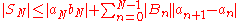Summation by parts
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, summation by parts transforms the summation
of products of sequences
into other summations, often simplifying the computation or (especially) estimation of certain types of sums. The summation by parts formula is sometimes called Abel's
lemma or Abel transformation.
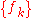 and
and 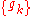 are two sequence
are two sequence
s. Then,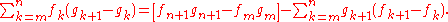
Using the forward difference operator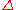 , it can be stated more succinctly as
, it can be stated more succinctly as
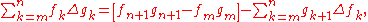
Note that summation by parts is an analogue to the integration by parts
formula,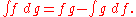
Note also that although applications almost always deal with convergence of sequences, the statement is purely algebraic and will work in any field
. It will also work when one sequence is in a vector space
, and the other is in the relevant field of scalars.
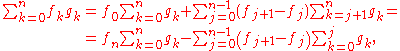
which represent a special cases (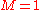 ) of the more general rule
) of the more general rule
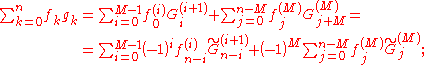
both result from iterated application of the initial formula. The auxiliary quantities are Newton series:
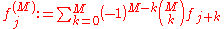
and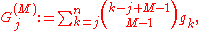
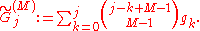
A remarkable, particular (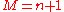 ) result is the noteworthy identity
) result is the noteworthy identity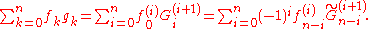
Here,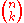 is the binomial coefficient
is the binomial coefficient
.
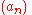 and
and 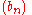 , with
, with 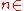 , one wants to study the sum of the following series:
, one wants to study the sum of the following series:
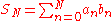
If we define
then for every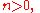
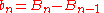 and
and
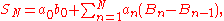
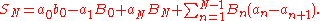
Finally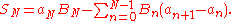
This process, called an Abel transformation, can be used to prove several criteria of convergence for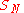 .
.
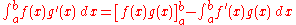
Beside the boundary conditions, we notice that the first integral contains two multiplied functions, one which is integrated in the final integral (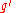 becomes
becomes 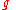 ) and one which is differentiated (
) and one which is differentiated ( 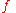 becomes
becomes 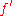 ).
).
The process of the Abel transformation is similar, since one of the two initial sequences is summed (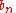 becomes
becomes 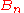 ) and the other one is differenced (
) and the other one is differenced ( 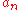 becomes
becomes 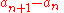 ).
).
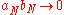 ; otherwise it is obvious that
; otherwise it is obvious that 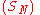 is a divergent series
is a divergent series
.
If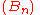 is bounded by a real M and
is bounded by a real M and 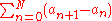 is absolutely convergent, then
is absolutely convergent, then 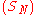 is a convergent series.
is a convergent series.
And the sum of the series verifies:
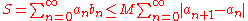
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, summation by parts transforms the summation
Summation
Summation is the operation of adding a sequence of numbers; the result is their sum or total. If numbers are added sequentially from left to right, any intermediate result is a partial sum, prefix sum, or running total of the summation. The numbers to be summed may be integers, rational numbers,...
of products of sequences
Séquences
Séquences is a French-language film magazine originally published in Montreal, Quebec by the Commission des ciné-clubs du Centre catholique du cinéma de Montréal, a Roman Catholic film society. Founded in 1955, the publication was edited for forty years by Léo Bonneville, a member of the Clerics...
into other summations, often simplifying the computation or (especially) estimation of certain types of sums. The summation by parts formula is sometimes called Abel's
Niels Henrik Abel
Niels Henrik Abel was a Norwegian mathematician who proved the impossibility of solving the quintic equation in radicals.-Early life:...
lemma or Abel transformation.
Statement
Suppose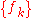 and
and 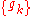 are two sequence
are two sequenceSequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an ordered list of objects . Like a set, it contains members , and the number of terms is called the length of the sequence. Unlike a set, order matters, and exactly the same elements can appear multiple times at different positions in the sequence...
s. Then,
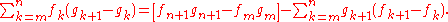
Using the forward difference operator
 , it can be stated more succinctly as
, it can be stated more succinctly as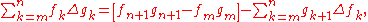
Note that summation by parts is an analogue to the integration by parts
Integration by parts
In calculus, and more generally in mathematical analysis, integration by parts is a rule that transforms the integral of products of functions into other integrals...
formula,
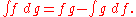
Note also that although applications almost always deal with convergence of sequences, the statement is purely algebraic and will work in any field
Field
-Places:* Field, British Columbia, Canada* Field, Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States* Field, Ontario, Canada* Field Island, Nunavut, Canada* Mount Field - Expanses of open ground :* Field...
. It will also work when one sequence is in a vector space
Vector space
A vector space is a mathematical structure formed by a collection of vectors: objects that may be added together and multiplied by numbers, called scalars in this context. Scalars are often taken to be real numbers, but one may also consider vector spaces with scalar multiplication by complex...
, and the other is in the relevant field of scalars.
Newton series
The formula is sometimes given in one of these - slightly different - forms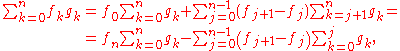
which represent a special cases (
 ) of the more general rule
) of the more general rule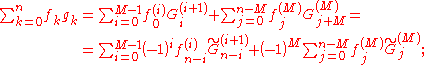
both result from iterated application of the initial formula. The auxiliary quantities are Newton series:
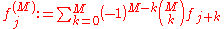
and
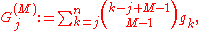
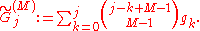
A remarkable, particular (
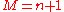 ) result is the noteworthy identity
) result is the noteworthy identity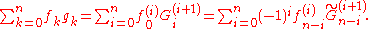
Here,
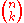 is the binomial coefficient
is the binomial coefficientBinomial coefficient
In mathematics, binomial coefficients are a family of positive integers that occur as coefficients in the binomial theorem. They are indexed by two nonnegative integers; the binomial coefficient indexed by n and k is usually written \tbinom nk , and it is the coefficient of the x k term in...
.
Method
For two given sequences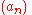 and
and 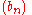 , with
, with 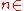 , one wants to study the sum of the following series:
, one wants to study the sum of the following series: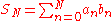
If we define

then for every
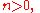
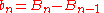 and
and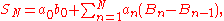
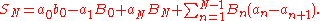
Finally
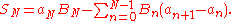
This process, called an Abel transformation, can be used to prove several criteria of convergence for
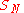 .
.Similarity with an integration by parts
The formula for an integration by parts is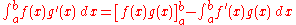
Beside the boundary conditions, we notice that the first integral contains two multiplied functions, one which is integrated in the final integral (
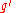 becomes
becomes 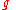 ) and one which is differentiated (
) and one which is differentiated ( 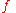 becomes
becomes 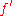 ).
).The process of the Abel transformation is similar, since one of the two initial sequences is summed (
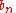 becomes
becomes 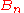 ) and the other one is differenced (
) and the other one is differenced ( 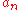 becomes
becomes 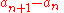 ).
).Applications
We suppose that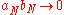 ; otherwise it is obvious that
; otherwise it is obvious that 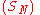 is a divergent series
is a divergent seriesDivergent series
In mathematics, a divergent series is an infinite series that is not convergent, meaning that the infinite sequence of the partial sums of the series does not have a limit....
.
If
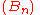 is bounded by a real M and
is bounded by a real M and 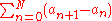 is absolutely convergent, then
is absolutely convergent, then 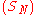 is a convergent series.
is a convergent series.And the sum of the series verifies:
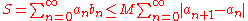
See also
- Convergent series
- Divergent seriesDivergent seriesIn mathematics, a divergent series is an infinite series that is not convergent, meaning that the infinite sequence of the partial sums of the series does not have a limit....
- Integration by partsIntegration by partsIn calculus, and more generally in mathematical analysis, integration by parts is a rule that transforms the integral of products of functions into other integrals...
- Cesàro summationCesàro summationIn mathematical analysis, Cesàro summation is an alternative means of assigning a sum to an infinite series. If the series converges in the usual sense to a sum A, then the series is also Cesàro summable and has Cesàro sum A...
- Abel's theoremAbel's theoremIn mathematics, Abel's theorem for power series relates a limit of a power series to the sum of its coefficients. It is named after Norwegian mathematician Niels Henrik Abel.-Theorem:...
- Abel sum formula