
Sun path
Encyclopedia
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
. The relative position of the sun is a major factor in the heat gain
Solar gain
Solar gain refers to the increase in temperature in a space, object or structure that results from solar radiation...
of buildings and in the performance of solar energy systems. Accurate location-specific knowledge of sun path and climatic conditions is essential for economic decisions about solar collector
Solar collector
-See also:*Solar thermal collector*Solar water heating*Solar air heating*Photovoltaic module*Renewable heat*Concentrating solar power...
area, orientation, landscaping, summer shading, and the cost-effective use of solar tracker
Solar tracker
A solar tracker is a generic term used to describe devices that orient various payloads toward the sun. Payloads can be photovoltaic panels, reflectors, lenses or other optical devices....
s.
Collecting Solar Energy
To gather solar energy effectively, a solar collector (glass, solar panel, etc.) should be within about twenty degrees either side of perpendicular to the sun. Also, shadeShade
Shade is the blocking of sunlight by any object, and also the shadow created by that object. Shade also consists of the colors grey, black, white, etc...
s need to be placed, so that the building does not warm up too much in summer and then thus requires cooling. The farther from perpendicular, the lower the solar gain. More than thirty-five degrees from perpendicular results in a significant portion of sunlight being reflected off the solar collector surface.
An effective solar energy system (passive solar, active solar
Active solar
Active solar technologies are employed to convert solar energy into another more useful form of energy. This would normally be a conversion to heat or electrical energy. Inside a building this energy would be used for heating, cooling, or off-setting other energy use or costs. Active solar uses...
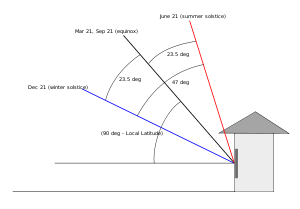
, building, equipment, etc.), takes into account the significant seasonal 47-degree solar elevation angle
Solar elevation angle
The solar elevation angle is the elevation angle of the sun. That is, the angle between the directionof the geometric center of the sun's apparent disk and the horizon...
difference above the horizon, and the sunrise/sunset solar azimuth angle
Solar azimuth angle
The solar azimuth angle is the azimuth angle of the sun. It is most often defined as the angle from due north in a clockwise direction.It can be calculated in various way. In different times, it has been explained in different ways. It can be calculated, to a good approximation, using the following...
from summer to winter.
Precise knowledge of the path of the sun is essential to accurately model
Scientific modelling
Scientific modelling is the process of generating abstract, conceptual, graphical and/or mathematical models. Science offers a growing collection of methods, techniques and theory about all kinds of specialized scientific modelling...
, and mathematically predict, annualized solar system performance - To explain, for example, why vertical equator
Equator
An equator is the intersection of a sphere's surface with the plane perpendicular to the sphere's axis of rotation and containing the sphere's center of mass....
-facing glass is cost-effective, the benefit of solar energy reflectivity
Reflectivity
In optics and photometry, reflectivity is the fraction of incident radiation reflected by a surface. In general it must be treated as a directional property that is a function of the reflected direction, the incident direction, and the incident wavelength...
off winter snow when the sun is low, and why roof-angled glass (in greenhouses, skylights and conservatories) can be a solar furnace during the summer, (when the sun is nearly perpendicular to the glass), and then lose more energy in the winter than it collects, (when the sun is 47-degrees lower on the horizon, and warm interior air rises
Convective heat transfer
Convective heat transfer, often referred to as convection, is the transfer of heat from one place to another by the movement of fluids. The presence of bulk motion of the fluid enhances the heat transfer between the solid surface and the fluid. Convection is usually the dominant form of heat...
and transfers heat
Heat transfer
Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the exchange of thermal energy from one physical system to another. Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as heat conduction, convection, thermal radiation, and phase-change transfer...
out of the building on cold winter nights).http://www.passivesolarenergy.info/#S1
Tilt of the Earth
Earth's rotation tilts about 23.5 degrees on its pole-to-pole axis, relative to the plane of Earth's solar systemSolar System
The Solar System consists of the Sun and the astronomical objects gravitationally bound in orbit around it, all of which formed from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud approximately 4.6 billion years ago. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun...
orbit
Orbit
In physics, an orbit is the gravitationally curved path of an object around a point in space, for example the orbit of a planet around the center of a star system, such as the Solar System...
around our sun. As the Earth orbits the sun, this creates the 47-degree peak solar altitude angle difference, and the hemisphere
Sphere
A sphere is a perfectly round geometrical object in three-dimensional space, such as the shape of a round ball. Like a circle in two dimensions, a perfect sphere is completely symmetrical around its center, with all points on the surface lying the same distance r from the center point...
-specific difference between summer and winter.
In the northern hemisphere
Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
, the winter sun rises in the southeast, peaks out at a low angle above the southern horizon, and then sets in the southwest. It is on the south (equator) side of the house all day long. Vertical south-facing (equator side) glass is excellent for capturing solar thermal energy
Solar thermal energy
Solar thermal energy is a technology for harnessing solar energy for thermal energy . Solar thermal collectors are classified by the United States Energy Information Administration as low-, medium-, or high-temperature collectors. Low-temperature collectors are flat plates generally used to heat...
.
In the southern hemisphere in winter (June, July, August), the sun rises in the northeast, peaks out nearly straight overhead (depending on latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
), and then sets in the northwest. A simple latitude-dependent equator-side overhang can easily be designed to block 100% of the direct solar gain from entering vertical equator-facing windows on the hottest days of the year. Roll-down exterior shade screens, interior translucent-or-opaque Window Quilts, drapes, shutters, movable trellises, etc. can be used for hourly, daily or seasonal sun and heat transfer control (without any active electrical air conditioning).
The latitude (and hemisphere)-specific solar path differences are critical to effective passive solar building design. They are essential data for optimal window and overhang seasonal design. Solar designers must know the precise solar path angles for each location they design for, and how they compare to place-based seasonal heating and cooling requirements.
In the U.S., the precise location-specific altitude-and-azimuth seasonal solar path numbers are available from NOAA - The "equator side" of a building is south in the northern hemisphere, and north in the Southern hemisphere
Southern Hemisphere
The Southern Hemisphere is the part of Earth that lies south of the equator. The word hemisphere literally means 'half ball' or "half sphere"...
, where the peak summer solstice solar altitude occurs on December 21. The sun rises roughly in the east and sets in the west everywhere on Earth, except in high latitudes in summer- and winter-time.
On the Equator, the sun will be straight overhead and a vertical stick will cast no shadow at noon (solar time) on March 21 and September 23, the equinox
Equinox
An equinox occurs twice a year, when the tilt of the Earth's axis is inclined neither away from nor towards the Sun, the center of the Sun being in the same plane as the Earth's equator...
. 23.5 degrees north of the equator on the Tropic of Cancer
Tropic of Cancer
The Tropic of Cancer, also referred to as the Northern tropic, is the circle of latitude on the Earth that marks the most northerly position at which the Sun may appear directly overhead at its zenith...
, a vertical stick will cast no shadow on June 21, the summer solstice for the northern hemisphere. The rest of the year, the noon shadow will point to the North pole
North Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is, subject to the caveats explained below, defined as the point in the northern hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface...
. 23.5 degrees south of the equator on the Tropic of Capricorn
Tropic of Capricorn
The Tropic of Capricorn, or Southern tropic, marks the most southerly latitude on the Earth at which the Sun can be directly overhead. This event occurs at the December solstice, when the southern hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun to its maximum extent.Tropic of Capricorn is one of the five...
, a vertical stick will cast no shadow on December 21, the summer solstice for the southern hemisphere, and the rest of the year its noon shadow will point to the South pole
South Pole
The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole or Terrestrial South Pole, is one of the two points where the Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on the surface of the Earth and lies on the opposite side of the Earth from the North Pole...
. North of the Tropic of Cancer, the noon shadow will always point north, and conversely, south of the Tropic of Capricorn, the noon shadow will always point south. North of the Arctic circle
Arctic Circle
The Arctic Circle is one of the five major circles of latitude that mark maps of the Earth. For Epoch 2011, it is the parallel of latitude that runs north of the Equator....
, and south of the Antarctic circle
Antarctic Circle
The Antarctic Circle is one of the five major circles of latitude that mark maps of the Earth. For 2011, it is the parallel of latitude that runs south of the Equator.-Description:...
there will be at least one day a year when the sun is not above the horizon for 24 hours, and at least one day (six months later) when the sun is above the horizon for 24 hours.
In the moderate latitudes (between the circles and tropics, where most humans live), the length of the day, solar altitude and azimuth vary from one day to the next, and from season to season. The difference between the length of a long summer day, versus a short winter day increases as you move farther away from the equator.
Solar path building design simulation
Before the days of modern, inexpensive, 3D computer graphics, a heliodonHeliodon
A heliodon is a device for adjusting the angle between a flat surface and a beam of light to match the angle between a horizontal plane at a specific latitude and the solar beam. Heliodons are used primarily by architects and students of architecture...
(precisely-movable light source) was used to show the angle of the sun on a physical model of a proposed building. Today, mathematical computer models calculate location-specific solar gain (shading) and seasonal thermal performance, with the ability to rotate and animate a 3D color graphic model of a proposed building design.
Passive solar building design
Passive solar building design
In passive solar building design, windows, walls, and floors are made to collect, store, and distribute solar energy in the form of heat in the winter and reject solar heat in the summer...
heating and cooling issues can be counterintuitive
Counterintuitive
The word "counterintuitive" literally means counter to intuition, and so it essentially means that something does not seem right or correct.A counterintuitive proposition is one that does not seem likely to be true when assessed using intuition or gut feelings...
(like roof-angled glass). Precise performance calculations and simulations are essential to help avoid reinventing the wheel
Reinventing the wheel
To reinvent the wheel is to duplicate a basic method that has already previously been created or optimized by others.The inspiration for this idiomatic metaphor lies in the fact that the wheel is the archetype of human ingenuity, both by virtue of the added power and flexibility it affords its...
and duplicating previously-made expensive experimental construction errors (like a summer solar furnace).
See also
- EclipticEclipticThe ecliptic is the plane of the earth's orbit around the sun. In more accurate terms, it is the intersection of the celestial sphere with the ecliptic plane, which is the geometric plane containing the mean orbit of the Earth around the Sun...
- Passive solar design
- PyranometerPyranometerA pyranometer is a type of actinometer used to measure broadband solar irradiance on a planar surface and is a sensor that is designed to measure the solar radiation flux density from a field of view of 180 degrees...
- PyrheliometerPyrheliometerA pyrheliometer is an instrument for direct measurement of solar irradiance. Sunlight enters the instrument through awindow and is directed onto a thermopile which converts heat to an electrical signal that can be recorded. The signal voltage is converted via a formula to measure watts per square...
- HeliostatHeliostatA heliostat is a device that includes a mirror, usually a plane mirror, which turns so as to keep reflecting sunlight toward a predetermined target, compensating for the sun's apparent motions in the sky. The target may be a physical object, distant from the heliostat, or a direction in space...
- DaylightingDaylightingDaylighting is the practice of placing windows or other openings and reflective surfaces so that during the day natural light provides effective internal lighting. Particular attention is given to daylighting while designing a building when the aim is to maximize visual comfort or to reduce energy...
- AnalemmaAnalemmaIn astronomy, an analemma is a curve representing the angular offset of a celestial body from its mean position on the celestial sphere as viewed from another celestial body relative to the viewing body's celestial equator...
- Effect of sun angle on climateEffect of sun angle on climateThe amount of heat energy received at any location on the globe is a direct effect of sun angle on climate, as the angle at which sunlight strikes the Earth varies by location, time of day, and season due to the Earth's orbit around the sun and the Earth's rotation around its tilted axis...

