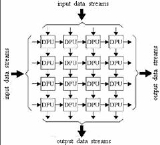
Systolic array
Encyclopedia
In computer architecture
, a systolic array is a pipe network arrangement of processing units called cells. It is a specialized form of parallel computing
, where cells (i.e. processors), compute data and store it independently of each other.
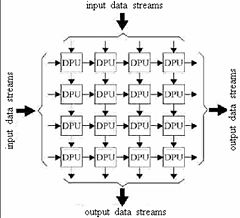
s (CPU)s, (except for the usual lack of a program counter
, since operation is transport-triggered, i.e., by the arrival of a data object). Each cell shares the information with its neighbours immediately after processing. The systolic array is often rectangular where data flows across the array between neighbour DPUs, often with different data flowing in different directions. The data streams entering and leaving the ports of the array are generated by auto-sequencing memory units, ASMs. Each ASM includes a data counter. In embedded system
s a data stream may also be input from and/or output to an external source.
An example of a systolic algorithm
might be designed for matrix multiplication
. One matrix is fed in a row at a time from the top of the array and is passed down the array, the other matrix is fed in a column at a time from the left hand side of the array and passes from left to right. Dummy values are then passed in until each processor has seen one whole row and one whole column. At this point, the result of the multiplication is stored in the array and can now be output a row or a column at a time, flowing down or across the array.
Systolic arrays are arrays of DPUs which are connected to a small number of nearest neighbour DPUs in a mesh-like topology. DPUs perform a sequence of operations on data that flows between them. Because the traditional systolic array synthesis methods have been practiced by algebraic algorithms, only uniform arrays with only linear pipes can be obtained, so that the architectures are the same in all DPUs. The consequence is, that only applications with regular data dependencies can be implemented on classical systolic arrays. Like SIMD
machines, clocked systolic arrays compute in "lock-step" with each processor undertaking alternate compute | communicate
phases. But systolic arrays with asynchronous handshake between DPUs are called wavefront arrays.
One well-known systolic array is Carnegie Mellon University's iWarp
processor, which has been manufactured by Intel. An iWarp system has a linear array processor connected by data buses going in both directions.
, instruction-stream-driven by a program counter. Because a systolic array usually sends and receives multiple data streams, and multiple data counters are needed to generate these data streams, it supports data parallelism
. The name
derives from analogy with the regular pumping of blood by the heart.
H. T. Kung
and Charles E. Leiserson
published the first paper describing systolic arrays in 1978; however, the first machine known to have used a similar technique was the Colossus Mark II
in 1944.
Horner's rule for evaluating a polynomial is:
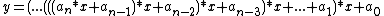
A linear systolic array in which the processors are arranged in pairs:
one multiplies its input by and passes the result to the right,
and passes the result to the right,
the next adds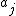 and passes the result to the right:
and passes the result to the right:
Cons
instead, Rainer Kress has introduced the generalized systolic array: the super systolic array. Its application is not restricted to applications with regular data dependencies.
, Configware Compiler, super systolic array and Configware/Software Co-Compiler
.
Because of the wide applicability of the super systolic array its reconfigurability makes sense: the Kress Array, having been pioneered by Rainer Kress for reconfigurable computing
.
Computer architecture
In computer science and engineering, computer architecture is the practical art of selecting and interconnecting hardware components to create computers that meet functional, performance and cost goals and the formal modelling of those systems....
, a systolic array is a pipe network arrangement of processing units called cells. It is a specialized form of parallel computing
Parallel computing
Parallel computing is a form of computation in which many calculations are carried out simultaneously, operating on the principle that large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which are then solved concurrently . There are several different forms of parallel computing: bit-level,...
, where cells (i.e. processors), compute data and store it independently of each other.

Description
A systolic array is composed of matrix-like rows of data processing units called cells. Data processing units (DPUs) are similar to central processing unitCentral processing unit
The central processing unit is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. The term has been in...
s (CPU)s, (except for the usual lack of a program counter
Program counter
The program counter , commonly called the instruction pointer in Intel x86 microprocessors, and sometimes called the instruction address register, or just part of the instruction sequencer in some computers, is a processor register that indicates where the computer is in its instruction sequence...
, since operation is transport-triggered, i.e., by the arrival of a data object). Each cell shares the information with its neighbours immediately after processing. The systolic array is often rectangular where data flows across the array between neighbour DPUs, often with different data flowing in different directions. The data streams entering and leaving the ports of the array are generated by auto-sequencing memory units, ASMs. Each ASM includes a data counter. In embedded system
Embedded system
An embedded system is a computer system designed for specific control functions within a larger system. often with real-time computing constraints. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including hardware and mechanical parts. By contrast, a general-purpose computer, such as a personal...
s a data stream may also be input from and/or output to an external source.
An example of a systolic algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
might be designed for matrix multiplication
Matrix multiplication
In mathematics, matrix multiplication is a binary operation that takes a pair of matrices, and produces another matrix. If A is an n-by-m matrix and B is an m-by-p matrix, the result AB of their multiplication is an n-by-p matrix defined only if the number of columns m of the left matrix A is the...
. One matrix is fed in a row at a time from the top of the array and is passed down the array, the other matrix is fed in a column at a time from the left hand side of the array and passes from left to right. Dummy values are then passed in until each processor has seen one whole row and one whole column. At this point, the result of the multiplication is stored in the array and can now be output a row or a column at a time, flowing down or across the array.
Systolic arrays are arrays of DPUs which are connected to a small number of nearest neighbour DPUs in a mesh-like topology. DPUs perform a sequence of operations on data that flows between them. Because the traditional systolic array synthesis methods have been practiced by algebraic algorithms, only uniform arrays with only linear pipes can be obtained, so that the architectures are the same in all DPUs. The consequence is, that only applications with regular data dependencies can be implemented on classical systolic arrays. Like SIMD
SIMD
Single instruction, multiple data , is a class of parallel computers in Flynn's taxonomy. It describes computers with multiple processing elements that perform the same operation on multiple data simultaneously...
machines, clocked systolic arrays compute in "lock-step" with each processor undertaking alternate compute | communicate
phases. But systolic arrays with asynchronous handshake between DPUs are called wavefront arrays.
One well-known systolic array is Carnegie Mellon University's iWarp
IWarp
iWarp was an experimental parallel supercomputer architecture developed as a joint project by Intel and Carnegie Mellon University. The project started in 1988, as a follow-up to CMU's previous WARP research project, in order to explore building an entire parallel-computing "node" in a single...
processor, which has been manufactured by Intel. An iWarp system has a linear array processor connected by data buses going in both directions.
History
The systolic array paradigm, data-stream-driven by data counters, is the counterpart of the von Neumann paradigmVon Neumann architecture
The term Von Neumann architecture, aka the Von Neumann model, derives from a computer architecture proposal by the mathematician and early computer scientist John von Neumann and others, dated June 30, 1945, entitled First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC...
, instruction-stream-driven by a program counter. Because a systolic array usually sends and receives multiple data streams, and multiple data counters are needed to generate these data streams, it supports data parallelism
Data parallelism
Data parallelism is a form of parallelization of computing across multiple processors in parallel computing environments. Data parallelism focuses on distributing the data across different parallel computing nodes...
. The name
Systole (medicine)
Systole is the contraction of the heart. Used alone, it usually means the contraction of the left ventricle.In all mammals, the heart has 4 chambers. The left and right ventricles pump together. The atria and ventricles pump in sequence...
derives from analogy with the regular pumping of blood by the heart.
H. T. Kung
H. T. Kung
H. T. Kung is a computer scientist. His current research is primarily in the area of communications networks and network security, but his interests have been broad-ranging, including computational complexity theory, database theory, VLSI design, and parallel computing.Kung received his bachelor...
and Charles E. Leiserson
Charles E. Leiserson
Charles Eric Leiserson is a computer scientist, specializing in the theory of parallel computing and distributed computing, and particularly practical applications thereof; as part of this effort, he developed the Cilk multithreaded language...
published the first paper describing systolic arrays in 1978; however, the first machine known to have used a similar technique was the Colossus Mark II
Colossus computer
Not to be confused with the fictional computer of the same name in the movie Colossus: The Forbin Project.Colossus was the world's first electronic, digital, programmable computer. Colossus and its successors were used by British codebreakers to help read encrypted German messages during World War II...
in 1944.
Applications
An application Example - Polynomial EvaluationHorner's rule for evaluating a polynomial is:
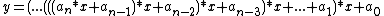
A linear systolic array in which the processors are arranged in pairs:
one multiplies its input by
 and passes the result to the right,
and passes the result to the right,the next adds
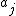 and passes the result to the right:
and passes the result to the right:Advantages and Disadvantages
Pros- Faster
- Scalable
Cons
- Expensive
- Highly specialized for particular applications
- Difficult to build
Super Systolic Array
The super systolic array is a generalization of the systolic array. Because the classical synthesis methods (algebraic, i. e. projection-based synthesis), yielding only uniform DPU arrays permitting only linear pipes, systolic arrays could be used only to implement applications with regular data dependencies. By using simulated annealingSimulated annealing
Simulated annealing is a generic probabilistic metaheuristic for the global optimization problem of locating a good approximation to the global optimum of a given function in a large search space. It is often used when the search space is discrete...
instead, Rainer Kress has introduced the generalized systolic array: the super systolic array. Its application is not restricted to applications with regular data dependencies.
KressArray
The KressArray is the reconfigurable version of the super systolic array. More information about the background may be obtained from the articles about Systolic array, Reconfigurable ComputingReconfigurable computing
Reconfigurable computing is a computer architecture combining some of the flexibility of software with the high performance of hardware by processing with very flexible high speed computing fabrics like field-programmable gate arrays...
, Configware Compiler, super systolic array and Configware/Software Co-Compiler
Configware/Software-Co-Compilation
Software/Configware Co-Compilation is used for Reconfigurable Computing to generate the code for both, an instruction-stream-based microprocessor and a reconfigurable accelerator interfaced to it...
.
Because of the wide applicability of the super systolic array its reconfigurability makes sense: the Kress Array, having been pioneered by Rainer Kress for reconfigurable computing
Reconfigurable computing
Reconfigurable computing is a computer architecture combining some of the flexibility of software with the high performance of hardware by processing with very flexible high speed computing fabrics like field-programmable gate arrays...
.
See also
- iWarpIWarpiWarp was an experimental parallel supercomputer architecture developed as a joint project by Intel and Carnegie Mellon University. The project started in 1988, as a follow-up to CMU's previous WARP research project, in order to explore building an entire parallel-computing "node" in a single...
- Systolic Array Computer, VLSI, Intel/CMU - KressArray - Reconfigurable version of Super systolic array
- SISALSISALSISAL is a general-purpose single assignment functional programming language with strict semantics, implicit parallelism, and efficient array handling. SISAL outputs a dataflow graph in Intermediary Form 1...
- WARP (systolic array)WARP (systolic array)The Warp machines were a series of increasingly general-purpose systolic array processors, created by Carnegie Mellon University , in conjunction with industrial partners G.E., Honeywell and Intel, and funded by the U.S. Defense Advances Research Projects Agency .The Warp projects were started in...
- Systolic Array Computer, GE/CMU

