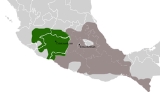
Tarascan state
Encyclopedia
The Tarascan state was a state in pre-Columbian Mesoamerica
, roughly covering the geographic area of the present-day Mexican state of Michoacán
. At the time of the Spanish conquest of Mexico
it was the second-largest state in Mexico. The state was founded in the early 14th century and lost its independence to the Spanish in 1530. In 1543 it officially became the governorship of Michoacán, from the Nahuatl name for the Tarascan state, Michoacán ("place of those who have fish"). In P'urhépecha
, language of the Tarascans, the name of the state was Iréchecua Tzintzuntzáni, the "lands of Tzintzuntzan".
The people of the Tarascan empire were mostly of P'urhépecha
ethnic affiliation but also included other ethnic groups such as the Nahua, Otomi
, Matlatzinca
and Chichimec. These ethnic groups were gradually assimilated into the P'urhépecha majority group.
The Tarascan state was constituted of a network of tributary systems and gradually became increasingly centralized, under the control of the "Caconzi", the ruler and king of the state. The Tarascan capital was located at Tzintzuntzan on the banks of Lake Pátzcuaro
, Michoacán, and, according to Tarascan oral tradition was founded by the first caconzi Taríacuri and dominated by his lineage the "Uacúsecha" ("Eagles" in P'urhépecha).
The Tarascan state was contemporary with and an enemy of the Aztec Empire, against which it fought many wars. The Tarascan empire blocked Aztec expansion to the northwest, and the Tarascans fortified and patrolled their frontiers with the Aztecs, possibly developing the first truly territorial state of Mesoamerica.
Due to its relative isolation within Mesoamerica, the Tarascan state had many cultural traits completely distinct from those of the Mesoamerican cultural group. It is particularly noteworthy for being among the few Mesoamerican civilizations to use metal for tools and ornamentation.

and Balsas River
s. Including temperate, subtropical and tropical climate zones, it is dominated by Cenozoic
volcanic mountains and lake basins above 2000 meters altitude, but also includes lower land in the southwestern coastal regions. Most common soil types in the central plateau are young volcanic Andosols, Luvisols and less fertile Acrisol
s. The vegetation is mainly pine, pine-oak and fir. Human occupation has focused on the lake basins, which are abundant in resources. In the north, near the Lerma river, there are obsidian
resources and thermal springs. The Tarascan state was centered around the Lake Pátzcuaro
basin.

. Early lithic evidence from before 2500 B.C. like fluted points
and stone utensils are found at some Megafauna
kill sites. The earliest radio-carbon dates of archeological sites fall around 1200 B.C. The best known early Pre-classic culture of Michoacán was the Chupicuaro culture. Chupícuaro sites are mostly found on lake islands which can be seen as a sign of it having traits relating it to the later Tarascan cultural patterns. In the early Classic period, ballcourts
and other artifacts demonstrate a Teotihuacan
influence in the Michoacán region.
According to the Relación de Michoacán a visionary leader of the P'orhépecha named Taríacuri decided to gather the communities around Lake Pátzcuaro into one strong state. Around 1300 he undertook the first conquests and installed his sons Hiripan and Tangáxoan as lords of Ihuatzio
and Tzintzuntzan
respectively, himself ruling from Pátzcuari city. By the death of Taríacuri (around 1350), his lineage was in control of all the major centers around Lake Pátzcuaro. His son Hiripan continued the expansion into the area surrounding Lake Cuitzeo
.
Hiripan and later his brother Tangáxuan I began to institutionalize the tributary system and consolidate the political unity of the empire. They created an administrative bureaucracy and divided responsibilities of and tributes from the conquered territories between lords and nobles. In the following years first the Tarascan sierra and then the Balsas basin was incorporated into the increasingly centralized state.
Under the rule of cazonci Tzitzipandáquare a number of regions were conquered, only to be lost again by rebellions or strategic retreats when confronted with Aztec expansion. In 1460 the Tarascan state reached the Pacific coast at Zacatula, advanced into the valley of Toluca, and also, on the northern rim, reached into the present day state of Guanajuato
. In the 1470s Aztecs under Axayacatl
captured a series of Tarascan frontier towns and closed in on the Tarascan heartland, but were eventually defeated. This experience prompted the Tarascan ruler to further fortify the Aztec frontier with military centers along the border, such as at Cutzamala
. He also allowed Otomi
es and Matlatzinca
s who had been driven out of their homelands by the Aztecs to settle in the border area under the condition that they took part in the defense of the Tarascan lands. From 1480 the Aztec ruler Ahuitzotl
intensified the conflict with the Tarascans. He supported attacks on Tarascan lands by other ethnic groups allied with or subjugated to the Aztecs such as Matlatzinca
s, Chontales, and Cuitlatec
s. The Tarascans, led by the Caconzi Zuangua, repelled the attacks but further Tarascan expansion was halted until the arrival of the Spaniards two years into the rule of the last Caconzi of an independent Tarascan state, Tangáxuan II
.

was sent into Tarascan territory and arrived at Tzintzuntzan within days. The Tarascan army numbered many thousands, perhaps as many as 100,000, but at the crucial moment they chose not to fight. Tangáxuan submitted to the Spanish administration, but for his cooperation was allowed a large degree of autonomy. This resulted in a strange arrangement where both Cortés and Tangáxuan considered themselves rulers of Michoacán for the following years: the population of the area paid tribute to them both. When the Spanish found out that Tangáxuan was still de facto ruler of his empire but only supplied the Spanish with a small part of the resources extracted from the population they sent the ruthless conquistador Nuño de Guzmán
, who allied himself with a Tarascan noble Don Pedro Panza Cuinierángari, and the Caconzi was executed. A period of violence and turbulence began. During the next decades Tarascan puppet rulers were installed by the Spanish government, but when Nuño de Guzman had been disgraced and recalled to Spain, Bishop Vasco de Quiroga
was sent to the area to clean up. He rapidly gained the respect and friendship of the natives who ceased hostilities towards the Spanish hegemony.
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a region and culture area in the Americas, extending approximately from central Mexico to Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica, within which a number of pre-Columbian societies flourished before the Spanish colonization of the Americas in the 15th and...
, roughly covering the geographic area of the present-day Mexican state of Michoacán
Michoacán
Michoacán officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Michoacán de Ocampo is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 113 municipalities and its capital city is Morelia...
. At the time of the Spanish conquest of Mexico
Spanish conquest of Mexico
The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire was one of the most important campaigns in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. The invasion began in February 1519 and was acclaimed victorious on August 13, 1521, by a coalition army of Spanish conquistadors and Tlaxcalan warriors led by Hernán Cortés...
it was the second-largest state in Mexico. The state was founded in the early 14th century and lost its independence to the Spanish in 1530. In 1543 it officially became the governorship of Michoacán, from the Nahuatl name for the Tarascan state, Michoacán ("place of those who have fish"). In P'urhépecha
P'urhépecha language
P'urhépecha is a language isolate or small language family spoken by more than 100,000 P'urhépecha people in the highlands of the Mexican state of Michoacán...
, language of the Tarascans, the name of the state was Iréchecua Tzintzuntzáni, the "lands of Tzintzuntzan".
The people of the Tarascan empire were mostly of P'urhépecha
P'urhépecha
The P'urhépecha, normally spelled Purépecha in Spanish and in English and traditionally referred to as Tarascans, are an indigenous people centered in the northwestern region of the Mexican state of Michoacán, principally in the area of the cities of Uruapan and Pátzcuaro...
ethnic affiliation but also included other ethnic groups such as the Nahua, Otomi
Otomi people
The Otomi people . Smaller Otomi populations exist in the states of Puebla, Mexico, Tlaxcala, Michoacán and Guanajuato. The Otomi language belonging to the Oto-Pamean branch of the Oto-Manguean language family is spoken in many different varieties some of which are not mutually intelligible.One of...
, Matlatzinca
Matlatzinca
Matlatzinca is a name used to refer to different indigenous ethnic groups in the Toluca Valley in the state of México, located in the central highlands of Mexico. The term is applied to the ethnic group inhabiting the valley of Toluca and to their language, Matlatzinca.When used as an ethnonym,...
and Chichimec. These ethnic groups were gradually assimilated into the P'urhépecha majority group.
The Tarascan state was constituted of a network of tributary systems and gradually became increasingly centralized, under the control of the "Caconzi", the ruler and king of the state. The Tarascan capital was located at Tzintzuntzan on the banks of Lake Pátzcuaro
Lake Pátzcuaro
Lake Pátzcuaro is a lake in the municipality of Pátzcuaro, Michoacán, Mexico.The natives believe that the lake is the place where the barrier between life and death is the thinnest....
, Michoacán, and, according to Tarascan oral tradition was founded by the first caconzi Taríacuri and dominated by his lineage the "Uacúsecha" ("Eagles" in P'urhépecha).
The Tarascan state was contemporary with and an enemy of the Aztec Empire, against which it fought many wars. The Tarascan empire blocked Aztec expansion to the northwest, and the Tarascans fortified and patrolled their frontiers with the Aztecs, possibly developing the first truly territorial state of Mesoamerica.
Due to its relative isolation within Mesoamerica, the Tarascan state had many cultural traits completely distinct from those of the Mesoamerican cultural group. It is particularly noteworthy for being among the few Mesoamerican civilizations to use metal for tools and ornamentation.

Geography and lithic occupation
The territory that would eventually form the setting of the Tarascan state is the high volcanic region constituting the western extension of the Mexican Mesa Central, in between two large rivers: the LermaLerma River
The Lerma Santiago River is Mexico's second longest river. It is a river in west-central Mexico that begins in Mexican Plateau at an altitude over above sea level, and ends where it empties into Lake Chapala, Mexico's largest lake, near Guadalajara, Jalisco...
and Balsas River
Balsas River
The Balsas River is a major river of south-central Mexico. The basin flows through the states of Puebla, Morelos, Guerrero, and Mexico. The river empties into the Pacific Ocean at Mangrove Point, adjacent to the city of Lázaro Cárdenas, Michoacán...
s. Including temperate, subtropical and tropical climate zones, it is dominated by Cenozoic
Cenozoic
The Cenozoic era is the current and most recent of the three Phanerozoic geological eras and covers the period from 65.5 mya to the present. The era began in the wake of the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous that saw the demise of the last non-avian dinosaurs and...
volcanic mountains and lake basins above 2000 meters altitude, but also includes lower land in the southwestern coastal regions. Most common soil types in the central plateau are young volcanic Andosols, Luvisols and less fertile Acrisol
Acrisol
An acrisol is a type of soil as classified by the Food and Agriculture Organization. It is clay-rich, and is associated with humid, tropical climates, such as those found in Brazil, and often supports forested areas. It is one of the 30 major soil groups of the World Reference Base for Soil Resources...
s. The vegetation is mainly pine, pine-oak and fir. Human occupation has focused on the lake basins, which are abundant in resources. In the north, near the Lerma river, there are obsidian
Obsidian
Obsidian is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed as an extrusive igneous rock.It is produced when felsic lava extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimum crystal growth...
resources and thermal springs. The Tarascan state was centered around the Lake Pátzcuaro
Lake Pátzcuaro
Lake Pátzcuaro is a lake in the municipality of Pátzcuaro, Michoacán, Mexico.The natives believe that the lake is the place where the barrier between life and death is the thinnest....
basin.
History of the Tarascan state

Early archaeological evidence
The Tarascan area has been inhabited at least since the early Pre-classic periodMesoamerican chronology
Mesoamerican chronology divides the history of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica into several periods: the Paleo-Indian , the Archaic , the Preclassic , the Classic , and the Postclassic...
. Early lithic evidence from before 2500 B.C. like fluted points
Folsom point
Folsom points are a distinct form of chipped stone projectile points associated with the Folsom Tradition of North America. The style of toolmaking was named after Folsom, New Mexico where the first sample was found within the bone structure of a bison in 1927....
and stone utensils are found at some Megafauna
Megafauna
In terrestrial zoology, megafauna are "giant", "very large" or "large" animals. The most common thresholds used are or...
kill sites. The earliest radio-carbon dates of archeological sites fall around 1200 B.C. The best known early Pre-classic culture of Michoacán was the Chupicuaro culture. Chupícuaro sites are mostly found on lake islands which can be seen as a sign of it having traits relating it to the later Tarascan cultural patterns. In the early Classic period, ballcourts
Mesoamerican ballgame
The Mesoamerican ballgame or Tlatchtli in Náhuatl was a sport with ritual associations played since 1,000 B.C. by the pre-Columbian peoples of Ancient Mexico and Central America...
and other artifacts demonstrate a Teotihuacan
Teotihuacan
Teotihuacan – also written Teotihuacán, with a Spanish orthographic accent on the last syllable – is an enormous archaeological site in the Basin of Mexico, just 30 miles northeast of Mexico City, containing some of the largest pyramidal structures built in the pre-Columbian Americas...
influence in the Michoacán region.
Ethnohistorical Sources
The most useful ethnohistorical source has been the Relación de Michoacán, written around 1540 by the Franciscan priest Fray Jeronimo de Acalá, containing translated and transcribed narratives from Tarascan noblemen. This Relación contains parts of the "official Tarascan history" as carried down through oral tradition: one part focuses on Tarascan state religion, the second on Tarascan society, and the last on Tarascan history and the Spanish conquest. Unfortunately the first part is only partly preserved. Other sources include a number of small pictorial manuscripts, the best known being the Lienzo de Jucutacuto.Foundation and expansion
In the late classic at least two non-P'urhépecha ethnic groups lived around Lake Pátzcuaro: Nahuatl speakers in Jarácuaro, and some Chichimecan cultures on the northern banks, with the Nahua population being the second largest.According to the Relación de Michoacán a visionary leader of the P'orhépecha named Taríacuri decided to gather the communities around Lake Pátzcuaro into one strong state. Around 1300 he undertook the first conquests and installed his sons Hiripan and Tangáxoan as lords of Ihuatzio
Ihuatzio
Ihuatzio is a city located near Lake Pátzcuaro in the Mexican state of Michoacán. It was once the capital of the P'urhépecha kingdom, also known as the Tarascan state...
and Tzintzuntzan
Tzintzuntzan
Tzintzuntzan was the ceremonial center of the pre-Columbian Tarascan state capital of the same name. The name comes from the P'urhépecha word Ts’intsuntsani, which means "place of hummingbirds". After being in Pátzcuaro for the first years of the Tarascan empire, power was consolidated in...
respectively, himself ruling from Pátzcuari city. By the death of Taríacuri (around 1350), his lineage was in control of all the major centers around Lake Pátzcuaro. His son Hiripan continued the expansion into the area surrounding Lake Cuitzeo
Lake Cuitzeo
Lake Cuitzeo is a lake in central part of Mexico, in the Michoacán State. It is located at around . It has an area of 300-400 km². The lake is astatic, and the volume and level of water in the lake fluctuates frequently. It is the second largest freshwater lake in Mexico.Lake Cuitzeo lies in an...
.
Hiripan and later his brother Tangáxuan I began to institutionalize the tributary system and consolidate the political unity of the empire. They created an administrative bureaucracy and divided responsibilities of and tributes from the conquered territories between lords and nobles. In the following years first the Tarascan sierra and then the Balsas basin was incorporated into the increasingly centralized state.
Under the rule of cazonci Tzitzipandáquare a number of regions were conquered, only to be lost again by rebellions or strategic retreats when confronted with Aztec expansion. In 1460 the Tarascan state reached the Pacific coast at Zacatula, advanced into the valley of Toluca, and also, on the northern rim, reached into the present day state of Guanajuato
Guanajuato
Guanajuato officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Guanajuato is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 46 municipalities and its capital city is Guanajuato....
. In the 1470s Aztecs under Axayacatl
Axayacatl
Axayacatl was the sixth Aztec Emperor, a ruler of the Postclassic Mesoamerican Aztec Empire and city of Tenochtitlan, who reigned from 1469 to 1481.He is chiefly remembered for subjugating Tlatelolco, Tenochtitlan's sister city, in 1473....
captured a series of Tarascan frontier towns and closed in on the Tarascan heartland, but were eventually defeated. This experience prompted the Tarascan ruler to further fortify the Aztec frontier with military centers along the border, such as at Cutzamala
Cutzamala (Mesoamerican site)
Cutzamala is an archaeological site in the northern Guerrero region of Mexico. During the Postclassic period in Mesoamerican chronology the settlement of Cutzamala served as a garrison outpost of the Tarascan state, and according to ethnohistorical sources such as the Relaciones geográficas was...
. He also allowed Otomi
Otomi people
The Otomi people . Smaller Otomi populations exist in the states of Puebla, Mexico, Tlaxcala, Michoacán and Guanajuato. The Otomi language belonging to the Oto-Pamean branch of the Oto-Manguean language family is spoken in many different varieties some of which are not mutually intelligible.One of...
es and Matlatzinca
Matlatzinca
Matlatzinca is a name used to refer to different indigenous ethnic groups in the Toluca Valley in the state of México, located in the central highlands of Mexico. The term is applied to the ethnic group inhabiting the valley of Toluca and to their language, Matlatzinca.When used as an ethnonym,...
s who had been driven out of their homelands by the Aztecs to settle in the border area under the condition that they took part in the defense of the Tarascan lands. From 1480 the Aztec ruler Ahuitzotl
Auítzotl
Ahuizotl was the eighth Aztec ruler, the Hueyi Tlatoani, of the city of Tenochtitlan. He was responsible for much of the expansion of the Mexica domain, and consolidated the empire's power after emulating his predecessor...
intensified the conflict with the Tarascans. He supported attacks on Tarascan lands by other ethnic groups allied with or subjugated to the Aztecs such as Matlatzinca
Matlatzinca
Matlatzinca is a name used to refer to different indigenous ethnic groups in the Toluca Valley in the state of México, located in the central highlands of Mexico. The term is applied to the ethnic group inhabiting the valley of Toluca and to their language, Matlatzinca.When used as an ethnonym,...
s, Chontales, and Cuitlatec
Cuitlatec
Cuitlatec was an indigenous ethnic group of Mexico's Pacific coast region, in the Río Balsas region of Guerrero state...
s. The Tarascans, led by the Caconzi Zuangua, repelled the attacks but further Tarascan expansion was halted until the arrival of the Spaniards two years into the rule of the last Caconzi of an independent Tarascan state, Tangáxuan II
Tangaxuan II
Tzimtzincha-Tangaxuan II was the last monarch of the Tarascan state, the kingdom of the P'urhépecha from 1520–1530. He was baptized Francisco when his realm made a peace treaty with Hernán Cortés. He was executed by burning by Nuño Beltrán de Guzmán....
.

Fall of the Tarascan state
After hearing about the fall of the Aztec Empire, the Tarascan Caconzi Tangáxuan II sent emissaries to the Spanish victors. A few Spaniards went with them to Tzintzuntzan where they were presented to the ruler and gifts were exchanged. They returned with samples of gold and Cortés' interest in the Tarascan state was awakened. In 1522 a Spanish force under the leadership of Cristobal de OlidCristóbal de Olid
Cristóbal de Olid was a Spanish adventurer, conquistador and rebel who played a part in the conquest of Mexico and Honduras.Born in Zaragoza, Olid grew up in the household of the governor of Cuba, Diego Velázquez de Cuéllar. In 1518 Velázquez sent Olid to relieve Juan de Grijalva, but en route a...
was sent into Tarascan territory and arrived at Tzintzuntzan within days. The Tarascan army numbered many thousands, perhaps as many as 100,000, but at the crucial moment they chose not to fight. Tangáxuan submitted to the Spanish administration, but for his cooperation was allowed a large degree of autonomy. This resulted in a strange arrangement where both Cortés and Tangáxuan considered themselves rulers of Michoacán for the following years: the population of the area paid tribute to them both. When the Spanish found out that Tangáxuan was still de facto ruler of his empire but only supplied the Spanish with a small part of the resources extracted from the population they sent the ruthless conquistador Nuño de Guzmán
Nuño Beltrán de Guzmán
Nuño Beltrán de Guzmán or sometimes Nuño de Guzmán was a Spanish conquistador and colonial administrator in New Spain. He was Governor of the province of Pánuco from 1525–1533, and of Nueva Galicia from 1529–1534, President of the first Audiencia from 1528-30. He founded several cities in...
, who allied himself with a Tarascan noble Don Pedro Panza Cuinierángari, and the Caconzi was executed. A period of violence and turbulence began. During the next decades Tarascan puppet rulers were installed by the Spanish government, but when Nuño de Guzman had been disgraced and recalled to Spain, Bishop Vasco de Quiroga
Vasco de Quiroga
Vasco de Quiroga was the first bishop of Michoacán, Mexico and one of the judges in the second Audiencia that governed New Spain from January 10, 1531 to April 16, 1535....
was sent to the area to clean up. He rapidly gained the respect and friendship of the natives who ceased hostilities towards the Spanish hegemony.

