
Sturm series
Encyclopedia
In mathematics, the Sturm series associated with a pair of polynomial
s is named after Jacques Charles François Sturm.
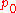 and
and 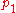 two univariate polynomials. Suppose that they do not have a common root and the degree of
two univariate polynomials. Suppose that they do not have a common root and the degree of 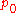 is greater than the degree of
is greater than the degree of 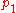 . The Sturm series is constructed by:
. The Sturm series is constructed by: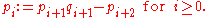
This is almost the same algorithm as Euclid's
but the remainder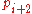 has negative sign.
has negative sign.
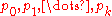 associated to a characteristic polynomial
associated to a characteristic polynomial
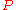 in the variable
in the variable 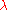 :
: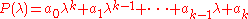
where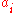 for
for 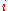 in
in 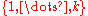 are rational functions in
are rational functions in 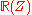 with the coordinate set
with the coordinate set  . The series begins with two polynomials obtained by dividing
. The series begins with two polynomials obtained by dividing 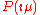 by
by 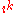 where
where  represents the imaginary unit equal to
represents the imaginary unit equal to  and separate real and imaginary parts:
and separate real and imaginary parts: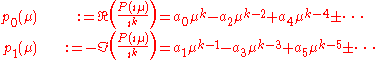
The remaining terms are defined with the above relation. Due to the special structure of these polynomials, they can be written in the form: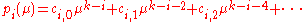
In these notations, the quotient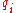 is equal to
is equal to 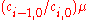 which provides the condition
which provides the condition 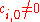 . Moreover, the polynomial
. Moreover, the polynomial 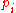 replaced in the above relation gives the following recursive formulas for computation of the coefficients
replaced in the above relation gives the following recursive formulas for computation of the coefficients 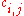 .
.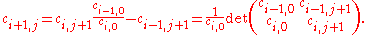
If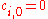 for some
for some 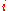 , the quotient
, the quotient 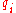 is a higher degree polynomial and the sequence
is a higher degree polynomial and the sequence 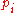 stops at
stops at 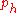 with
with 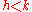 .
.
Polynomial
In mathematics, a polynomial is an expression of finite length constructed from variables and constants, using only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents...
s is named after Jacques Charles François Sturm.
Definition
Let and
and 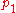 two univariate polynomials. Suppose that they do not have a common root and the degree of
two univariate polynomials. Suppose that they do not have a common root and the degree of  is greater than the degree of
is greater than the degree of 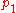 . The Sturm series is constructed by:
. The Sturm series is constructed by: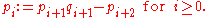
This is almost the same algorithm as Euclid's
Euclidean algorithm
In mathematics, the Euclidean algorithm is an efficient method for computing the greatest common divisor of two integers, also known as the greatest common factor or highest common factor...
but the remainder
 has negative sign.
has negative sign.Sturm series associated to a characteristic polynomial
Let us see now Sturm series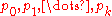 associated to a characteristic polynomial
associated to a characteristic polynomialCharacteristic polynomial
In linear algebra, one associates a polynomial to every square matrix: its characteristic polynomial. This polynomial encodes several important properties of the matrix, most notably its eigenvalues, its determinant and its trace....
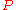 in the variable
in the variable 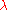 :
: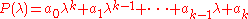
where
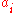 for
for 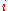 in
in  are rational functions in
are rational functions in 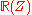 with the coordinate set
with the coordinate set  . The series begins with two polynomials obtained by dividing
. The series begins with two polynomials obtained by dividing 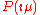 by
by 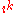 where
where  represents the imaginary unit equal to
represents the imaginary unit equal to  and separate real and imaginary parts:
and separate real and imaginary parts: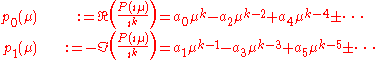
The remaining terms are defined with the above relation. Due to the special structure of these polynomials, they can be written in the form:
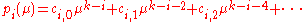
In these notations, the quotient
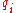 is equal to
is equal to 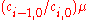 which provides the condition
which provides the condition 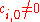 . Moreover, the polynomial
. Moreover, the polynomial 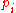 replaced in the above relation gives the following recursive formulas for computation of the coefficients
replaced in the above relation gives the following recursive formulas for computation of the coefficients 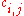 .
.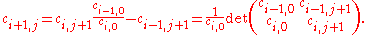
If
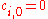 for some
for some  , the quotient
, the quotient 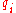 is a higher degree polynomial and the sequence
is a higher degree polynomial and the sequence 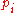 stops at
stops at 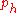 with
with  .
.

