
Synaptotagmin
Encyclopedia

Cell membrane
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell...
-trafficking proteins that are characterized by an N-terminal transmembrane region (TMR), a variable linker, and two C-terminal C2 domain
C2 domain
A C2 domain is a protein structural domain involved in targeting proteins to cell membranes. It is a beta-sandwich composed of 8 β-strands that co-ordinates two or three calcium ions, which bind in a cavity formed by the first and final loops of the domain, on the membrane binding face.-Coupling...
s - C2A and C2B. There are 15 members in the mammalian synaptotagmin family. There are several C2-domain containing protein families that are related to synaptotagmins, including transmembrane (Ferlins, E-Syts, and MCTPs) and soluble (RIMs, Munc13s, synaptotagmin-related proteins and B/K) proteins.
Functions
Based on their brain/endocrine distribution and biochemical properties, in particular C2 domains of certain synaptotagmins bound to calcium, synaptotagmins were proposed to function as calcium sensors in the regulation of neurotransmitter release and hormone secretion. Although synaptotagmins share a similar domain structure and a high degree of homology in the C2 domains, not all synaptotagmins bind to calcium. In fact, only eight out of the fifteen synaptotagmins are capable of calcium binding. The calcium binding synaptotagmins include synaptotagmins 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 9, and 10. The remaining seven synaptotagmins do not bind to calcium due to the lack of calcium coordinating residues or spatial orientation of the acidic residues (see the section on C2 domains for details).Calcium-binding Synaptotagmins act as Ca2+ sensors and are involved in both:
- (i) early synaptic vesicle dockingExocytosisExocytosis , also known as 'The peni-cytosis', is the durable process by which a cell directs the contents of secretory vesicles out of the cell membrane...
to the presynaptic membrane via interaction with β-neurexinNeurexinA neurexin is a presynaptic protein that helps to glue together neurons at the synapse. Neurexins are type I membrane proteins that can be classified into two types, α-NRXNs and β-NRXNs. The α-NRXNs are larger and have different amino-terminal extracellular sequences...
or SNAP-25SNAP-25Synaptosomal-associated protein 25 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNAP25 gene. The SNAP-25 protein is a component of the SNARE complex, which is proposed to account for the specificity of membrane fusion and to directly execute fusion by forming a tight complex that brings the... - (ii) late steps of Ca2+ evoked synaptic vesicleSynaptic vesicleIn a neuron, synaptic vesicles store various neurotransmitters that are released at the synapse. The release is regulated by a voltage-dependent calcium channel. Vesicles are essential for propagating nerve impulses between neurons and are constantly recreated by the cell...
fusionExocytosisExocytosis , also known as 'The peni-cytosis', is the durable process by which a cell directs the contents of secretory vesicles out of the cell membrane...
with the presynaptic membraneSynapseIn the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another cell...
.
It was recently shown that synaptotagmin 1 can displace complexin
Complexin
Complexin is a cytoplasmic nerve tissue protein which binds to the SNARE protein complex with a high affinity. The transport vesicle protein synaptotagmin, among others, in the presence of Ca2+, displaces complexin allowing the SNARE protein complex to bind the transport vesicle to the...
from the SNARE complex
SNARE (protein)
SNARE proteins are a large protein superfamily consisting of more than 60 members in yeast and mammalian cells....
in the presence of calcium. This is thought to be one of the last steps in exocytosis
Exocytosis
Exocytosis , also known as 'The peni-cytosis', is the durable process by which a cell directs the contents of secretory vesicles out of the cell membrane...
.
C-terminal C2-domains
The C2 domain is a widely occurring conserved sequence motif of 130-140 amino acid residues, which was first defined as the second constant sequence in PKC isoforms. The C2 domain was first shown to bind to calcium in synaptotagmin-1. Subsequent atomic structure analysis of synaptotagmin-1 at 1.9 Å resolution indicated that its C2 domains are composed of a stable eight-stranded β-sandwich with flexible loops emerging from the top and bottom. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) studies of synaptotagmin-1 revealed that calcium binds exclusively to the top loops, and the binding pockets are coordinated by five conserved aspartate residues: three calcium ions bind to C2A via D172, D178, D230, D232, S235 and D238, and two calcium ions bind to C2B via D303, D309, D363, 365 and D371. Not all synaptotagmin C2 domains bind to calcium. In fact, based on sequence similarities and subsequent confirmation by biochemical analyses, only eight synaptotagmins bind to calcium, namely, synaptotagmin-1, -2, -3, -5, -6, -7, -9 and -10. The lack of critical residues involved in calcium binding accounts for the majority of failure in calcium-binding by the other synaptotagmins. This includes both C2 domains of synaptotagmin-11, -12, -13, -14 and -15, and C2A domain of synaptotagmin-4 and -8. Synaptotagmin-4 and -11 C2B domains, which possess all five acidic residues in the top loops, however, do not bind to calcium due to spatial orientation of the calcium ligands that fail to form proper calcium binding sites. For calcium-binding synaptotagmins, although amino acid residues in the top loops other than those mentioned above are not directly involved in coordinating calcium binding, they affect calcium binding affinity, such as R233 in synaptotagmin-1. The diversity of sequences and structures flanking the calcium-coordinating amino acid residues renders the eight synaptotagmins bind to calcium at various affinities, covering the full range of calcium requirements for regulated exocytosis.The C2A domain regulates the fusion step of synaptic vesicle
Synaptic vesicle
In a neuron, synaptic vesicles store various neurotransmitters that are released at the synapse. The release is regulated by a voltage-dependent calcium channel. Vesicles are essential for propagating nerve impulses between neurons and are constantly recreated by the cell...
exocytosis
Exocytosis
Exocytosis , also known as 'The peni-cytosis', is the durable process by which a cell directs the contents of secretory vesicles out of the cell membrane...
. Consistent with this, the kinetics of
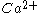 -dependent phospholipid binding activity of the C2A domain in vitro are compatible with the very fast nature of neurotransmitter release (within 200 μs). The C2A domain was shown to bind negatively charged phospholipids in a
-dependent phospholipid binding activity of the C2A domain in vitro are compatible with the very fast nature of neurotransmitter release (within 200 μs). The C2A domain was shown to bind negatively charged phospholipids in a  -dependent fashion.
-dependent fashion.  -binding alters the protein-protein interactions of synaptotagmin such as increasing the affinity of synaptotagmin for syntaxin
-binding alters the protein-protein interactions of synaptotagmin such as increasing the affinity of synaptotagmin for syntaxinSyntaxin
Syntaxins are a family of membrane integrated Q-SNARE proteins participating in exocytosis.- Domains :Syntaxins possess a single C-terminal transmembrane domain, a SNARE domain , and an N-terminal regulatory domain ....
.
The C2B domain binds to phosphatidyl-inositol-3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3) in the absence of calcium ions and to phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP2) in their presence, suggesting that a lipid-interaction switch occurs during depolarization
Depolarization
In biology, depolarization is a change in a cell's membrane potential, making it more positive, or less negative. In neurons and some other cells, a large enough depolarization may result in an action potential...
. Ca2+-binding to the C2B domain confers synaptotagmin dimerization involved in the fusion step of synaptic vesicles by
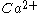 -dependent self-clustering via the C2B domain.
-dependent self-clustering via the C2B domain.  -independent is the interaction between the C2B domain and SNAP-25
-independent is the interaction between the C2B domain and SNAP-25SNAP-25
Synaptosomal-associated protein 25 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNAP25 gene. The SNAP-25 protein is a component of the SNARE complex, which is proposed to account for the specificity of membrane fusion and to directly execute fusion by forming a tight complex that brings the...
, and between the C2B domain and the "synprint" (synaptic protein interaction) motif of the pore-forming subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels. The C2B domain regulates also the recycling step of synaptic vesicles by binding to the clathrin
Clathrin
Clathrin is a protein that plays a major role in the formation of coated vesicles. Clathrin was first isolated and named by Barbara Pearse in 1975. It forms a triskelion shape composed of three clathrin heavy chains and three light chains. When the triskelia interact they form a polyhedral lattice...
assembly protein, AP-2.

