
Synthetic musk
Encyclopedia

Aroma compound
An aroma compound, also known as odorant, aroma, fragrance or flavor, is a chemical compound that has a smell or odor...
created by chemist and fragrance companies to emulate the scent of deer musk
Deer musk
Deer musk is a substance with a persistent odor obtained from a gland of the male musk deer situated between its back/rectal area. The substance has been extensively used as a perfume fixative, incense material, and medicine, since ancient times. It was, and is still one of the most expensive...
or other natural musk
Musk
Musk is a class of aromatic substances commonly used as base notes in perfumery. They include glandular secretions from animals such as the musk deer, numerous plants emitting similar fragrances, and artificial substances with similar odors. Musk was a name originally given to a substance with a...
. Synthetic musks have a clean, smooth and sweet scent lacking the fecal/"animalic" notes of natural musks and are sometimes attributed as having notes of blackberry
Blackberry
The blackberry is an edible fruit produced by any of several species in the Rubus genus of the Rosaceae family. The fruit is not a true berry; botanically it is termed an aggregate fruit, composed of small drupelets. The plants typically have biennial canes and perennial roots. Blackberries and...
, ambrette or ambergris
Ambergris
Ambergris is a solid, waxy, flammable substance of a dull gray or blackish color produced in the digestive system of and regurgitated or secreted by sperm whales....
. These compounds are essential in modern perfume
Perfume
Perfume is a mixture of fragrant essential oils and/or aroma compounds, fixatives, and solvents used to give the human body, animals, objects, and living spaces "a pleasant scent"...
ry and form the base note foundations of most perfume formulas. Most, if not all musk fragrance used in perfumery today is synthetic.
Synthetic musks can be divided into three major classes — aromatic nitro musks, polycyclic musk compounds, and macrocyclic musk compounds. The first two groups have broad uses in industry ranging from cosmetics
Cosmetics
Cosmetics are substances used to enhance the appearance or odor of the human body. Cosmetics include skin-care creams, lotions, powders, perfumes, lipsticks, fingernail and toe nail polish, eye and facial makeup, towelettes, permanent waves, colored contact lenses, hair colors, hair sprays and...
to detergent
Detergent
A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with "cleaning properties in dilute solutions." In common usage, "detergent" refers to alkylbenzenesulfonates, a family of compounds that are similar to soap but are less affected by hard water...
s. However, the detection of the first two chemical groups in human and environmental samples as well as their carcinogenic properties initiated a public debate on the use of these compounds and a ban or reduction of their use in many regions of the world. Research indicates that these musks don’t break down in the environment, can accumulate in human bodies, are potential hormone disruptors and may break down the body’s defenses against other toxic chemical exposures. Macrocyclic musk compounds are expected to replace them since these compounds appear to be safer.
Nitro-musks
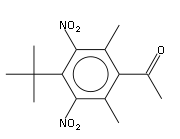
Toluene
Toluene, formerly known as toluol, is a clear, water-insoluble liquid with the typical smell of paint thinners. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, i.e., one in which a single hydrogen atom from the benzene molecule has been replaced by a univalent group, in this case CH3.It is an aromatic...
with isobutyl bromide in the presence of aluminium chloride
Aluminium chloride
Aluminium chloride is the main compound of aluminium and chlorine. It is white, but samples are often contaminated with iron trichloride, giving it a yellow colour. The solid has a low melting and boiling point. It is mainly produced and consumed in the production of aluminium metal, but large...
, and nitrating the product. It was discovered accidentally as a result of Baur's attempts at producing a more effective form of trinitrotoluene (TNT). It appears that the odour depends upon the symmetry of the three nitro group.
- Moskene
Polycyclic musks

World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
and slowly supplanted the nitro-musks in popularity due to the latter's toxicity and molecular instability.
The creation of this class of musks was largely prompted through the need for eliminating the nitro
Nitro compound
Nitro compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more nitro functional groups . They are often highly explosive, especially when the compound contains more than one nitro group and is impure. The nitro group is one of the most common explosophores used globally...
functional group from nitro-musks due to their photochemical reactivity and their instability in alkaline medium. This shown to be possible through the discovery of ambral, a non-nitro aromatic musk, which promoted research in the development of nitro-free musks. This led to the eventual discovery of phantolide, so named due to its commercialization by Givaudan
Givaudan
Givaudan is a Swiss manufacturer of flavorings and fragrances. As of 2008, it is the world's largest company in the industry.-Background:The company's scents and flavors are developed most often for food and beverage makers, but they are also used frequently in household goods, as well as grooming...
without initial knowledge of it chemical structure (elucidated 4 years later). While poorer in smell strength, the performance and stability of this compound class in harsh detergents led to its common use, which spurred further development of other polycyclic musks including Galaxolide.
However it was discovered in the 1990s that polycyclic musks are also potentially harmful which the "immediate consequence of inhibition of efflux transporters is that normally excluded xenobiotics will now be able to enter the cell." Studies show that exposure to polycyclic musks may break down the body’s defenses against other toxic exposures, and these chemicals are linked to increased risk of breast cancer and hormone disruption. Many of these musks were used in large quantities to scent laundry detergents. Levels of these musks in human bodies appear to be associated with the frequency of use of fragranced products, meaning that the more individuals use fragrance, the higher the levels of chemicals like galaxolide and tonalide. Polycyclic musks have been detected in blood, breast milk, and newborns. Commonly used polycyclic musks include:
- Galaxolide (HHCB)
- Tonalide (Musk Plus, AHTN)
- Phantolide
- Celestolide (Crysolide)
- Traesolide
Macrocyclic musks
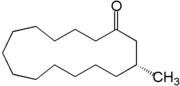
Lactone
In chemistry, a lactone is a cyclic ester which can be seen as the condensation product of an alcohol group -OH and a carboxylic acid group -COOH in the same molecule...
s, all animal derived macrocyclic musks are ketone
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
s.
Although muscone, the primary macrocyclic compound of musk was long known, it was only in 1926 that Leopold Ruzicka was able to synthesize this compound in very small quantities. Despite this discovery and the discovery of other pathways for synthesis of macrocyclic musks, compound of this class were not commercially produced and commonly utilized until the late 1990s due to difficulties in their synthesis and consequently higher price.
About half the human population are anosmic (unable to smell) to macrocyclic musks, possibly due to its high molecular weight. Common macrocyclic musks include:
- Ethylene brassilate
- Globalide (also available as Habanolide, trademark of Firmenich SA)
- Ambrettolide
- Muscone
- Thibetolide (Exaltolide)
- Velvione
Alicyclic musks
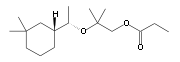
Firmenich
Firmenich SA is a private Swiss company in the perfume and flavor business, it is the largest privately-owned company in the perfume and flavor business, and ranks number two worldwide., Firmenich has created many of the world’s favorite perfumes for over 100 years and produced a number of the most...
that a compound of this class was produced at a commercial scale. ROMANDOLIDE, a more ambrette and less fruity alicyclic musk compared to HELVETOLIDE was introduced ten years later. Common musks of this class include:
- Cyclomusk
- Helvetolide (trademark of Firmenich SA)
- Romandolide (trademark of Firmenich SA)

