arrived in 1983. The Post Office system evolved into British Telecom and was privatised in 1984.
Broadcast transmitters, which belonged to the BBC and IBA, were privatised during the 1990s and now belong to National Grid Wireless, VT Communications
and Arqiva
.
Regulation of communications has changed many times during the same period, and most of the bodies have been merged into Ofcom
, the independent regulator and competition authority for the UK communications industries http://www.ofcom.org.uk/.
. Most are carried via national optical fibre
networks. There are several companies with national fibre networks, including BT, Virgin Media
, Cable & Wireless
, Easynet
and Thus. Microwave
links are used up to the 155 Mbit/s level, but are seldom cost-effective at higher bit rate
s.
s, which are now mostly digital optical fibre cables. There are many satellite links too, but these now provide a relatively small part of the international bandwidth.
Virgin Media is the second biggest player in the residential telephone line market.
Other companies provide fixed telephone lines too, but mainly to large companies in the major cities.
There are many other providers who sell fixed telephone services carried over BT lines. They have no network infrastructure of their own.
Both companies ran ETACS
analogue mobile phone networks.
The 3rd generation stems from technological improvements and is in essence an improvement of the available bandwidth, enabling new services to be provided to customers.
Such services include streaming of live radio or video, video calls and live TV.
Orange have biggest 3G coverage, currently standing at 93.2% (Q3 2009). However Vodafone and Orange have a good amount of coverage. T-Mobile has fairly good coverage as does O2 but generally only in major cities and less so in smaller towns, however T-Mobile and 3 have recently struck a deal whereby they can use each others 3G coverage but 3 customers cannot use T-Mobile 2G coverage. Three also have an additional agreement with Orange until 2010 in which Orange 2G coverage is available to three subscribers where no 3G signal exists. It is unknown whether this agreement will continue if the merger between Orange and T-Mobile is approved.
O2 will be trialling LTE
technology within the next few years. It is expected other networks will follow.
, there are 35 million (2002) main line telephones.
The telephone service in the United Kingdom
was originally provided by private companies and local city councils, but by 1912,–13 all except the telephone service of Kingston upon Hull
, Yorkshire
and Guernsey
had been bought out by the Post Office
. Post Office Telephones also operated telephone services in Jersey
and the Isle of Man
until 1969 when the islands took over responsibility for their own postal and telephone services.
Post Office Telephones was reorganised in 1980–81 http://www.bt.com/archives/history/19811983.htm#1981 as British Telecommunications (British Telecom, or BT), and was the first nationalised industry to be privatised by the Conservative government. The Hull Telephone Department was itself sold by Hull City Council as Kingston Communications
in the late 1990s and celebrated its centenary in 2004.
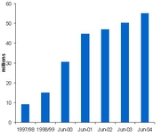
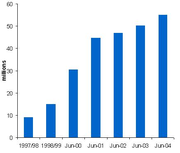 As of January 2005, there are now more mobile phone
As of January 2005, there are now more mobile phone
s than people - over 55 million - in the UK. However, this does not compare with Luxembourg
, which has achieved 133% market penetration.
Each of the five network operators (see Infrastructure above) sells mobile phone services to the public. In addition, companies such as Virgin Media
and Tesco
operate "virtual" networks on the infrastructure of other companies.
), which replaced the Office of Telecommunications (Oftel
) in 2003. Each number consists of an area code—one for each of the large towns and cities and their surroundings—and a subscriber number—the individual number.
, 431 on FM
and 3 on shortwave. There are 84.5 million radio receiver sets (1997).
There are five major analogue networks - BBC One
, BBC Two
, ITV
, Channel 4
and Five. Other networks include BSkyB, who are the main provider of satellite television in the UK and UKTV
. The major cable television
company is Virgin Media
, and the digital terrestrial television
company Freeview.
for United Kingdom web pages is
is the
At the end of 2004, 52% of households (12.6 million) were reported to have access to the internet
(Source: Office for National Statistics
Omnibus Survey). broadband
connections accounted for 50.7% of all internet connections in July 2005, with one broadband connection being created every ten seconds. Broadband connections grew by nearly 80% in 2004. In 1999, there were 364 Internet Service Provider
s (ISPs). Public libraries also provide access to the internet, sometimes for a fee.
Bibliography
Monopoly
A monopoly exists when a specific person or enterprise is the only supplier of a particular commodity...
known (since reorganisation in 1969) as Post Office Telecommunications
Post Office Telecommunications
Post Office Telecommunications was set up as a separate department of the UK Post Office, in October 1969. The Post Office Act of that year was passed to provide for greater efficiency in post and telephone services; rather than run a range of services, each organisation would be able to focus on...
. Broadcasting of radio and television was a duopoly of the BBC
BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation is a British public service broadcaster. Its headquarters is at Broadcasting House in the City of Westminster, London. It is the largest broadcaster in the world, with about 23,000 staff...
and Independent Broadcasting Authority
Independent Broadcasting Authority
The Independent Broadcasting Authority was the regulatory body in the United Kingdom for commercial television - and commercial/independent radio broadcasts...
(IBA): these two organisations controlled all broadcast services, and directly owned and operated the broadcast transmitter sites. Mobile phone and Internet services did not then exist.
The civil telecomms monopoly ended when Mercury Communications
Mercury Communications
Mercury Communications was a national telephone company in the United Kingdom. The company was formed in 1981 as a subsidiary of Cable & Wireless to challenge the monopoly of British Telecom which was privatised in 1984...
arrived in 1983. The Post Office system evolved into British Telecom and was privatised in 1984.
Broadcast transmitters, which belonged to the BBC and IBA, were privatised during the 1990s and now belong to National Grid Wireless, VT Communications
VT Communications
VT Communications was a part of VT Group plc. VT Communications was essentially the company formed from the privatisation of the BBC World Service transmitter sites. It was initially named Merlin Communications, then, after acquisition by VT, VT Merlin Communications...
and Arqiva
Arqiva
Arqiva is a telecommunications company which provides infrastructure and broadcast transmission facilities in the United Kingdom and Republic of Ireland. The present company, with headquarters located at Crawley Court in the village of Crawley, Hampshire, was formed by National Grid Wireless...
.
Regulation of communications has changed many times during the same period, and most of the bodies have been merged into Ofcom
Ofcom
Ofcom is the government-approved regulatory authority for the broadcasting and telecommunications industries in the United Kingdom. Ofcom was initially established by the Office of Communications Act 2002. It received its full authority from the Communications Act 2003...
, the independent regulator and competition authority for the UK communications industries http://www.ofcom.org.uk/.
Infrastructure
| Communications in the United Kingdom | ||
|---|---|---|
| Radio broadcast stations (1998) | 663 | |
| Telephone lines (2002) | 35m | |
| Internet access | ||
| Percent household access (total), 2004 | 52% of households (12.6 million) | |
| Percent broadband household access | Half of internet connections | |
| Internet Service Provider Internet service provider An Internet service provider is a company that provides access to the Internet. Access ISPs directly connect customers to the Internet using copper wires, wireless or fiber-optic connections. Hosting ISPs lease server space for smaller businesses and host other people servers... s (1999) |
364 | |
| country code top-level domain Country code top-level domain A country code top-level domain is an Internet top-level domain generally used or reserved for a country, a sovereign state, or a dependent territory.... |
.uk .uk .uk is the Internet country code top-level domain for the United Kingdom. , it is the fourth most popular top-level domain worldwide , with over 9.5 million registrations.... |
|
Domestic Trunk Infrastructure
All communications trunks are now digitalDigital
A digital system is a data technology that uses discrete values. By contrast, non-digital systems use a continuous range of values to represent information...
. Most are carried via national optical fibre
Optical fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
networks. There are several companies with national fibre networks, including BT, Virgin Media
Virgin Media
Virgin Media Inc. is a company which provides fixed and mobile telephone, television and broadband internet services to businesses and consumers in the United Kingdom...
, Cable & Wireless
Cable & Wireless
Cable & Wireless Worldwide PLC is a global telecommunications company headquartered in Bracknell, United Kingdom. Cable & Wireless specialises in providing communication networks and services to large corporates, governments, carrier customers and resellers...
, Easynet
Easynet
Easynet Global Services are a provider of managed network, hosting and telepresence solutions for businesses and enterprises worldwide.Founded in 1994, Easynet Global Services are part of the Easynet group of companies, along with Easynet Connect and UK Online.It was a part of BSkyB, a FTSE top 50...
and Thus. Microwave
British Telecom microwave network
The British Telecom microwave network was a network of point-to-point microwave radio links in the United Kingdom, operated at first by the General Post Office, and subsequently by its successor BT plc...
links are used up to the 155 Mbit/s level, but are seldom cost-effective at higher bit rate
Bit rate
In telecommunications and computing, bit rate is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time....
s.
International Trunks
The UK is a focal point for many of the world's submarine communications cableSubmarine communications cable
A submarine communications cable is a cable laid on the sea bed between land-based stations to carry telecommunication signals across stretches of ocean....
s, which are now mostly digital optical fibre cables. There are many satellite links too, but these now provide a relatively small part of the international bandwidth.
Broadcast Transmission
Most broadcasting organisations, BBC and commercial, lease transmission facilities from one or more of the transmission companies. The main exception is the smaller local radio stations, some of which find it more cost-effective to provide their own.Fixed Phone Lines
BT is still the main provider of fixed telephones lines, both POTS and ISDN, and it has a universal service obligation, although companies can now contract Openreach to install a phoneline on their behalf, rather than telling the customer to get BT to install it, then transfer over.Virgin Media is the second biggest player in the residential telephone line market.
Other companies provide fixed telephone lines too, but mainly to large companies in the major cities.
There are many other providers who sell fixed telephone services carried over BT lines. They have no network infrastructure of their own.
First Generation Networks
- Cellnet: A company originally jointly owned by British Telecom and SecuricorSecuricorSecuricor plc was one of the United Kingdom's largest security businesses. It was once a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index but merged with Group 4 Falck in 2004.-History:...
. BT eventually bought out Securicor's stake. The network became BT Cellnet and was then demerged to become O2O2 plcTelefónica Europe plc is a European broadband and telecommunications company that trades as O2 . The company originated as a collection of worldwide telecommunications companies, known in the later half of the 1990s as BT Wireless, and a global mobile data business known then as Genie Internet,...
. - VodafoneVodafoneVodafone Group Plc is a global telecommunications company headquartered in London, United Kingdom. It is the world's largest mobile telecommunications company measured by revenues and the world's second-largest measured by subscribers , with around 341 million proportionate subscribers as of...
Both companies ran ETACS
Advanced Mobile Phone System
Advanced Mobile Phone System was an analog mobile phone system standard developed by Bell Labs, and officially introduced in the Americas in 1983, Israel in 1986, and Australia in 1987. It was the primary analog mobile phone system in North America through the 1980s and into the 2000s...
analogue mobile phone networks.
First and Second Generation Networks
- O2O2 plcTelefónica Europe plc is a European broadband and telecommunications company that trades as O2 . The company originated as a collection of worldwide telecommunications companies, known in the later half of the 1990s as BT Wireless, and a global mobile data business known then as Genie Internet,...
: now owned by Telefonica. Runs a GSM-900 network - VodafoneVodafoneVodafone Group Plc is a global telecommunications company headquartered in London, United Kingdom. It is the world's largest mobile telecommunications company measured by revenues and the world's second-largest measured by subscribers , with around 341 million proportionate subscribers as of...
: Runs a GSM-900 network. - OrangeOrange SAOrange is the brand used by France Télécom for its mobile network operator and Internet service provider subsidiaries. It is the fifth largest telecom operator in the world, with 210 million customers . The brand was created in 1994 for Hutchison Telecom's UK mobile phone network, which was...
: runs a GSM-1800 network - T-MobileT-MobileT-Mobile International AG is a German-based holding company for Deutsche Telekom AG's various mobile communications subsidiaries outside Germany. Based in Bonn, Germany, its subsidiaries operate GSM and UMTS-based cellular networks in Europe, the United States, Puerto Rico and the US Virgin Islands...
: originally called One-2-One, this network is also GSM-1800
Third Generation Networks
The four 2G companies all won 3G licences in a competitive auction, as did a new entrant known as 3. They have now rolled out their networks. 3 does not operate a 2G network, but has an agreement with Orange whereby customers who lose a 3G signal roam with Orange. They previously had an agreement with O2 to provide the same service.The 3rd generation stems from technological improvements and is in essence an improvement of the available bandwidth, enabling new services to be provided to customers.
Such services include streaming of live radio or video, video calls and live TV.
Orange have biggest 3G coverage, currently standing at 93.2% (Q3 2009). However Vodafone and Orange have a good amount of coverage. T-Mobile has fairly good coverage as does O2 but generally only in major cities and less so in smaller towns, however T-Mobile and 3 have recently struck a deal whereby they can use each others 3G coverage but 3 customers cannot use T-Mobile 2G coverage. Three also have an additional agreement with Orange until 2010 in which Orange 2G coverage is available to three subscribers where no 3G signal exists. It is unknown whether this agreement will continue if the merger between Orange and T-Mobile is approved.
O2 will be trialling LTE
3GPP Long Term Evolution
3GPP Long Term Evolution, usually referred to as LTE, is a standard for wireless communication of high-speed data for mobile phones and data terminals. It is based on the GSM/EDGE and UMTS/HSPA network technologies, increasing the capacity and speed using new modulation techniques...
technology within the next few years. It is expected other networks will follow.
Fixed Telephones
In the United KingdomUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, there are 35 million (2002) main line telephones.
The telephone service in the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
was originally provided by private companies and local city councils, but by 1912,–13 all except the telephone service of Kingston upon Hull
Kingston upon Hull
Kingston upon Hull , usually referred to as Hull, is a city and unitary authority area in the ceremonial county of the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. It stands on the River Hull at its junction with the Humber estuary, 25 miles inland from the North Sea. Hull has a resident population of...
, Yorkshire
Yorkshire
Yorkshire is a historic county of northern England and the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its great size in comparison to other English counties, functions have been increasingly undertaken over time by its subdivisions, which have also been subject to periodic reform...
and Guernsey
Guernsey
Guernsey, officially the Bailiwick of Guernsey is a British Crown dependency in the English Channel off the coast of Normandy.The Bailiwick, as a governing entity, embraces not only all 10 parishes on the Island of Guernsey, but also the islands of Herm, Jethou, Burhou, and Lihou and their islet...
had been bought out by the Post Office
Post office
A post office is a facility forming part of a postal system for the posting, receipt, sorting, handling, transmission or delivery of mail.Post offices offer mail-related services such as post office boxes, postage and packaging supplies...
. Post Office Telephones also operated telephone services in Jersey
Jersey
Jersey, officially the Bailiwick of Jersey is a British Crown Dependency off the coast of Normandy, France. As well as the island of Jersey itself, the bailiwick includes two groups of small islands that are no longer permanently inhabited, the Minquiers and Écréhous, and the Pierres de Lecq and...
and the Isle of Man
Isle of Man
The Isle of Man , otherwise known simply as Mann , is a self-governing British Crown Dependency, located in the Irish Sea between the islands of Great Britain and Ireland, within the British Isles. The head of state is Queen Elizabeth II, who holds the title of Lord of Mann. The Lord of Mann is...
until 1969 when the islands took over responsibility for their own postal and telephone services.
Post Office Telephones was reorganised in 1980–81 http://www.bt.com/archives/history/19811983.htm#1981 as British Telecommunications (British Telecom, or BT), and was the first nationalised industry to be privatised by the Conservative government. The Hull Telephone Department was itself sold by Hull City Council as Kingston Communications
Kingston Communications
KCOM Group , formerly known as Kingston Communications, is a UK communications and IT services provider. Its headquarters is in Kingston upon Hull, East Riding of Yorkshire, where subsidiary business unit KC serves local residents and businesses with Internet and telephony services...
in the late 1990s and celebrated its centenary in 2004.
Mobile Telephones

Mobile phone
A mobile phone is a device which can make and receive telephone calls over a radio link whilst moving around a wide geographic area. It does so by connecting to a cellular network provided by a mobile network operator...
s than people - over 55 million - in the UK. However, this does not compare with Luxembourg
Luxembourg
Luxembourg , officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg , is a landlocked country in western Europe, bordered by Belgium, France, and Germany. It has two principal regions: the Oesling in the North as part of the Ardennes massif, and the Gutland in the south...
, which has achieved 133% market penetration.
Each of the five network operators (see Infrastructure above) sells mobile phone services to the public. In addition, companies such as Virgin Media
Virgin Media
Virgin Media Inc. is a company which provides fixed and mobile telephone, television and broadband internet services to businesses and consumers in the United Kingdom...
and Tesco
Tesco
Tesco plc is a global grocery and general merchandise retailer headquartered in Cheshunt, United Kingdom. It is the third-largest retailer in the world measured by revenues and the second-largest measured by profits...
operate "virtual" networks on the infrastructure of other companies.
Numbering
There is a set numbering plan for phone numbers within the United Kingdom, which is regulated by the Office of Communications (OfcomOfcom
Ofcom is the government-approved regulatory authority for the broadcasting and telecommunications industries in the United Kingdom. Ofcom was initially established by the Office of Communications Act 2002. It received its full authority from the Communications Act 2003...
), which replaced the Office of Telecommunications (Oftel
Oftel
Oftel has been superseded as the British telecommunications regulator by Ofcom .----The Office of Telecommunications was a department in the United Kingdom government, under civil service control, charged with promoting competition and maintaining the interests of consumers in the UK...
) in 2003. Each number consists of an area code—one for each of the large towns and cities and their surroundings—and a subscriber number—the individual number.
Radio
In 1998, there are 663 radio broadcast stations: 219 on AMAmplitude modulation
Amplitude modulation is a technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting information via a radio carrier wave. AM works by varying the strength of the transmitted signal in relation to the information being sent...
, 431 on FM
Frequency modulation
In telecommunications and signal processing, frequency modulation conveys information over a carrier wave by varying its instantaneous frequency. This contrasts with amplitude modulation, in which the amplitude of the carrier is varied while its frequency remains constant...
and 3 on shortwave. There are 84.5 million radio receiver sets (1997).
Television
As of 1997, there are 30.5 million households with television sets.There are five major analogue networks - BBC One
BBC One
BBC One is the flagship television channel of the British Broadcasting Corporation in the United Kingdom. It was launched on 2 November 1936 as the BBC Television Service, and was the world's first regular television service with a high level of image resolution...
, BBC Two
BBC Two
BBC Two is the second television channel operated by the British Broadcasting Corporation in the United Kingdom. It covers a wide range of subject matter, but tending towards more 'highbrow' programmes than the more mainstream and popular BBC One. Like the BBC's other domestic TV and radio...
, ITV
ITV
ITV is the major commercial public service TV network in the United Kingdom. Launched in 1955 under the auspices of the Independent Television Authority to provide competition to the BBC, it is also the oldest commercial network in the UK...
, Channel 4
Channel 4
Channel 4 is a British public-service television broadcaster which began working on 2 November 1982. Although largely commercially self-funded, it is ultimately publicly owned; originally a subsidiary of the Independent Broadcasting Authority , the station is now owned and operated by the Channel...
and Five. Other networks include BSkyB, who are the main provider of satellite television in the UK and UKTV
UKTV
UKTV is a digital cable and satellite television network, formed through a joint venture between BBC Worldwide, a commercial subsidiary of the British Broadcasting Corporation, and Scripps Networks Interactive, spun off from The E.W Scripps Company in 2008...
. The major cable television
Cable television
Cable television is a system of providing television programs to consumers via radio frequency signals transmitted to televisions through coaxial cables or digital light pulses through fixed optical fibers located on the subscriber's property, much like the over-the-air method used in traditional...
company is Virgin Media
Virgin Media
Virgin Media Inc. is a company which provides fixed and mobile telephone, television and broadband internet services to businesses and consumers in the United Kingdom...
, and the digital terrestrial television
Digital terrestrial television
Digital terrestrial television is the technological evolution of broadcast television and advance from analog television, which broadcasts land-based signals...
company Freeview.
Internet
The country code top-level domainCountry code top-level domain
A country code top-level domain is an Internet top-level domain generally used or reserved for a country, a sovereign state, or a dependent territory....
for United Kingdom web pages is
.uk.uk.uk is the Internet country code top-level domain for the United Kingdom. , it is the fourth most popular top-level domain worldwide , with over 9.5 million registrations....
. Nominet UKNominet UK
Nominet UK is the .uk domain name registry in the United Kingdom, which was founded by Dr Willie Black and five others on 14 May 1996 when its predecessor, the 'Naming Committee' was unable to deal with the volume of registrations then being sought under the .uk domain. Nominet is a non-profit...
is the
.uk. Network Information Centre and second-level domains must be used.At the end of 2004, 52% of households (12.6 million) were reported to have access to the internet
Internet
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
(Source: Office for National Statistics
Office for National Statistics
The Office for National Statistics is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department which reports directly to the Parliament of the United Kingdom.- Overview :...
Omnibus Survey). broadband
Broadband Internet access
Broadband Internet access, often shortened to just "broadband", is a high data rate, low-latency connection to the Internet— typically contrasted with dial-up access using a 56 kbit/s modem or satellite Internet with inherently high latency....
connections accounted for 50.7% of all internet connections in July 2005, with one broadband connection being created every ten seconds. Broadband connections grew by nearly 80% in 2004. In 1999, there were 364 Internet Service Provider
Internet service provider
An Internet service provider is a company that provides access to the Internet. Access ISPs directly connect customers to the Internet using copper wires, wireless or fiber-optic connections. Hosting ISPs lease server space for smaller businesses and host other people servers...
s (ISPs). Public libraries also provide access to the internet, sometimes for a fee.
See also
- List of postcode areas in the United Kingdom - (about 120)
- List of postal districts in the United Kingdom - (about 2900)
- List of United Kingdom dialling codes
- British Telephone SocketsBritish telephone socketsBritish telephone sockets were introduced in their current plug and socket form on 19 November 1981 by British Telecom to allow subscribers to connect their own telephones...
- Ukphonebook.comUkphonebook.comukphonebook.com was the first free online telephone directory to use the official British Telecom data. Created in 1999, the site now has over 2 million registered users from 28 countries.- History :...
Sources
NotesBibliography

