
Ta Prohm
Encyclopedia
Ta Prohm is the modern name of a temple at Angkor
, Siem Reap Province, Cambodia
, built in the Bayon
style largely in the late 12th and early 13th centuries and originally called Rajavihara (in Khmer
: រាជវិហារ). Located approximately one kilometre east of Angkor Thom
and on the southern edge of the East Baray
, it was founded by the Khmer
King Jayavarman VII
as a Mahayana Buddhist monastery and university. Unlike most Angkorian temples, Ta Prohm has been left in much the same condition in which it was found: the photogenic and atmospheric combination of trees growing out of the ruins and the jungle
surroundings have made it one of Angkor's most popular temples with visitors.
embarked on a massive program of construction and public works. Rajavihara ("royal temple"), today known as Ta Prohm ("ancestor Brahma"), was one of the first temples founded pursuant to that program. The stele
commemorating the foundation gives a date of 1186 A.D.
Jayavarman VII constructed Rajavihara in honor of his family. The temple's main image, representing Prajnaparamita
, the personification of wisdom, was modelled on the king's mother. The northern and southern satellite temples in the third enclosure were dedicated to the king's guru and his elder brother respectively. As such, Ta Prohm formed a complementary pair with the temple monastery of Preah Khan
, dedicated in 1191 A.D., the main image of which represented the Bodhisattva
of compassion Lokesvara and was modelled on the king's father.
The temple's stele
records that the site was home to more than 12,500 people (including 18 high priests and 615 dancers), with an additional 80,000 souls in the surrounding villages working to provide services and supplies. The stele also notes that the temple amassed considerable riches, including gold, pearls and silks. Expansions and additions to Ta Prohm continued as late as the rule of Srindravarman at the end of the 13th century.
in the 15th century, the temple of Ta Prohm was abandoned and neglected for centuries. When the effort to conserve and restore the temples of Angkor
began in the early 20th century, the École française d'Extrême-Orient
decided that Ta Prohm would be left largely as it had been found, as a "concession to the general taste for the picturesque." According to pioneering Angkor scholar Maurice Glaize
, Ta Prohm was singled out because it was "one of the most imposing [temples] and the one which had best merged with the jungle, but not yet to the point of becoming a part of it". Nevertheless, much work has been done to stabilize the ruins, to permit access, and to maintain "this condition of apparent neglect."
As of 2010, however, it seems authorities have started to take a more aggressive approach to restoration. All the plants and shrubs have been cleared from the site and some of trees are also getting removed. A crane has been erected and a large amount of building work is underway to restore the temple, with much of the work seemingly just rebuilding the temple from scratch as at other sites. Wooden walkways, platforms, and roped railings have been put in place around the site which now block some of the previously famous postcard photo opportunities.

were added to the gopuras. Some of the face towers have collapsed. At one time, moats could be found inside and outside the fourth enclosure.
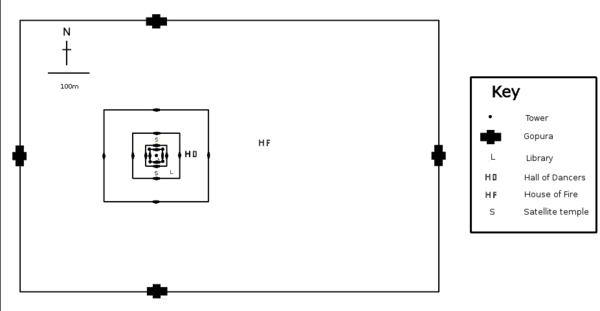
The three inner enclosures of the temple proper are galleried, while the corner towers of the first enclosure form a quincunx with the tower of the central sanctuary. This basic plan is complicated for the visitor by the circuitous access necessitated by the temple's partially collapsed state, as well as by the large number of other buildings dotting the site, some of which represent later additions. The most substantial of these other buildings are the libraries in the southeast corners of the first and third enclosures; the satellite temples on the north and south sides of the third enclosure; the Hall of Dancers between the third and fourth eastern gopuras; and a House of Fire east of the fourth eastern gopura.

 Ta Prohm has not many narrative bas-reliefs(compared to Angkor Wat or Angkor Thom). One explanation that has been proffered for this dearth is that much of the temple's original Buddhist narrative artwork must have been destroyed by Hindu iconoclasts following the death of Jayavarman VII. At any rate, some depictions of scenes from Buddhist mythology do remain. One badly eroded bas-relief illustrates the "Great Departure" of Siddhartha
Ta Prohm has not many narrative bas-reliefs(compared to Angkor Wat or Angkor Thom). One explanation that has been proffered for this dearth is that much of the temple's original Buddhist narrative artwork must have been destroyed by Hindu iconoclasts following the death of Jayavarman VII. At any rate, some depictions of scenes from Buddhist mythology do remain. One badly eroded bas-relief illustrates the "Great Departure" of Siddhartha
, the future Buddha
, from his father's palace. The temple also features stone reliefs of devatas (minor female deities), meditating monks or ascetics, and dvarapalas or temple guardians.
, and the smaller is either the strangler fig
(Ficus gibbosa). or Gold Apple (Diospyros decandra). Indulging in what might be regarded as "descriptive excess," Angkor scholar Maurice Glaize
observed, "On every side, in fantastic over-scale, the trunks of the silk-cotton trees soar skywards under a shadowy green canopy, their long spreading skirts trailing the ground and their endless roots coiling more like reptiles than plants."
. Although the film took visual liberties with other Angkor
ian temples, its scenes of Ta Prohm were quite faithful to the temple's actual appearance, and made use of its eerie qualities.
Some believe that one of the carvings resembles a stegosaurus
.
Angkor
Angkor is a region of Cambodia that served as the seat of the Khmer Empire, which flourished from approximately the 9th to 15th centuries. The word Angkor is derived from the Sanskrit nagara , meaning "city"...
, Siem Reap Province, Cambodia
Cambodia
Cambodia , officially known as the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia...
, built in the Bayon
Bayon
The Bayon is a well-known and richly decorated Khmer temple at Angkor in Cambodia. Built in the late 12th century or early 13th century as the official state temple of the Mahayana Buddhist King Jayavarman VII, the Bayon stands at the centre of Jayavarman's capital, Angkor Thom...
style largely in the late 12th and early 13th centuries and originally called Rajavihara (in Khmer
Khmer language
Khmer , or Cambodian, is the language of the Khmer people and the official language of Cambodia. It is the second most widely spoken Austroasiatic language , with speakers in the tens of millions. Khmer has been considerably influenced by Sanskrit and Pali, especially in the royal and religious...
: រាជវិហារ). Located approximately one kilometre east of Angkor Thom
Angkor Thom
Angkor Thom , located in present day Cambodia, was the last and most enduring capital city of the Khmer empire. It was established in the late twelfth century by king Jayavarman VII. It covers an area of 9 km², within which are located several monuments from earlier eras as well as those...
and on the southern edge of the East Baray
East Baray
The East Baray is a now-dry baray, or artificial body of water, at Angkor, Cambodia, oriented east-west and located just east of the walled city Angkor Thom. It was built around the year 900 AD during the reign of King Yasovarman...
, it was founded by the Khmer
Khmer Empire
The Khmer Empire was one of the most powerful empires in Southeast Asia. The empire, which grew out of the former kingdom of Chenla, at times ruled over and/or vassalized parts of modern-day Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, Burma, and Malaysia. Its greatest legacy is Angkor, the site of the capital city...
King Jayavarman VII
Jayavarman VII
Jayavarman VII was a king of the Khmer Empire in present day Siem Reap, Cambodia. He was the son of King Dharanindravarman II and Queen Sri Jayarajacudamani. He married Jayarajadevi and then, after her death, married her sister Indradevi...
as a Mahayana Buddhist monastery and university. Unlike most Angkorian temples, Ta Prohm has been left in much the same condition in which it was found: the photogenic and atmospheric combination of trees growing out of the ruins and the jungle
Jungle
A Jungle is an area of land in the tropics overgrown with dense vegetation.The word jungle originates from the Sanskrit word jangala which referred to uncultivated land. Although the Sanskrit word refers to "dry land", it has been suggested that an Anglo-Indian interpretation led to its...
surroundings have made it one of Angkor's most popular temples with visitors.
Foundation and expansion
After ascending the throne of Cambodia in 1181 A.D., Jayavarman VIIJayavarman VII
Jayavarman VII was a king of the Khmer Empire in present day Siem Reap, Cambodia. He was the son of King Dharanindravarman II and Queen Sri Jayarajacudamani. He married Jayarajadevi and then, after her death, married her sister Indradevi...
embarked on a massive program of construction and public works. Rajavihara ("royal temple"), today known as Ta Prohm ("ancestor Brahma"), was one of the first temples founded pursuant to that program. The stele
Stele
A stele , also stela , is a stone or wooden slab, generally taller than it is wide, erected for funerals or commemorative purposes, most usually decorated with the names and titles of the deceased or living — inscribed, carved in relief , or painted onto the slab...
commemorating the foundation gives a date of 1186 A.D.
Jayavarman VII constructed Rajavihara in honor of his family. The temple's main image, representing Prajnaparamita
Prajnaparamita
Prajñāpāramitā in Buddhism, means "the Perfection of Wisdom." The word Prajñāpāramitā combines the Sanskrit words prajñā with pāramitā . Prajñāpāramitā is a central concept in Mahāyāna Buddhism and its practice and understanding are taken to be indispensable elements of the Bodhisattva Path...
, the personification of wisdom, was modelled on the king's mother. The northern and southern satellite temples in the third enclosure were dedicated to the king's guru and his elder brother respectively. As such, Ta Prohm formed a complementary pair with the temple monastery of Preah Khan
Preah Khan
Preah Khan , sometimes transliterated as Prah Khan, is a temple at Angkor, Cambodia, built in the 12th century for King Jayavarman VII. It is located northeast of Angkor Thom and just west of the Jayatataka baray, with which it was associated. It was the centre of a substantial organisation,...
, dedicated in 1191 A.D., the main image of which represented the Bodhisattva
Bodhisattva
In Buddhism, a bodhisattva is either an enlightened existence or an enlightenment-being or, given the variant Sanskrit spelling satva rather than sattva, "heroic-minded one for enlightenment ." The Pali term has sometimes been translated as "wisdom-being," although in modern publications, and...
of compassion Lokesvara and was modelled on the king's father.
The temple's stele
Stele
A stele , also stela , is a stone or wooden slab, generally taller than it is wide, erected for funerals or commemorative purposes, most usually decorated with the names and titles of the deceased or living — inscribed, carved in relief , or painted onto the slab...
records that the site was home to more than 12,500 people (including 18 high priests and 615 dancers), with an additional 80,000 souls in the surrounding villages working to provide services and supplies. The stele also notes that the temple amassed considerable riches, including gold, pearls and silks. Expansions and additions to Ta Prohm continued as late as the rule of Srindravarman at the end of the 13th century.
Abandonment and restoration
After the fall of the Khmer empireKhmer Empire
The Khmer Empire was one of the most powerful empires in Southeast Asia. The empire, which grew out of the former kingdom of Chenla, at times ruled over and/or vassalized parts of modern-day Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, Burma, and Malaysia. Its greatest legacy is Angkor, the site of the capital city...
in the 15th century, the temple of Ta Prohm was abandoned and neglected for centuries. When the effort to conserve and restore the temples of Angkor
Angkor
Angkor is a region of Cambodia that served as the seat of the Khmer Empire, which flourished from approximately the 9th to 15th centuries. The word Angkor is derived from the Sanskrit nagara , meaning "city"...
began in the early 20th century, the École française d'Extrême-Orient
École française d'Extrême-Orient
The École française d'Extrême-Orient is a French institute dedicated to the study of Asian societies. Translated into English, it approximately means the French School of the Far East. It was founded in 1900 with headquarters in Hanoi in what was then French Indochina. After independence, its...
decided that Ta Prohm would be left largely as it had been found, as a "concession to the general taste for the picturesque." According to pioneering Angkor scholar Maurice Glaize
Maurice Glaize
Maurice Glaize was a French architect and archeologist, Conservator of Angkor from 1937 to 1945.-Early years: education, wedding, war and professional experiences:...
, Ta Prohm was singled out because it was "one of the most imposing [temples] and the one which had best merged with the jungle, but not yet to the point of becoming a part of it". Nevertheless, much work has been done to stabilize the ruins, to permit access, and to maintain "this condition of apparent neglect."
As of 2010, however, it seems authorities have started to take a more aggressive approach to restoration. All the plants and shrubs have been cleared from the site and some of trees are also getting removed. A crane has been erected and a large amount of building work is underway to restore the temple, with much of the work seemingly just rebuilding the temple from scratch as at other sites. Wooden walkways, platforms, and roped railings have been put in place around the site which now block some of the previously famous postcard photo opportunities.
The site

Layout
The design of Ta Prohm is that of a typical "flat" Khmer temple (as opposed to a temple-pyramid or temple-mountain, the inner levels of which are higher than the outer). Five rectangular enclosing walls surround a central sanctuary. Like most Khmer temples, Ta Prohm is oriented to the east, so the temple proper is set back to the west along an elongated east-west axis. The outer wall of 1000 by 650 metres encloses an area of 650,000 square metres that at one time would have been the site of a substantial town, but that is now largely forested. There are entrance gopuras at each of the cardinal points, although access today is now only possible from the east and west. In the 13th century, face towers similar to those found at the BayonBayon
The Bayon is a well-known and richly decorated Khmer temple at Angkor in Cambodia. Built in the late 12th century or early 13th century as the official state temple of the Mahayana Buddhist King Jayavarman VII, the Bayon stands at the centre of Jayavarman's capital, Angkor Thom...
were added to the gopuras. Some of the face towers have collapsed. At one time, moats could be found inside and outside the fourth enclosure.
The three inner enclosures of the temple proper are galleried, while the corner towers of the first enclosure form a quincunx with the tower of the central sanctuary. This basic plan is complicated for the visitor by the circuitous access necessitated by the temple's partially collapsed state, as well as by the large number of other buildings dotting the site, some of which represent later additions. The most substantial of these other buildings are the libraries in the southeast corners of the first and third enclosures; the satellite temples on the north and south sides of the third enclosure; the Hall of Dancers between the third and fourth eastern gopuras; and a House of Fire east of the fourth eastern gopura.

Representational art


Gautama Buddha
Siddhārtha Gautama was a spiritual teacher from the Indian subcontinent, on whose teachings Buddhism was founded. In most Buddhist traditions, he is regarded as the Supreme Buddha Siddhārtha Gautama (Sanskrit: सिद्धार्थ गौतम; Pali: Siddhattha Gotama) was a spiritual teacher from the Indian...
, the future Buddha
Gautama Buddha
Siddhārtha Gautama was a spiritual teacher from the Indian subcontinent, on whose teachings Buddhism was founded. In most Buddhist traditions, he is regarded as the Supreme Buddha Siddhārtha Gautama (Sanskrit: सिद्धार्थ गौतम; Pali: Siddhattha Gotama) was a spiritual teacher from the Indian...
, from his father's palace. The temple also features stone reliefs of devatas (minor female deities), meditating monks or ascetics, and dvarapalas or temple guardians.
Trees
The trees growing out of the ruins are perhaps the most distinctive feature of Ta Prohm, and "have prompted more writers to descriptive excess than any other feature of Angkor." Two species predominate, but sources disagree on their identification: the larger is either the silk-cotton tree (Ceiba pentandra) or thitpok Tetrameles nudifloraTetrameles nudiflora
Tetrameles nudiflora is a species of plant in the Tetramelaceae family. It is a tree found in Queensland , Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Burma, Sri Lanka, Cambodia, Thailand, and Vietnam...
, and the smaller is either the strangler fig
Strangler Fig
Strangler fig is the common name for a number of tropical and subtropical plant species, including some banyans and unrelated vines, including among many other species:* Ficus aurea, also known as the Florida Strangler Fig...
(Ficus gibbosa). or Gold Apple (Diospyros decandra). Indulging in what might be regarded as "descriptive excess," Angkor scholar Maurice Glaize
Maurice Glaize
Maurice Glaize was a French architect and archeologist, Conservator of Angkor from 1937 to 1945.-Early years: education, wedding, war and professional experiences:...
observed, "On every side, in fantastic over-scale, the trunks of the silk-cotton trees soar skywards under a shadowy green canopy, their long spreading skirts trailing the ground and their endless roots coiling more like reptiles than plants."
In popular media
The temple of Ta Prohm was used as a location in the film Tomb RaiderLara Croft: Tomb Raider
Lara Croft: Tomb Raider is a 2001 adventure thriller film adapted from the Tomb Raider video game series. Directed by Simon West and starring Angelina Jolie as Lara Croft, it was released in U.S. theaters on June 15, 2001. The film was a commercial success...
. Although the film took visual liberties with other Angkor
Angkor
Angkor is a region of Cambodia that served as the seat of the Khmer Empire, which flourished from approximately the 9th to 15th centuries. The word Angkor is derived from the Sanskrit nagara , meaning "city"...
ian temples, its scenes of Ta Prohm were quite faithful to the temple's actual appearance, and made use of its eerie qualities.
Some believe that one of the carvings resembles a stegosaurus
Stegosaurus
Stegosaurus is a genus of armored stegosaurid dinosaur. They lived during the Late Jurassic period , some 155 to 150 million years ago in what is now western North America. In 2006, a specimen of Stegosaurus was announced from Portugal, showing that they were present in Europe as well...
.

